Comments
- No comments found

This year marks the 50th anniversary since Nixon suspended the convertibility of the USD into Gold.
This began the era of a global fiat money debt-fueled economy. Since then, crises are more frequent but also shorter and always “solved” by adding more debt and more money printing.
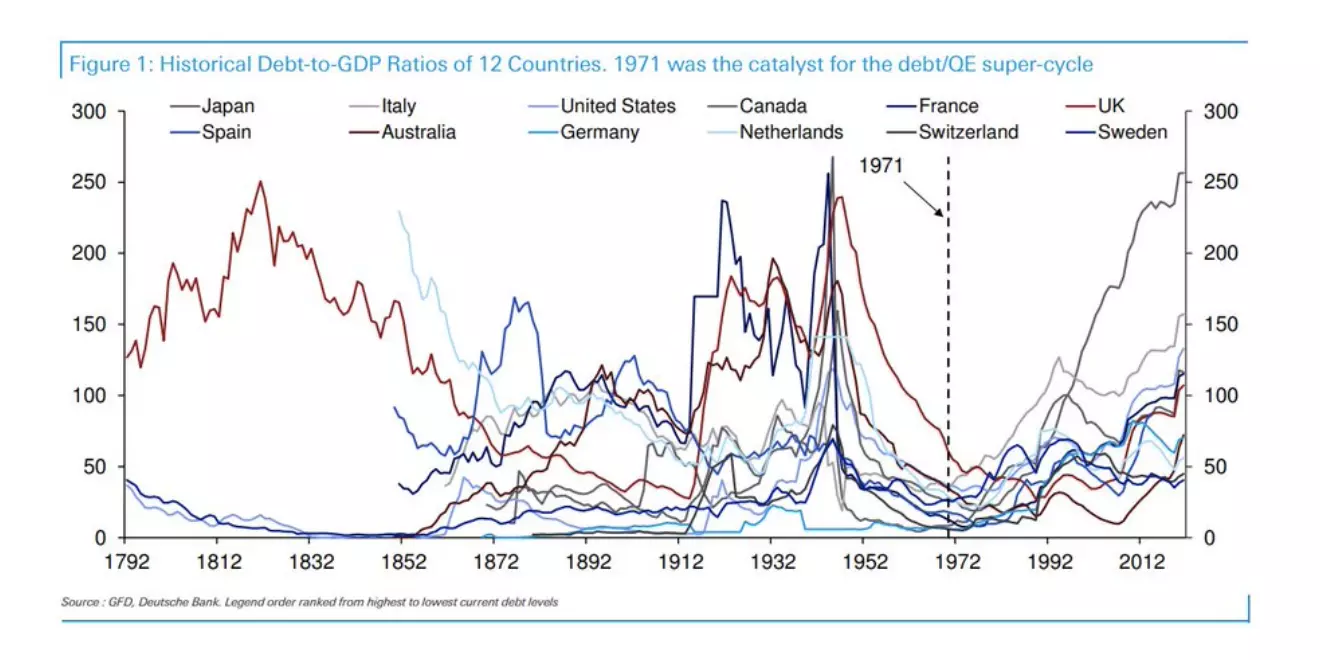
The suspension of the gold standard was a catalyst to trigger massive global credit expansion and cement the position of the US dollar as the world’s reserve currency as it de-facto substituted gold as the reserve for the main central banks.
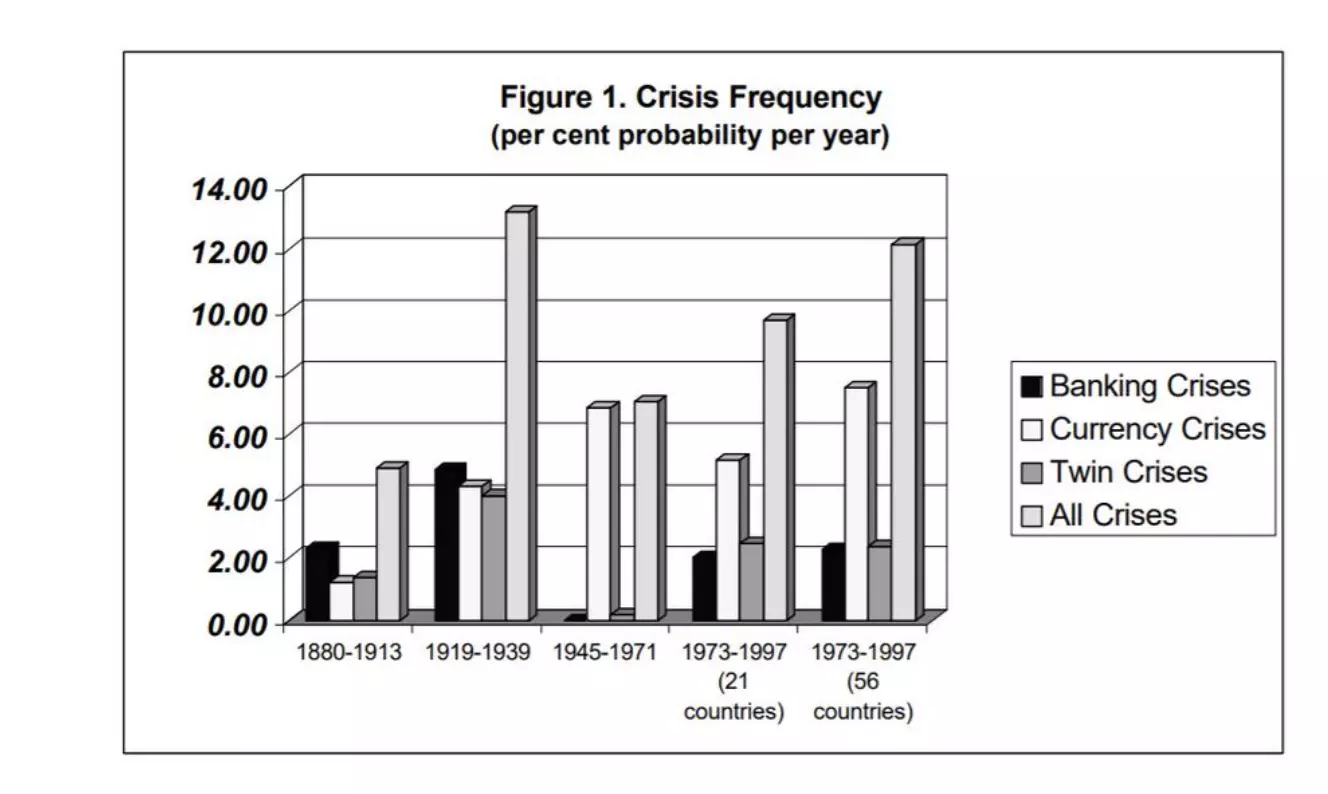
Thus, since the breakdown of the gold standard, financial crises are more frequent but also shorter than before.
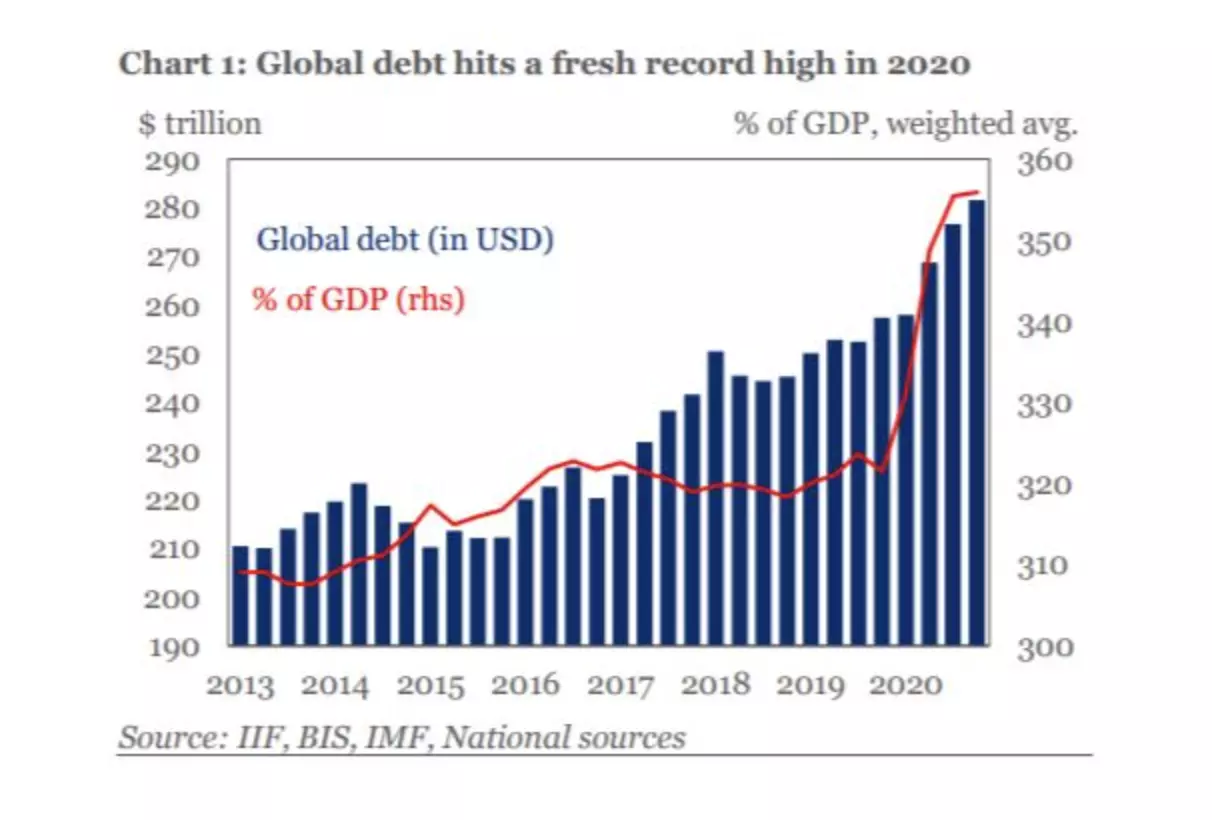
The level of global debt has skyrocketed to more than 350% of GDP, and what is mistakenly called “the financial economy”, which is actually the credit-based economy, has multiplied.
The gold standard supposed a limit to the monetary and fiscal voracity of governments and suspending it unleashed an unprecedented push to increase indebtedness and the perverse incentive of the states to pass on the current imbalances to future generations.
By substituting gold for the US dollar as a global reserve, the United States has been able to borrow and increase money supply massively without triggering hyperinflation because it exports its monetary imbalances to the rest of the world. Other currencies follow the same monetary expansion without the global demand that the US dollar enjoys, so the rising imbalances always end up making those currencies weaker versus the greenback and the economies more dependent on the US dollar.
This race to zero pursued by most central banks has also achieved that there is no real alternative to the US dollar as a reserve because the rest of the countries abandoned the monetary and fiscal orthodoxy at the same time, weakening their ability to be a world reserve alternative.
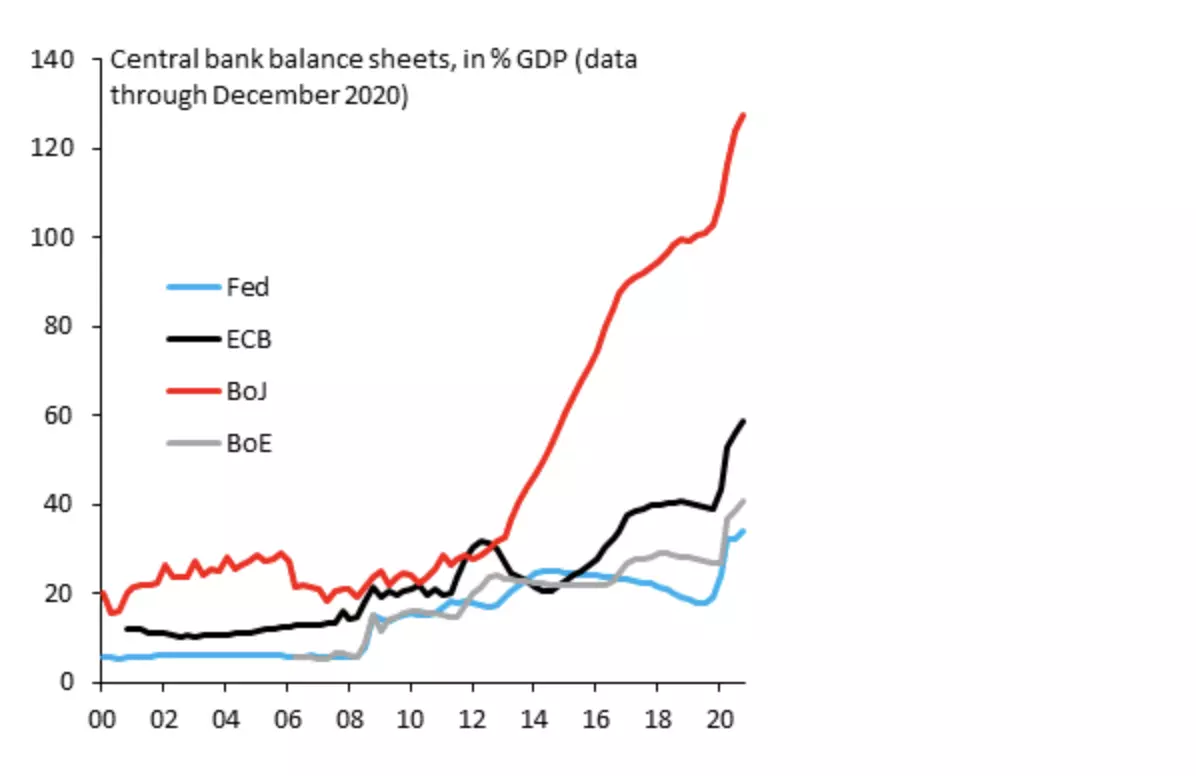
In the 1960s, any currency from a leading country could compete with the dollar if its gold reserves were sufficient. Today, no one among the fiat currencies can compete with the dollar either in financial capacity or as a reserve. The example of the Yuan is paradigmatic. The Chinese economy is almost 17% of the world’s GDP and its currency is used in less than 4% of global transactions, according to the Bank Of International Settlements.
With the suspension of the gold standard, Nixon cemented and guaranteed the financial and monetary hegemony of the United States for the long term while unleashing a global credit-fueled economy where financial risk disproportionately exceeds the real economy.
The defenders of the suspension of the gold standard contend that financial crises are shorter and that the global economy has strengthened in the period. However, it is more than debatable to consider that massive debt expansion is the cause of progress. Non-productive debt has soared and the tax wedge on citizens is elevated, while the severity of financial crises has also increased, which are always “solved” by adding more debt and more risk-taking. A debt-fueled economy and massive money creation disproportionately benefit the first recipients of money and credit, which are government and the wealthy, creating a larger problem for middle-classes and the poor to access better standards of living when asset prices are artificially inflated but real wages rise slower than the price of essential expenses like housing, healthcare, and utilities, while taxes rise.
A return to the gold standard may be unfeasible today given the size of the global monetary imbalance versus gold, which could create a giant financial crisis, but a Taylor-rule based system in monetary policy that limits central bank balance sheet expansion and a strict deficit and debt limit can be implemented if there is a political will.
Daniel Lacalle is one the most influential economists in the world. He is Chief Economist at Tressis SV, Fund Manager at Adriza International Opportunities, Member of the advisory board of the Rafael del Pino foundation, Commissioner of the Community of Madrid in London, President of Instituto Mises Hispano and Professor at IE Business School, London School of Economics, IEB and UNED. Mr. Lacalle has presented and given keynote speeches at the most prestigious forums globally including the Federal Reserve in Houston, the Heritage Foundation in Washington, London School of Economics, Funds Society Forum in Miami, World Economic Forum, Forecast Summit in Peru, Mining Show in Dubai, Our Crowd in Jerusalem, Nordea Investor Summit in Oslo, and many others. Mr Lacalle has more than 24 years of experience in the energy and finance sectors, including experience in North Africa, Latin America and the Middle East. He is currently a fund manager overseeing equities, bonds and commodities. He was voted Top 3 Generalist and Number 1 Pan-European Buyside Individual in Oil & Gas in Thomson Reuters’ Extel Survey in 2011, the leading survey among companies and financial institutions. He is also author of the best-selling books: “Life In The Financial Markets” (Wiley, 2014), translated to Portuguese and Spanish ; “The Energy World Is Flat” (Wiley, 2014, with Diego Parrilla), translated to Portuguese and Chinese ; “Escape from the Central Bank Trap” (2017, BEP), translated to Spanish. Mr Lacalle also contributes at CNBC, World Economic Forum, Epoch Times, Mises Institute, Hedgeye, Zero Hedge, Focus Economics, Seeking Alpha, El Español, The Commentator, and The Wall Street Journal. He holds a PhD in Economics, CIIA financial analyst title, with a post graduate degree in IESE and a master’s degree in economic investigation (UCV).
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest