Comments
- No comments found

A frequent use of social media can lead to mental health issues including anxiety, loneliness and depression.
Excessive internet consumption can fuel disrupted sleep, memory loss, and poor academic performance.
On average people spend an estimated 192 minutes per day online, primarily via smartphone.
Addiction, depression, anxiety, misinformation and other negative aspects resulting from social media could be prevented by introducing a digital safety pin to monitor navigation.
The purpose is to cut back the negative impact of internet consumption including social media, websites, forums, gaming, e-commerce, online stores, e-mail, apps, headsets, wearable devices, and so on.
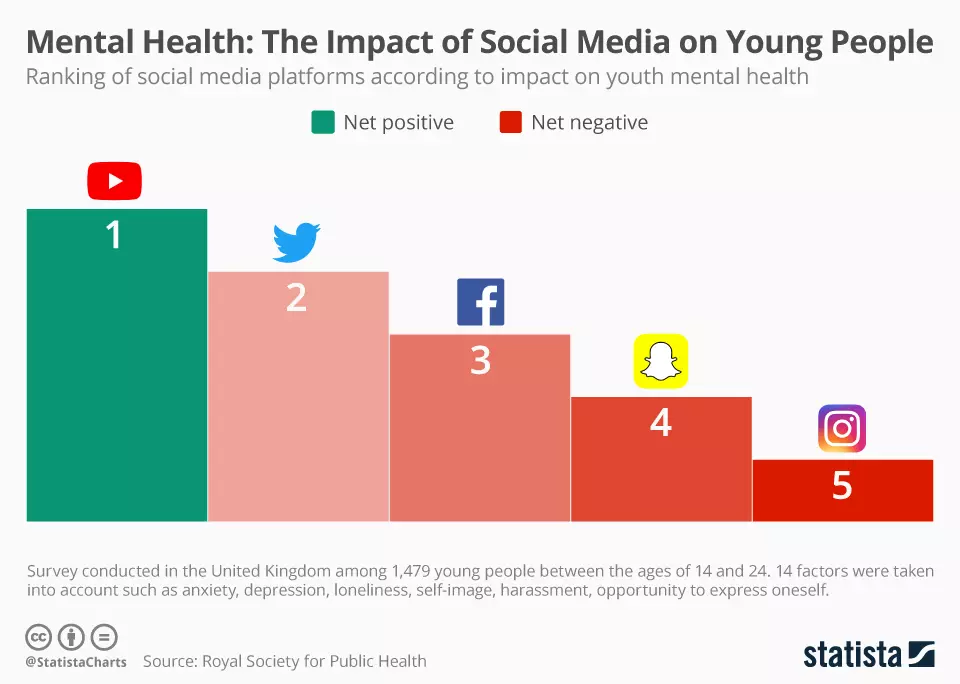
There are several reports on the adverse effects of social media on mental health. There are unpleasant outcomes after what some saw or presumed by what was found online. There are information casualties of falsehoods, something that continues to fester regardless of fact checking sources.
It is highly imperative to append a mental health detour, across platforms and recommend it, with the possibility to limit continuous usage except with intervals of getting briefed by the mental health supply.
The most important information to share is that technologies are sensory inputs — vision, auditory and touch mostly. These inputs are integrated in the thalamus, then relayed to the cerebral cortex.
Integration first, then relay to various locations including knowing, feeling and reacting. To know is the memory, primarily by stores. Interactions of whatever is known are by stores transported to groups. Though climate change is known, its interactions for people are different, with some proceeding to a group for action, and for others, dismissal.
After the memory, there is a procession to the destination of feeling effects, for fear, pleasure, and so on. There are neurochemicals that may be secreted simultaneously, in the process of going to those locations, then reactions may follow.
Every aspect of use for social media has a different set of transport. There are also different equivalents of senses, to inputs in the brain.
Sensory integration is into a uniform unit. It is this unit that is then relayed. It is postulated that the unit is thought of or its form. So the device in the external is a thought version to the brain, same with words, gaming plays, pictures and so on. Thought versions have different constructs as well as differing speeds. They also hold different binds in how their stores linger in groups in the memory.
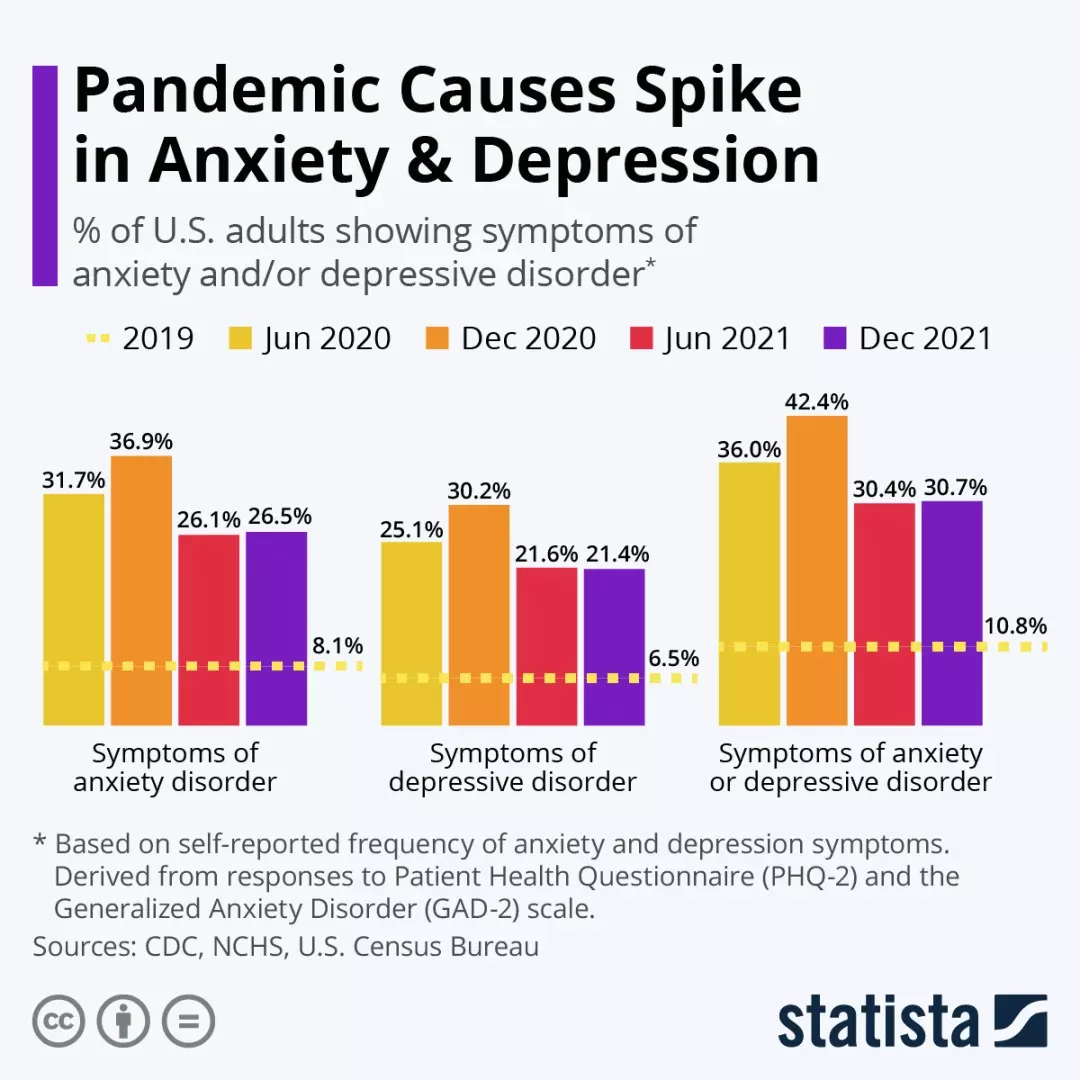
The reliance on social media can have a detrimental effect on mental health.
Cutting daily social media usage by 1 hour could leave people more satisfied with life.
One of the best ways to ensure a better use of technology going into the future is mental health safety features to promote a safer internet.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest