Comments (4)
Andrew Cummings
This is one of the best articles I've read in a while.
Beth Mackinnon
You said it perfectly. Thanks for the insights.
Jordan Gidney
I will take the time to learn that by myself.....
Kieren Davison
Impressive

Let’s face it; we investors are all after the same thing: return. While individual risk tolerances and expectations might vary, the purpose of investing is universal: to preserve and/or increase wealth using that which we already have. It’s a distinctly human activity. While there may seem like an infinite number of ways to invest—and in fact there are—at the end of the day, I believe you can boil each down to either a discretionary or systematic approach. Why just these two methods? Investing draws heavily upon one’s cognitive ability. Human reasoning operates in just two ways, through induction and deduction. I find that the discretionary and systematic categories align quite well with these.
Today, we are witnessing a seismic shift in the investment markets. “New” quantitative approaches are encroaching upon the turf where fundamental and technical analysts had traditionally grazed. At first these “quants” were largely an afterthought as they were relatively small and relegated to the backwaters of the financial markets. However, that thought is long gone.
Being a fundamental investor myself, I can’t help but wonder if I’m living in an analogy. There was a point in time when Neanderthals were the dominant humanoid species. Several offshoots evolved over the years posing little threat at first. However, when the Homo sapiens arrived … well, we all know how that story ends. I find myself constantly questioning whether I am—professionally speaking—a Neanderthal naively wandering through my career, unaware of my impending fate. Must I upgrade or even radically enhance my skillset in order to survive? After all, I have postulated before that markets constantly evolve.
Driven by both a sense of fascination for the new and a survival-based terror, I found myself immersed in the quant world for a while: reading papers, binging on podcasts, harassing people on Twitter, contemplating computer science degree requirements, etc. I woke up in cold sweats anxious about my choice in profession. After several tortured months, I finally came to an important realization that allowed me to confidently move on: quants are people too (is that better as a tee shirt or hashtag?). I mean this both in a literal and abstract sense.
I realize that sounds silly. Hear me out.
First, I’d like to reframe our terminology, borrowing some of the genius of others. I will refer to quants as systematic investors and fundamentalists and technicians as discretionary ones. While there can be some overlap between categories (i.e. some fundamentalists may attempt to systematize their approach, and some quant strategies might be frequently monitored and scrutinized once in place, etc.), I find these labels to generally capture the essence of each approach.
The smart folks over at AQR Capital Management have explored this topic in some depth, publishing both a paper and podcast. The study’s authors explain the different approaches as follows:
“… systematic (commonly associated with the term ‘quant’) generally applies a more repeatable and data driven approach, relying on computers to identify investment opportunities across many securities; in contrast, a discretionary approach involves in-depth analysis across a smaller number of securities and relies more on information that is not always easily codified.”
— AQR, Alternative Thinking: Systematic vs Discretionary | 3Q17
Those seem like pretty reasonable definitions to me. While AQR does not explicitly make reference to practitioners of technical analysis, I find their approach to meet the discretionary label requirements. The authors go on to thoroughly explore many of the distinct concrete characteristics of each strategy. They note that discretionary portfolios can be more concentrated than systematic ones; that systematic strategies can capture different types of excess returns while still reaping diversification benefits, etc.
While the AQR team compiled an impressive list, I find there to be a deeper, epistemological angle to explore. I believe each operates according to a specific way in which we humans think; that discretionary approaches resemble induction and that systematic strategies align with deductive reasoning.
Without getting any deeper into philosophy or psychology, we can all observe the basic methods for how we acquire information about the world. No advanced degree is required, just some simple introspection. New knowledge is discovered by either building upon that which we already know (induction) or applying known conclusions to new areas (deduction).
When we induce concepts, we combine information in such a way that we learn something new. Imagine Sir Isaac Newton getting struck on the head by a fallen apple. Combing this fact with the observation that other (if not all) objects behave in a similar fashion allowed him to surmise that a force such as gravity must exist. He then went out to prove its existence. This is induction. Gravity—as a scientific theory—was not something formally understood before.
Now imagine yourself as a paleontologist somewhere in fields of Thermopolis, Wyoming. You unearth a fossilized bone. In order to identify it you would compare it to the database of known specimens. Find a match and your job is done. But what if you don’t? What if it’s a new species? Still, you could draw many conclusions about your new creature from the fossil. Perhaps you could tell which body part it came from, whether it lived in the sea or on land, if it walked on all fours, if it was a carnivore or herbivore, etc. Existing knowledge about all sorts of animals could be applied to a new situation. This is deduction.
Both induction and deduction are basic human survival techniques. Early humans relied on their minds rather than their brawn to navigate the wild and dangerous African plains from which we evolved. While we’ve come a long way from those primitive days, the tools at our disposal have not. We still primarily employ cognition to meet our needs. Even “menial” jobs require a healthy dose of thinking. Just think, could a dog do one? Of course not. Investing, in particular, makes heavily use of these skills. (Please note, I am not making any judgments about various professions; I am merely stating facts.)
Discretionary investing methods are those with which many of us would be familiar. A future state of the world is created and a portfolio built around it. This might involve purchasing individual stocks, bonds, index funds, real estate, bitcoin … really anything, including sitting on cash. The defining characteristic is not the assets, sizing, or even holding periods, but rather the approach. It is the way in which one enters, manages, and exits positions. A discretionary approach entails forming a hypothesis and entering into a trade. Its performance is monitored in order to ascertain whether or not the thesis is playing out (i.e. if it is being validated). Additional actions may be taken according to one’s evaluation. Theorize; act; validate; this describes how fundamental and technical investors behave.
An example: an analyst might spend his time studying the automotive industry. He might devise a forecast range for a particular stock’s performance based upon his financial model (earnings forecast, scenario analysis, etc.) and may even judge the “setup” based on technical analysis. He might target an entry point to minimize his loss potential and an exit point where the stock would be deemed to have reached fair value and no longer considered attractive. The stock is added to his portfolio and vigilantly watched to see whether the market validates or invalidates his forecast.
Similarly, a trader might think a trend is forming in a particular commodity. Perhaps its price crossed the 50-day moving average or breached an overhead resistance point. She might purchase it theorizing that a new trend is being established and expects it to continue. She cannot know with certainty of course, but she recognizes this particular pattern from prior experience which gives her some degree of confidence, at least enough to risk some capital. A trade is put on, but limit orders set at levels that would indicate her thesis is wrong. Similarly, she targets prices at which to buy more, where her conviction would be strengthened.
In both situations, the real skill comes in after the position is established. Performance will most likely be determined not by which securities were selected, but by how the trades were managed. The investors will be searching for clues, both from fundamental information (such as news flow) and price movements, and will either buy more, sell, or hold based upon his/her read of what’s unfolding. Time—well, really price—will eventually validate or invalidate his/her actions.
To me, this is seems like an inductive approach. One creates a theory about the future state of the world (and specifically the price of an investment) from current information and then seeks to prove it. This plays out over time, be it an hour, a day, a year, or a decade. One is looking to create a new understanding of the world (again, specifically the price of an investment) from the information currently at his/her disposal. One must keep an open mind and constantly question whether or not he/she is right. Those who are quick, honest, and objective typically succeed. As David Riccardo famously said: “Cut short your losses … Let your profits run.” This is easier said than done.
Systematic approaches operate on a fundamentally different premise. The focus is on “system building.” Finding repeatable, reliable strategies that can more or less be created and left alone is the goal (though AQR is quite right to note that good systematic approaches still maintain a level of human oversight). The “work” is done upfront in hopes of removing/mitigating the requirement to manage the trade. One first forms a hypothesis, tests it against a historical data set—refines, retests, repeats, etc.—and then implements it with minimum touch. The thesis validation work is done up front. The strategy is left to run its course for some time before revisiting. In fact, a big virtue of systematic strategies is this feature. They seek to defeat common behavioral biases that notoriously plague investors—namely selling into panics and buying into manias. The systematic approach is to theorize; validate; act.
An example of a systematic approach might go as follows: a quant analyst has an idea for a trading system. He believes that certain characteristics of a company—aka factors—lead to outsized investment returns. Perhaps a portfolio containing stocks with a certain type of “cheapness” and that display positive momentum are found to outperform the broad market with lower volatilities— investment panacea! Back-tests would be performed and statistical significance would be evaluated. If the strategy passed muster it would be implemented in “live trading”, either with real money behind it or not. It would be left to run for some time before its results evaluated.
I find this approach analogous to deductive reasoning. Existing knowledge (such as how a portfolio of certain stocks performed in the past) is applied to future situations/markets in the hope of being repeatable. We know this hasworked in the past and are theorizing that it will continue to do so. Of course one can’t be certain so there is an element of oversight required. However, the skill here largely lies in the strategy creation, testing, and evaluation phase rather than in the management of live trading.
Both systematic and discretionary approaches to investing have their virtues and vices. Systematic strategies attempt to neutralize return-killing behavioral biases. The drawback is that they require the past to persist. Discretionary systems acknowledge that the world is ever changing. But the capacity for induction also creates the potential to over-abstract. The world is complex and sometimes overconfidence can lead to bad investment decisions. 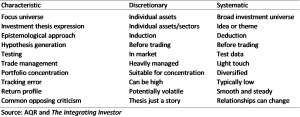
Some essential characteristics of discretionary and systematic approaches
Typical for AQR, the team conducted a study to investigate whether discretionary or systematic approaches produce superior investment returns. They concluded that:
“Overall, the evidence suggests that the two approaches yield similar performance, with somewhat lower active risk in systematic strategies. If anything, the risk-adjusted returns (information ratios) appear mildly higher for systematic, but we do not think that this is the main point here. The key takeaway is that both approaches have their merit and can be valuable in the context of an investor’s overall portfolio. We are big believers in diversification. To the extent investors can find two skilled and lowly correlated managers, they should pursue both and diversify across investment processes.”
Such a finding is perhaps unsurprising. While civilization has thankfully removed the proximal threat of survival, it has not dampened competition for generating investment returns. Given the intensity we investors face, utilizing any and all tools at our disposals seems rational. None is more powerful than the human mind. By incorporating both discretionary and systematic techniques into our practices we can fully engage with the entirety of our human faculty—not merely to survive the investment markets, but to thrive.
This is one of the best articles I've read in a while.
You said it perfectly. Thanks for the insights.
I will take the time to learn that by myself.....
Impressive
Seth Levine is a professional, institutional investor focused on selecting high yield bond positions for a financial services company. He is also the creator of The Integrating Investor where he blogs about macroeconomic and investment strategy related themes. Seth holds a Bachelor of Science degree in Mechanical Engineering from Cornell University and is a CFA charterholder. You can learn more about Seth at www.integratinginvestor.com and follow him on Twitter at @SethLevine2. Please note that any opinions and views he expresses are solely his own and do not reflect those of his current or former employers.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest