Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to surpass human intelligence (HI) in the near future.
Despite huge advances in technology, artificial intelligence is still far from complete.
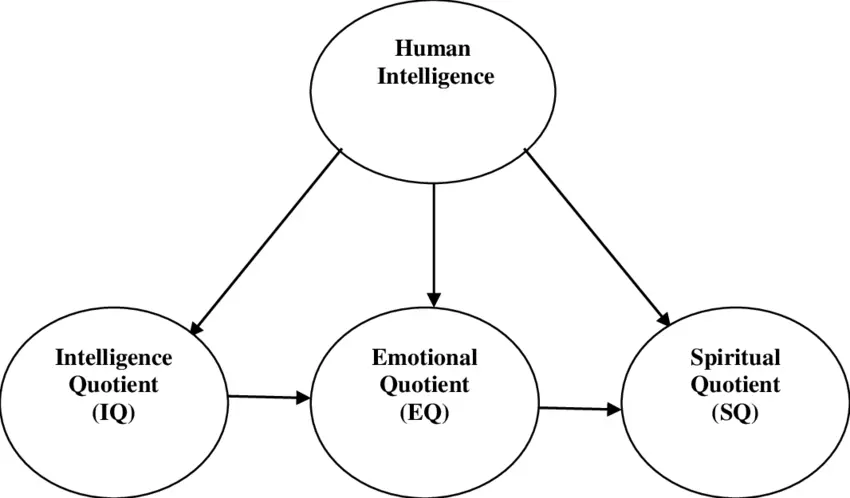
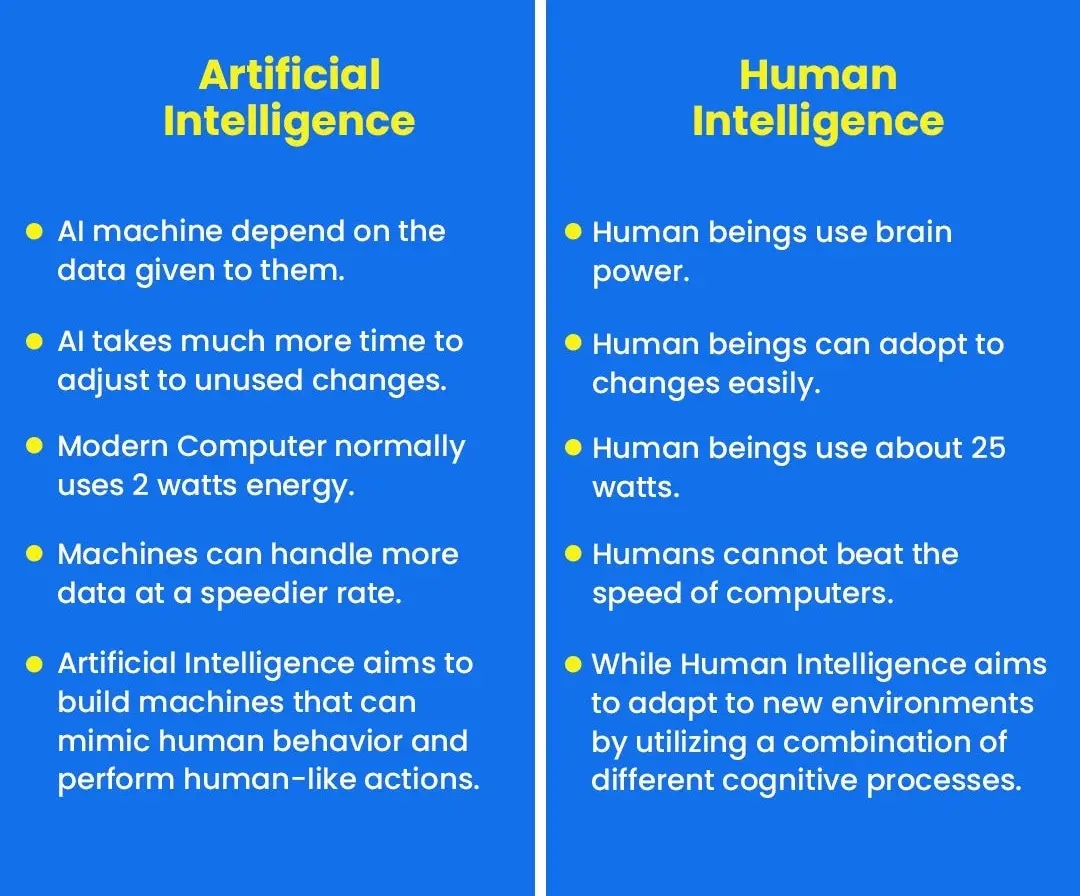
Human intelligence aims to learn from experience and adapt to new environments via different cognitive processes, while artificial Intelligence (AI) aims to mimic and surpass human actions and behaviour.
How to Measure Human Intelligence
Human intelligence is measured by either a group or individually administered test. It only takes a few minutes after meeting someone for most of us to judge how smart, competent, or quick-witted we think they are.
Philosophers and psychologists have long debated how to conceptualize and measure intelligence, how many types of intelligence there are, the role of nature versus nurture in intelligence, the social, biological and environmental determinants of intelligence, or how intelligence is represented in the brain.
In the 1900s, Binet and Simon developed the first intelligence test, “Intelligence Tests in Schools”, which consisted of a wide variety of questions that included the ability to name objects, define words, draw pictures, complete sentences, compare items, and construct sentences.
Intelligence quotient (IQ) is widely adopted as a measure of intelligence that is adjusted for age.
IQ is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence.
The Stanford-Binet, is a measure of general intelligence made up of a wide variety of tasks including vocabulary, memory for pictures, naming of familiar objects, repeating sentences, and following commands.
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is the most widely used IQ test for adults in the US.
What Are the Different Types of IQ Tests?
The most common types of IQ tests are:
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
Universal Nonverbal Intelligence
Differential Ability Scales
Peabody Individual Achievement Test
Wechsler Individual Achievement Test
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
Woodcock Johnson III Tests of Cognitive Disabilities
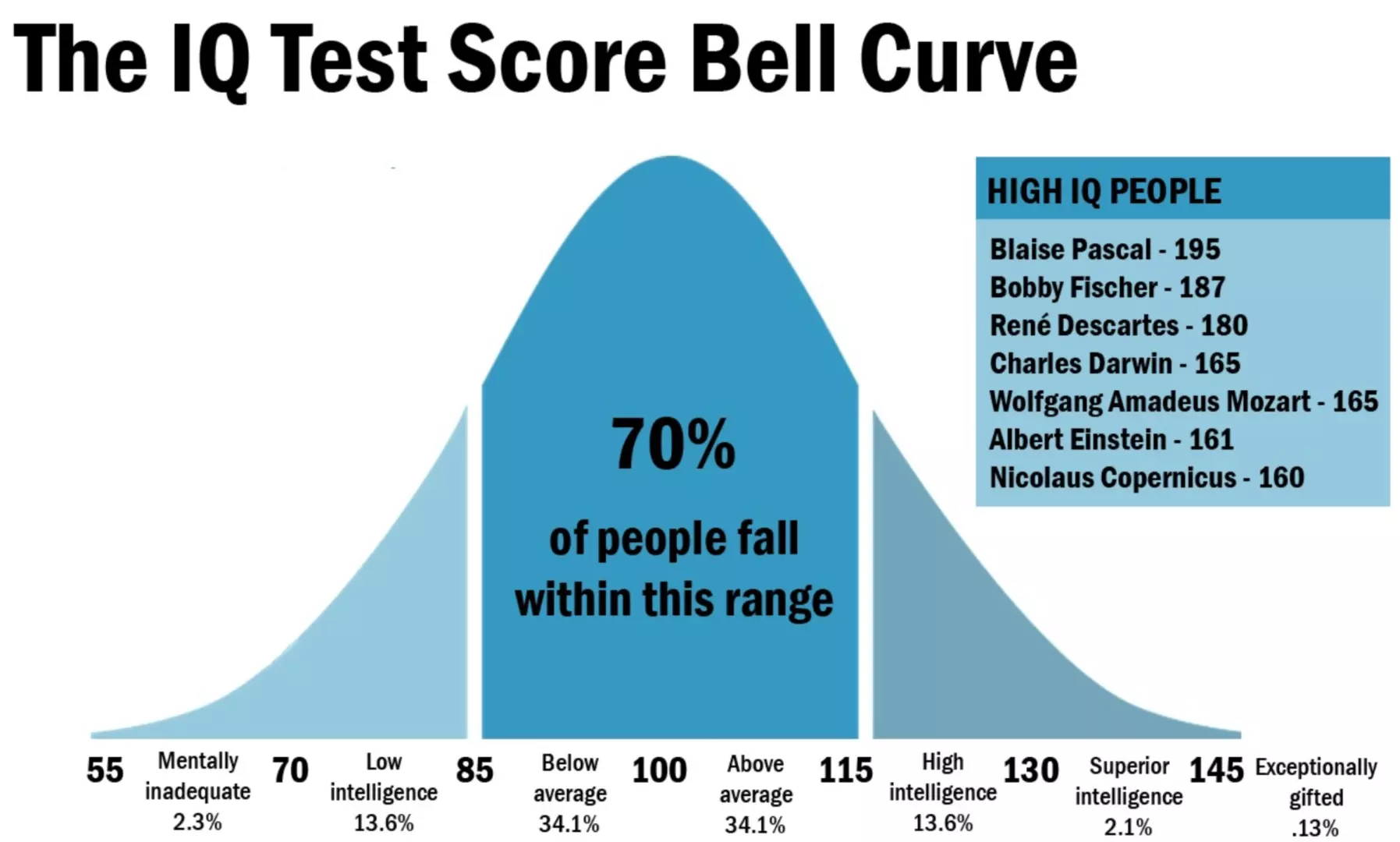
A high IQ score, over 130, is typically associated with high intelligence.
Scores below 70 are usually a cause for concern. They may indicate an underlying learning disability.
Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Human Intelligence
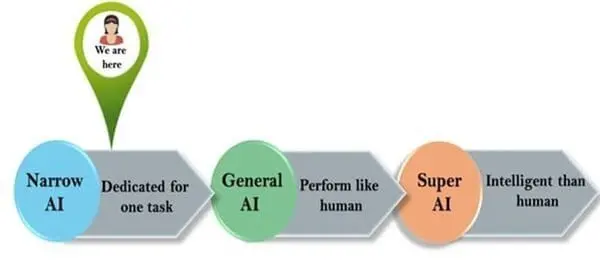
What Are the 3 Types of Artificial Intelligence
Advances in AI have allowed us to make progress in all kinds of disciplines.
There are 3 types of AI:
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), which has a limited range of capabilities
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which has attributes that are on par with human capabilities
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), which has skills that surpass humans and can make them obsolete
How To Measure Intelligence in Artificial Intelligence
Intelligence in an artificial intelligence (AI) system can be measured in mainly 4 ways:
Breadth: Most systems we know to be intelligent such as the human brain have broad capabilities. A child learns a lot of tasks such as walking, talking and many more things. An AI system that should be considered intelligent should also have such similar broad capabilities. The so-called strong AI system should be able to learn any task without any modification directly to its source code by human engineers. But we all know about the no free lunch theorem which states that an algorithm that is good at a particular set of tasks pays for that by performing poorly on the other remaining set of tasks. That means that to have such a broad AI system we need a set of fundamental learning algorithms and not just one, this is a very active area of research and high profile groups like DeepMind are searching for such a set of general purpose learning algorithms to solve artificial general intelligence (AGI), which is a broader version of AI. In fact just this one ability can definitely help us measure how intelligent an AI system is.
Data requirements: A strong AI system should be able to model the problem from as little data as possible but it should also be able to consume huge Google scale data and make sense of that too. The ability to generalize from very little training data is a strong indicator of intelligence as opposed to requiring huge amounts of data in order to model the problem.
Supervised vs unsupervised: It is clear that we need both supervised and unsupervised learning in AI based on the application scope but since there is more unlabeled than labelled data around, unsupervised learning is more attractive. Unsupervised learning indicates intelligence because a system that learns on its own with minimal supervision is considered more intelligent than the other that requires more supervision. This is strongly evident in human intelligence, a child capable of picking up tasks like coding on their own are considered more intelligent.
Predictive: Intelligence is also based on having an idea of what comes next, this is a very powerful capability because planning is very important for really intelligent systems. Predictive capabilities are essential to planning and reasoning. Humans have strong predictive capabilities, we always expect something and try to plan for it in both long and short term. Short term prediction is when you want to catch a ball thrown at you, you will be able to predict the trajectory of the ball and catch it. Long term prediction is called planning, you literally plan how you can act in order to achieve your goal. You plan how to make that vacation trip to Hawaii because of some predictive nature of your mind, prediction is intelligence.






Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest