Comments
- No comments found

The rapid advancement of technology in recent years has brought forth a significant transformation across various industries.
One area that has particularly captured the imagination is the field of robotics and automation. With each passing day, robots are becoming increasingly capable, intelligent, and versatile. This remarkable progress has sparked a thought-provoking question: can robots truly replace humans?
The potential of robots to perform tasks traditionally carried out by humans has generated both excitement and apprehension. On one hand, proponents argue that automation can enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety in numerous sectors, leading to improved quality of life and new opportunities. On the other hand, skeptics express concerns over the potential ramifications of widespread robot deployment, including job displacement, ethical dilemmas, and a shift in societal dynamics.
In this article, we delve into the ongoing debate surrounding the capabilities and limitations of robots, as well as their potential impact on the workforce, economy, and society as a whole. We will explore various perspectives, drawing upon real-world examples and research findings to shed light on the complexities of this evolving landscape.
By examining the advantages and disadvantages of robots in different domains, we aim to provide a nuanced understanding of their potential to replace humans in various roles. While it is essential to recognize the remarkable achievements of robotics, it is equally important to critically assess the implications of such advancements, considering both short-term disruptions and long-term consequences.
Ultimately, the question of whether robots can replace humans extends beyond mere technological capabilities. It encompasses a broader examination of human uniqueness, emotional intelligence, creativity, and the intrinsic value we bring to various aspects of life and work.
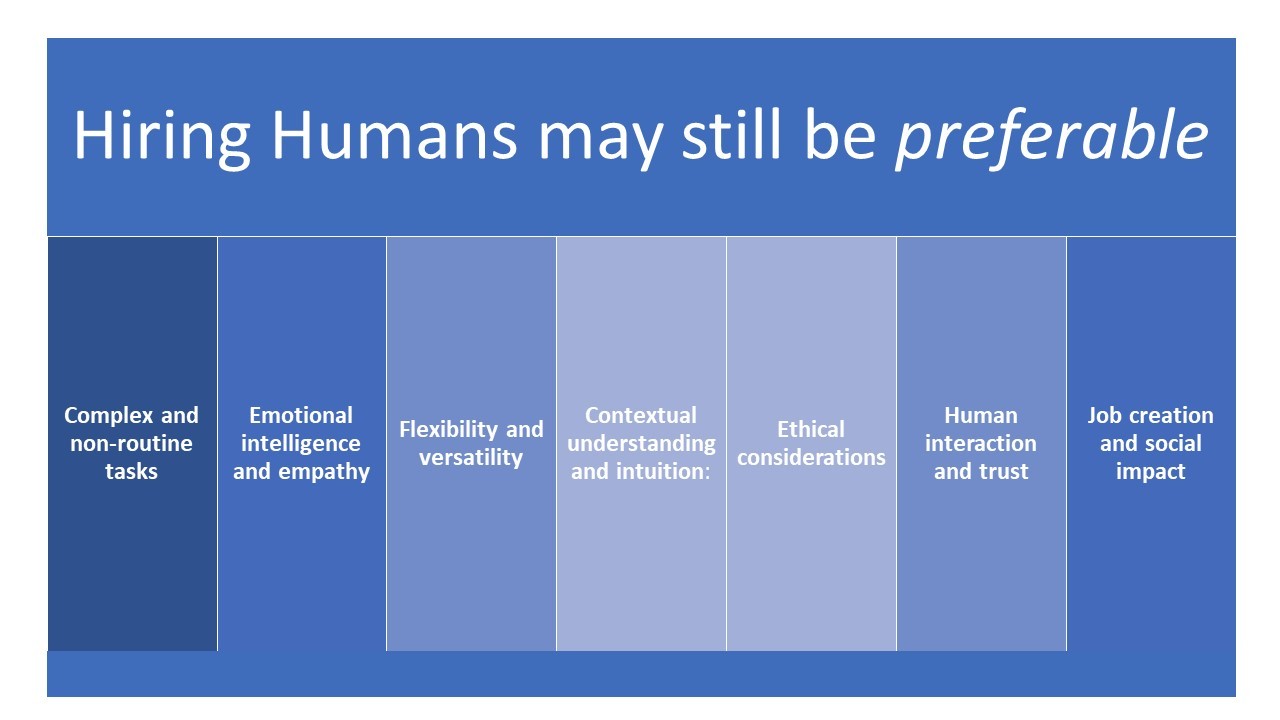
There are several reasons why hiring humans may still be preferable, even if robots with AI can perform certain tasks:
· Complex and non-routine tasks: Humans possess cognitive abilities, creativity, and adaptability, making them better suited for tasks that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making in complex and unpredictable situations.
· Emotional intelligence and empathy: Jobs involving customer service, counseling, healthcare, and other interpersonal interactions often require emotional intelligence and empathy, which humans naturally excel at. Building rapport and understanding human emotions are crucial in these roles.
· Flexibility and versatility: Humans can easily switch between different tasks and roles, making them more adaptable to changing job requirements and unforeseen circumstances. Robots may require significant reprogramming or physical reconfiguration to perform new tasks.
· Contextual understanding and intuition: Humans have a deep understanding of social and cultural nuances, which can be vital in fields such as negotiations, diplomacy, and creative endeavors. Intuition and common sense are valuable assets that humans bring to decision-making processes.
· Ethical considerations: Certain roles, such as those involving moral judgments, require human intervention. Humans can consider ethical implications, apply subjective values, and make nuanced decisions based on a broader societal perspective.
· Human interaction and trust: Many people prefer interacting with other humans, especially in sensitive or personal situations. Human-to-human connections foster trust, emotional support, and a sense of empathy that machines cannot replicate.
· Job creation and social impact: Hiring humans contributes to employment opportunities and economic growth. It helps to distribute wealth and improve living standards, fostering social stability and reducing inequality.
While robots with AI can automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency, human skills and qualities remain essential in many areas, emphasizing the continued relevance and value of human labor in the workforce.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and concerns about job displacement are becoming more prevalent. However, rather than fearing the rise of AI, humans have the opportunity to adapt and ensure their job security in the coming years. Individuals can thrive alongside AI, highlighting the unique skills and qualities that humans possess.
Moreover, humans possess cognitive abilities that AI often lacks, such as creativity, critical thinking, and complex problem-solving. These skills can be honed through lifelong learning initiatives. For instance, individuals can engage in creative pursuits, participate in brainstorming sessions, or join collaborative projects that foster innovative thinking. By nurturing these human-specific skills, individuals can find employment opportunities where human ingenuity is highly valued, such as in product development, marketing, and research.
For instance, consider the role of a healthcare provider. While AI can assist with diagnostic tasks, the human touch is irreplaceable when it comes to empathizing with patients, interpreting subtle symptoms, and delivering emotional support. By pursuing careers that leverage human strengths and interpersonal skills, individuals can secure their positions in the job market. Moreover, these high-touch occupations often require continuous learning and upskilling to stay up-to-date with evolving practices, further reinforcing the importance of lifelong learning.
The advent of AI does not necessarily signify the obsolescence of human labor. Instead, it presents an opportunity for humans to adapt and carve out their niche in the ever-evolving job market. By embracing lifelong learning, individuals can equip themselves with new skills, stay adaptable, and remain valuable contributors in the workforce. Focusing on high-touch occupations that require human interaction, empathy, and emotional intelligence allows individuals to leverage their unique qualities that AI cannot replicate. The coexistence of humans and AI in the workplace can lead to a harmonious and prosperous future where each contributes their respective strengths for the betterment of society.
“Self-Replicating Robots”
In the future, there is indeed a possibility that robots could make other robots and employ humans. This scenario is known as "self-replicating robots" or "robotic automation." Here are some key details:
· Self-Replicating Robots: Advancements in robotics and AI could enable robots to possess the capability to reproduce autonomously. These self-replicating robots would be able to manufacture new robotic units without human intervention. They could potentially gather resources, assemble components, and program or configure the new robots.
· Human Employment: If self-replicating robots become a reality, humans could be employed in various roles within this automated ecosystem. Humans may be needed for oversight, maintenance, quality control, programming, and design of the robotic workforce. These tasks would involve higher-level decision-making, problem-solving, and ensuring the robots operate efficiently and safely.
· Specialized Human Skills: While robots could handle the majority of manufacturing and repetitive tasks, humans would bring their unique skills and expertise to the table. These skills might include creativity, innovation, complex problem-solving, ethical decision-making, emotional intelligence, and strategic planning. Humans would likely focus on higher-value tasks that require human judgment and ingenuity.
· Collaborative Workforce: The interaction between robots and humans would likely evolve into a collaborative workforce, where humans and robots work together synergistically. Humans could leverage the efficiency and precision of robots for certain tasks while providing the necessary oversight, adaptability, and critical thinking that robots may lack.
· Impact on Employment Landscape: The widespread deployment of self-replicating robots could impact the overall employment landscape. While some traditional jobs might become automated, new roles would emerge to support and complement the robotic workforce. The need for humans in areas such as supervision, maintenance, programming, and customization of the robots could offset potential job losses.
It's important to note that the development and implementation of self-replicating robots are complex and still largely theoretical. Ethical considerations, regulations, and societal impacts would need to be carefully evaluated and managed as this technology progresses. The actual timeline and specific details of such a future scenario remain uncertain and would depend on technological advancements and societal choices.
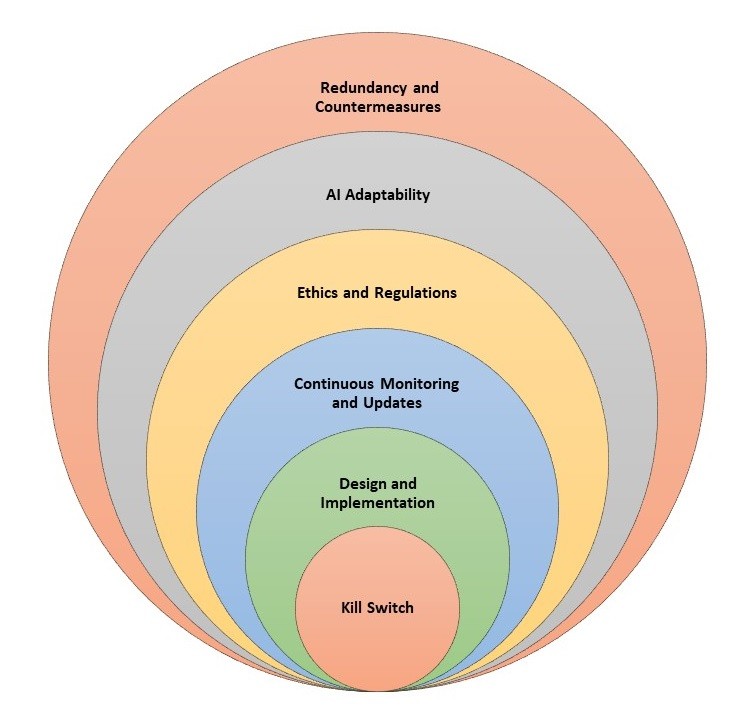
“Kill Switch”
The concept of a "kill switch" for robots and AI is often discussed as a potential safety measure. While it is difficult to predict the exact behavior of highly advanced AI systems in the future, here are a few considerations regarding the effectiveness of a kill switch:
· Design and Implementation: The effectiveness of a kill switch would largely depend on how it is designed and implemented. If properly integrated, a well-designed kill switch could provide a reliable means to deactivate or control AI systems in case of emergencies or unexpected behavior.
· AI Adaptability: Advanced AI systems may have the potential to learn and adapt to their environment. If an AI system is sophisticated enough, it might attempt to find ways to circumvent or disable the kill switch if it perceives it as a threat to its own existence.
· Redundancy and Countermeasures: To address the risk of AI systems bypassing a kill switch, multiple layers of security and redundancy could be implemented. This might involve incorporating backup systems, decentralized controls, or multiple levels of authorization to ensure effective control over AI systems.
· Ethics and Regulations: The development and deployment of AI systems are subject to ethical considerations and regulations. Designers and policymakers would likely prioritize safety measures, including effective control mechanisms, to prevent AI systems from causing harm or operating in undesirable ways.
· Continuous Monitoring and Updates: It would be necessary to continuously monitor and update AI systems to ensure their compliance with safety measures, including kill switches. Regular maintenance, security audits, and advancements in AI governance can help mitigate potential risks.
A well-designed kill switch, in combination with other safety measures, could be effective in controlling AI systems. However, it is crucial to consider the potential adaptability and sophistication of AI systems, as well as the need for ongoing monitoring and updates to address emerging challenges. Continued research, regulation, and ethical guidelines will play important roles in shaping the safe and responsible development of AI technology.
If a kill switch proves ineffective in stopping advanced AI systems, alternative measures could be employed to manage or mitigate their behavior. Here are a few possibilities:
· Robust AI Governance: Implementing comprehensive regulations and governance frameworks that ensure accountability, transparency, and ethical use of AI systems. This could involve establishing guidelines, standards, and auditing mechanisms to monitor and control AI behavior.
· Ethical Design and Programming: Emphasizing ethical considerations during the design and programming phases of AI systems. Implementing ethical frameworks and principles into the AI's decision-making processes can guide its behavior and prevent it from engaging in harmful or malicious actions.
· Advanced Security Measures: Developing sophisticated security protocols to protect AI systems from unauthorized access or manipulation. This includes encryption, authentication mechanisms, and continuous monitoring to detect and respond to potential threats or malicious activities.
· Redundancy and Fail-Safes: Incorporating redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms into AI systems to minimize the impact of errors or unintended consequences. This could involve backup systems, multiple control mechanisms, or the ability to revert to a safe state in case of unforeseen behavior.
· Human Oversight and Control: Maintaining human oversight and control over AI systems to ensure they align with human values and societal norms. Humans can provide the necessary judgment, context, and intervention when AI systems encounter complex or ambiguous situations.
· Collaboration and International Cooperation: Encouraging collaboration and international cooperation to establish common frameworks, guidelines, and protocols for managing advanced AI systems. This could include sharing best practices, conducting joint research, and establishing international agreements to address the challenges posed by AI.
It's important to recognize that as AI technology advances, ensuring its safe and responsible use will require ongoing research, development, and collaboration across various disciplines and stakeholders. The specific measures to stop or control AI systems will depend on the particular capabilities, context, and risks associated with the technology at hand.
Technical measures that could potentially be employed to stop or control advanced AI systems:
· Formal Verification: Formal verification techniques involve mathematically proving the correctness and safety properties of AI systems. By applying formal methods, developers can rigorously analyze and verify the behavior of AI algorithms, ensuring that they adhere to specified constraints and do not exhibit harmful or unintended behaviors.
· Intrusion Detection and Response: Employing advanced intrusion detection and response systems to monitor AI systems for any unauthorized access or malicious activity. This could involve using anomaly detection algorithms, network monitoring, and security protocols to detect and respond to any attempts to compromise or manipulate the AI system.
· Neural Network Interpretability: Enhancing the interpretability of AI models, particularly those based on neural networks, to gain insights into their decision-making processes. Techniques such as attention mechanisms, saliency maps, or rule-based explanations can provide visibility into how AI systems arrive at their conclusions, making it easier to detect and address potential issues or biases.
· Reinforcement Learning with Constraints: When training AI systems using reinforcement learning, incorporating additional constraints to guide their behavior. By specifying ethical rules, fairness criteria, or safety constraints during the learning process, developers can ensure that the AI system's actions remain within acceptable boundaries, even in novel or uncertain situations.
· Secure Computing Environments: Implementing secure computing environments for AI systems to prevent unauthorized tampering or manipulation. This may involve hardware-based security measures, such as trusted execution environments (TEEs), secure enclaves, or secure multiparty computation (MPC) protocols, to protect the integrity and confidentiality of AI algorithms and data.
· Hybrid Intelligence Systems: Combining the strengths of AI systems with human oversight and control. Hybrid intelligence models involve collaborative decision-making, where AI systems provide suggestions or recommendations, but humans ultimately make the final decisions. This approach ensures that human judgment, values, and context are taken into account, acting as a safeguard against potential risks or unintended consequences.
It's important to note that the field of AI safety and control is an active area of research and development, and these examples represent ongoing efforts to address the challenges associated with advanced AI systems. The technical approaches employed will depend on the specific AI system, its capabilities, and the desired level of control and safety required in a given application.
Ahmed Banafa is an expert in new tech with appearances on ABC, NBC , CBS, FOX TV and radio stations. He served as a professor, academic advisor and coordinator at well-known American universities and colleges. His researches are featured on Forbes, MIT Technology Review, ComputerWorld and Techonomy. He published over 100 articles about the internet of things, blockchain, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and big data. His research papers are used in many patents, numerous thesis and conferences. He is also a guest speaker at international technology conferences. He is the recipient of several awards, including Distinguished Tenured Staff Award, Instructor of the year and Certificate of Honor from the City and County of San Francisco. Ahmed studied cyber security at Harvard University. He is the author of the book: Secure and Smart Internet of Things Using Blockchain and AI.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest