Comments
- No comments found

Finding new power sources is one of the most important goals for technology today.
The world’s energy needs are rising, but growing environmental concerns mean traditional fossil fuel-based power can’t sustain our future. Hydrogen power is one possible alternative.
Hydrogen power has been around for longer than many people realise, though it’s still a developing technology. Here’s a closer look at how it works, its benefits, disadvantages and use cases.
At the heart of hydrogen power are devices called fuel cells. Like a battery, fuel cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy, but unlike batteries, they use an external supply of hydrogen instead of storing chemical power inside.
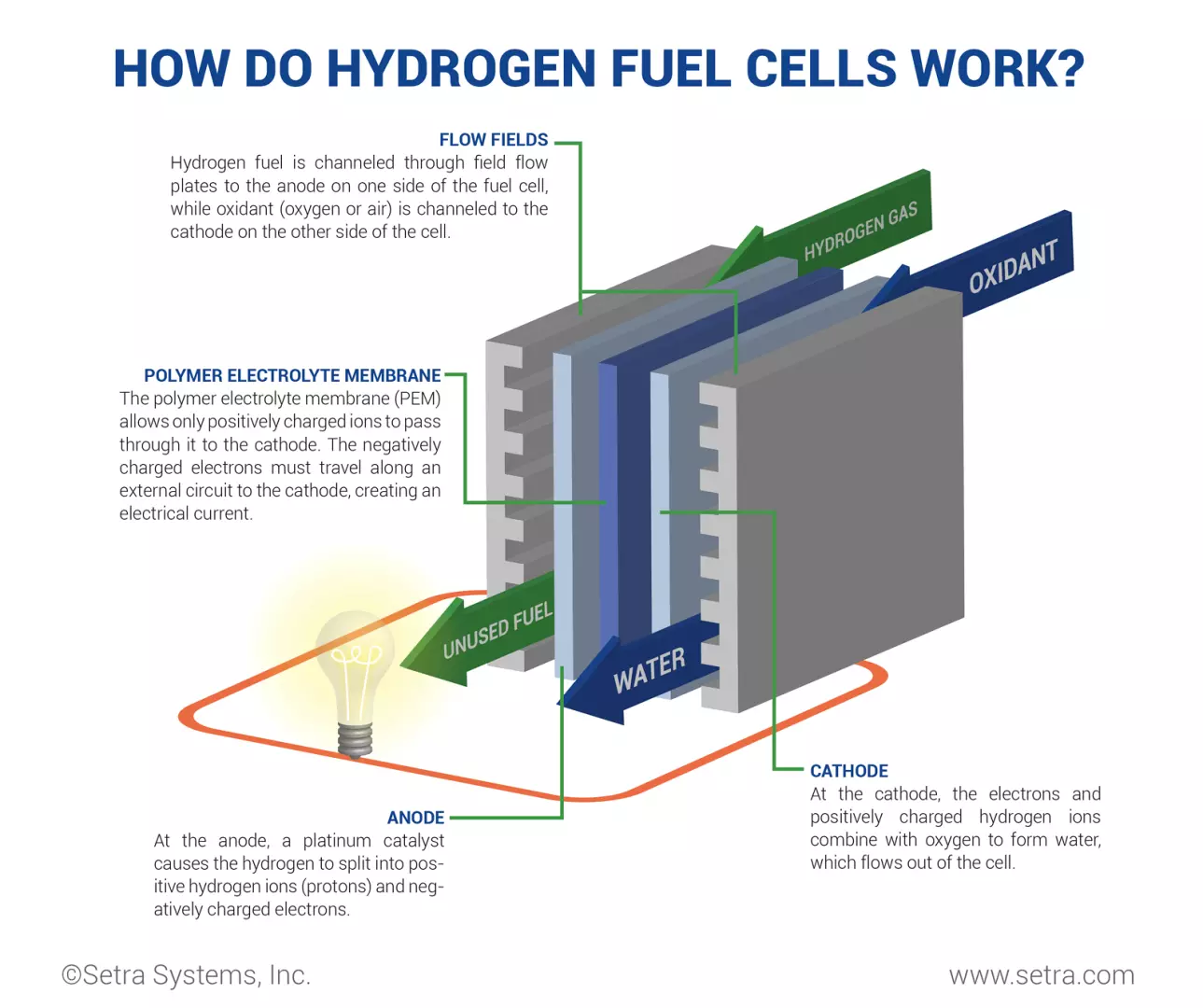
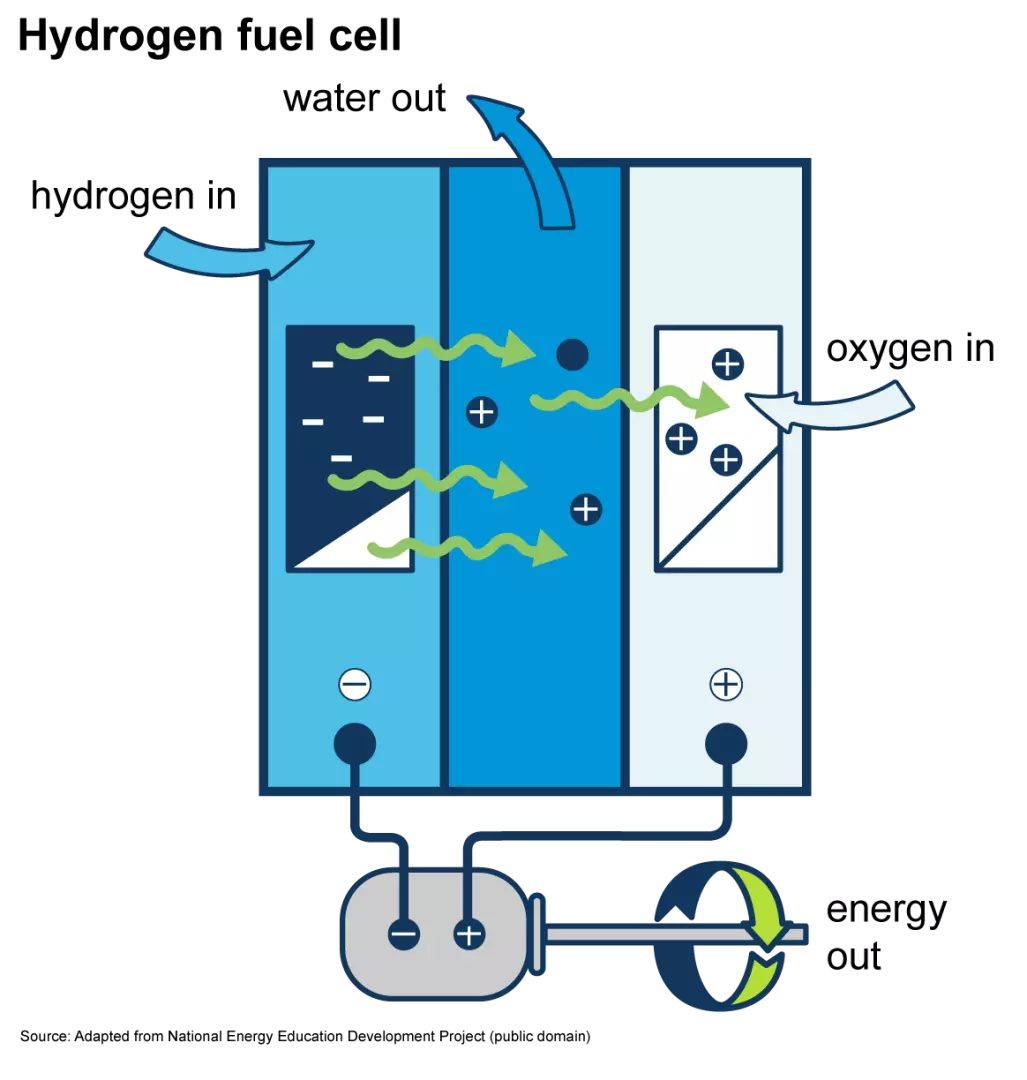
Hydrogen gas passes over the anode of a fuel cell, which breaks it into protons and electrons. The protons react with oxygen from the fuel cell’s cathode, most often from the air, as the electrons go through an external circuit. This cycle generates electricity from the electrons while the protons and oxygen combine to produce water as a byproduct.
Each fuel cell typically generates between 0.5 and 0.8 volts of electricity. However, combining multiple cells in a stack increases the voltage, and expanding the cell area creates more reaction areas. It’s possible to generate a considerable amount of electricity from hydrogen fuel cells when this is done.
Hydrogen has many advantages as a power source. Here are a few of the most significant of these benefits.
The main advantage of hydrogen power is that it offers a greener alternative to fossil fuels. Fuel cells only need hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, so they provide energy without direct greenhouse gas emissions. The only outputs are heat and water.
Hydrogen’s sustainability is particularly important in the realm of zero-emissions vehicles. Transportation accounts for roughly one-quarter of all energy-related carbon emissions, so moving away from petrol and diesel-powered cars is crucial. Battery-electric versions are the most popular alternative, but most electricity comes from fossil fuels, so these still have related emissions. Hydrogen cars, if using green hydrogen, don’t.
Hydrogen is also the most abundant element in nature. Consequently, running out of resources isn’t a big concern with hydrogen power.
Hydrogen fuel cells are also highly efficient, even compared to fossil fuel sources. Like most vehicle engines, traditional energy production methods rely on combustion to generate power, resulting in lots of waste through heat and friction. Fuel cells use chemistry, making them far more efficient than combustion engines.
Fuel cells are also more efficient than batteries in vehicles, mostly because of their weight. Battery-electric cars are heavy, with some batteries weighing as much as a Honda Civic, requiring more power to go the same distance. Fuel cell vehicles don’t have these massive batteries, so they can go farther without refuelling.
This increased efficiency could help convince more people to switch to zero-emission vehicles. In non-vehicle use cases, it means power companies can provide more energy with fewer resources.
Hydrogen power is also more flexible than some other options. This is because hydrogen is technically an energy storage medium, not an actual source. Although it takes more to extract and convert it to power, it is a helpful resource for other energy applications.
Electrical grids can use hydrogen as backup power or a way to store unused energy. When demand rises, they can use fuel cells to convert it back into electricity and provide emissions-free power to an area. This storage and on-demand supply will help expand sustainable energy grids.
This flexibility is important for renewable energy. Things like wind and solar don’t produce power on demand, so supply and demand may not always match up. Using hydrogen as storage helps work around this issue, ensuring renewable energy is practical.
Despite these benefits, hydrogen power still isn’t all that common. That’s because several challenges still stand in the way of large-scale use. Here are some of hydrogen power’s biggest downsides.
One of the most substantial barriers holding hydrogen power back is its cost. It has seen dropping prices, but extracting, storing and using it requires expensive infrastructure changes.
Hydrogen is difficult to store. At room temperature and normal pressure, 1 kilogram of the gas occupies more than 11 cubic meters, which isn’t economically feasible at large scales. Hydrogen is also highly flammable and can degrade some materials. These factors mean storage solutions need advanced materials and designs, which costs money.
Fuel cells themselves are also expensive, especially more efficient stacks. Some systems may have to change to use them instead of fossil fuels, too. These upfront cost barriers may slow hydrogen down as a renewable alternative.
Hydrogen also carries some environmental concerns. Fuel cells produce just water and heat, but that isn’t always true of hydrogen itself. Despite its abundance, it doesn’t appear naturally. Companies must separate it from other elements, which requires electricity.
Power plants running on fossil fuels produce nearly 40% of CO2 emissions, which are the most common energy sources today. Consequently, using hydrogen as a fuel source often means contributing to this pollution.
“Green hydrogen,” which uses renewable energy to power the extraction process, solves this problem. However, renewables will have to grow much more for wide-scale production.
These downsides may hold hydrogen power back, but it’s already in use today. Most notably, the International Space Station uses hydrogen fuel cells to power some systems and provide oxygen for the crew. Researchers are also looking into using this technology for future space exploration and life-support systems on other planets.
Hydrogen power has also made its way into ground transportation. Hydrogen cars may not be common, but they’re available, and some countries have 80 or more refilling stations. The delivery service DHL runs a fleet of 100 hydrogen-powered vans performing some last-mile deliveries.
Hydrogen power has several challenges in front of it, but its advantages are promising. Fuel cells could help move the world away from fossil fuels as technology advances, ensuring a healthier, safer future. Understanding how these systems work and what they can do is the first step to taking full advantage of them.
Emily Newton is the Editor-in-Chief of Revolutionized. She is a science and technology journalist with over three years covering industry trends and research.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest