Comments
- No comments found
Artificial intelligence is providing disruptive changes in the 4th industrial revolution (Industry 4.0) by increasing interconnectivity and smart automation.
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the way companies manufacture, improve and distribute their products.
Artificial intelligence (AI) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs and perform human-like tasks.
It allows computers to think and behave like humans, but at much faster speeds and with much more processing power than the human brain can produce.
AI offers advantages of new and innovative services, and the potential to improve scale, speed and accuracy.
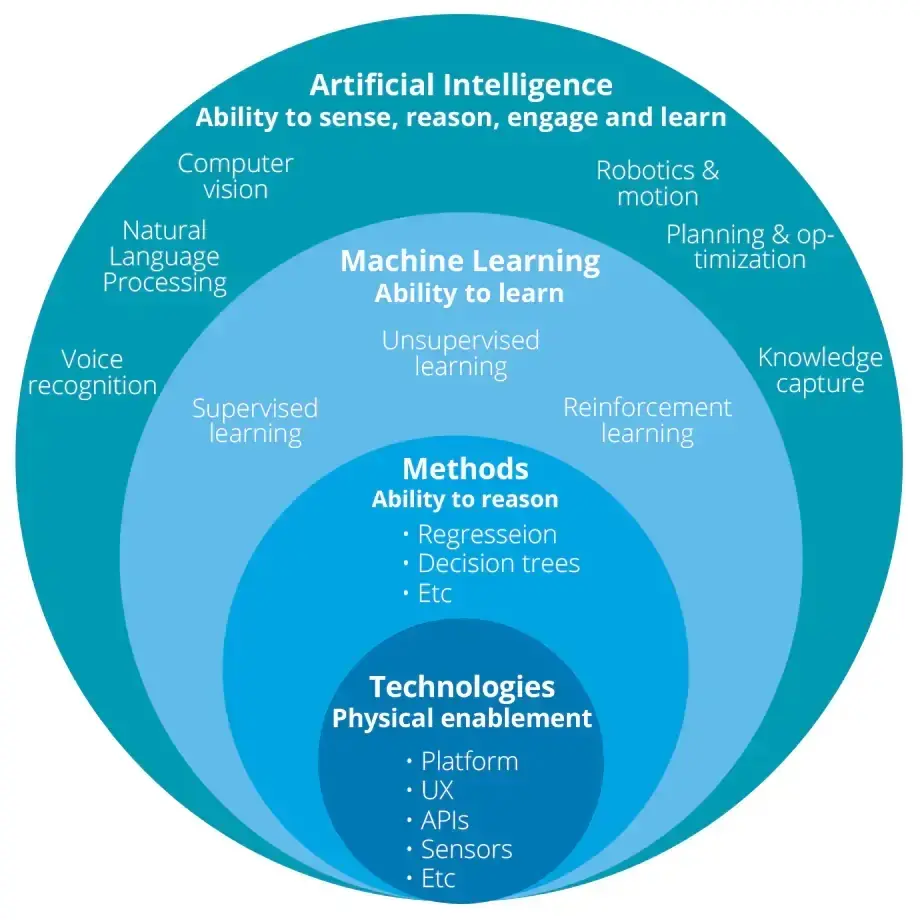
There are 3 types of artificial intelligence:
Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI), which has a narrow range of abilities.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI), which is on par with human capabilities.
Artificial superintelligence (ASI), which is more capable than a human.
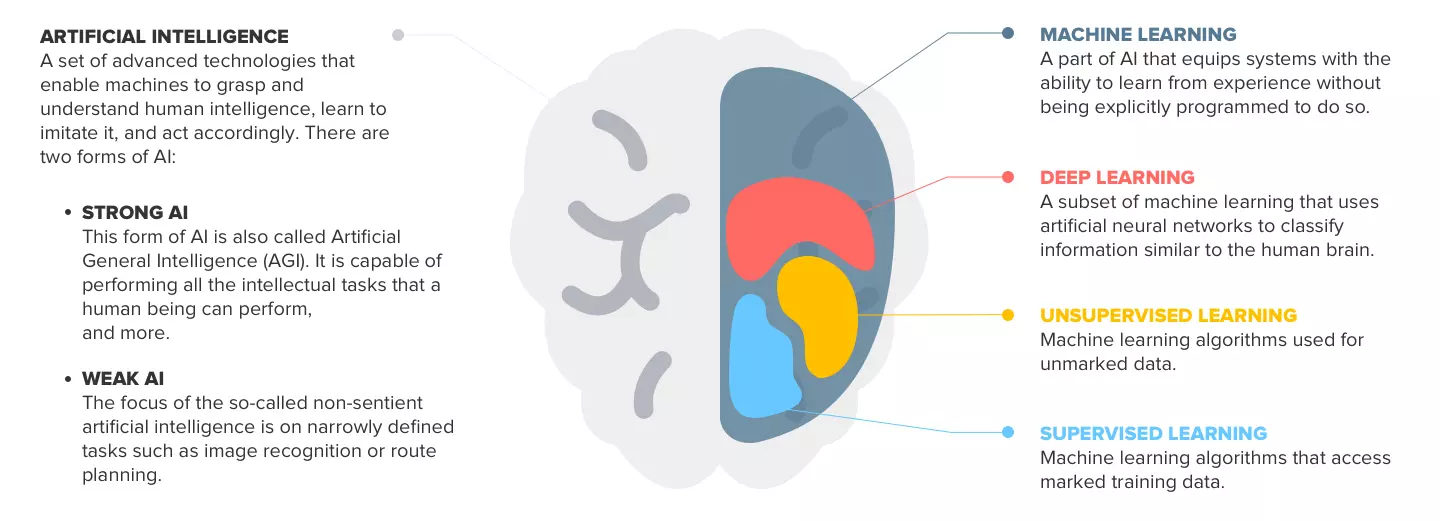
Artificial intelligence can also be classified as weak or strong.
Weak AI refers to systems that are programmed to accomplish a wide range of problems but operate within a predetermined or pre-defined range of functions. Strong AI, on the other hand, refers to machines that exhibit human intelligence.
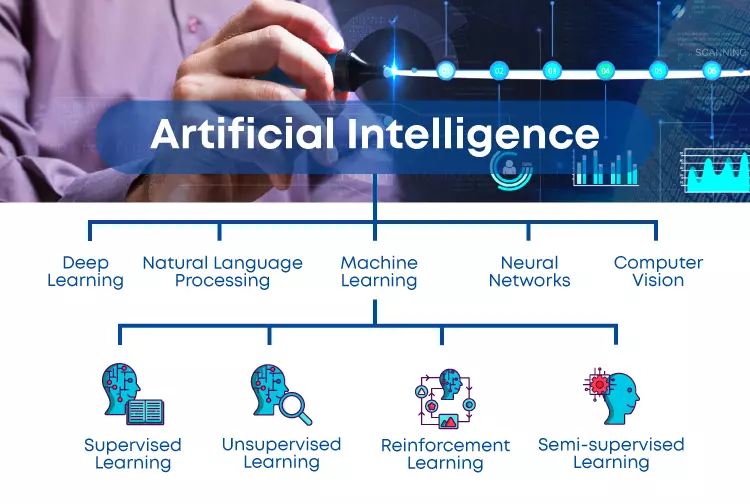
Artificial intelligence has several subsets:
Machine learning.
Deep learning.
Computer vision
Natural language processing.
Expert system.
Robotics.
Machine vision.
Most AI examples that you hear about today – from chess-playing computers to self-driving cars – rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing.
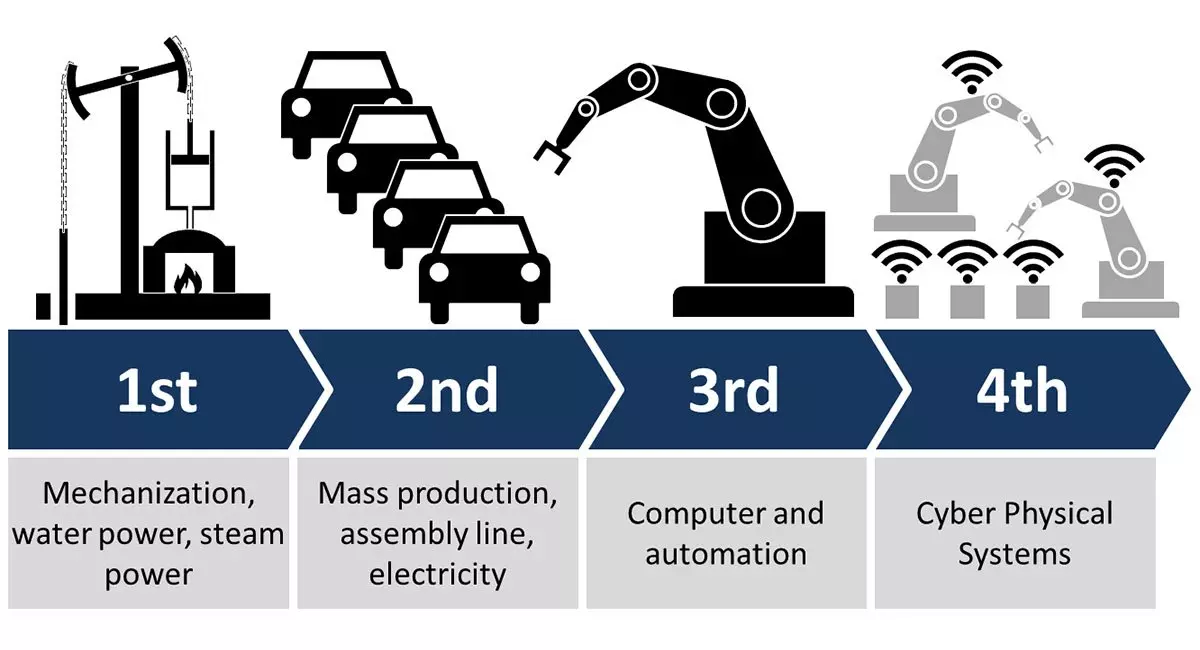
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is the current and developing environment in which disruptive technologies and trends such as the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) are changing the way modern people live and work. The integration of these technologies into manufacturing practices is known as Industry 4.0.
The first industrial revolution used water and steam power to mechanize production.
The second used electric power to create mass production.
The third used electronics and information technology to automate production.
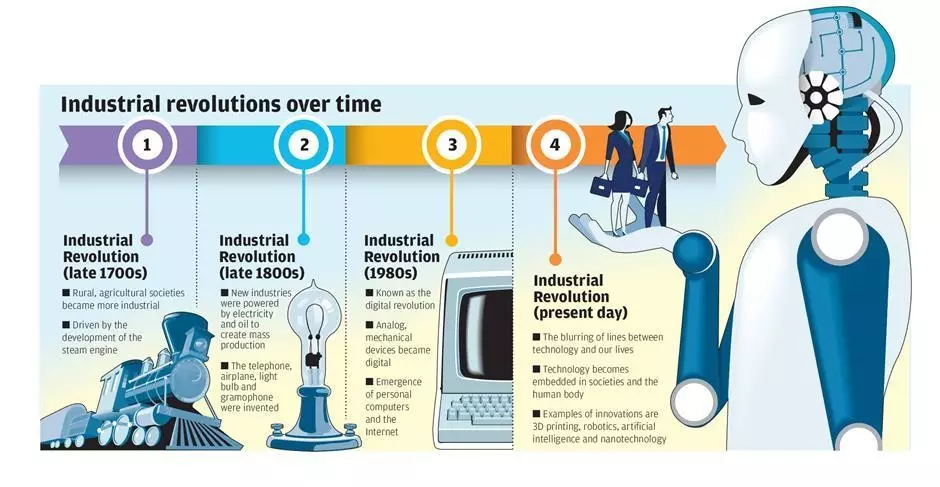
The fourth Industrial revolution is characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres, with rising emerging technologies, as real AI, Narrow AI/ML/DL, robotics, automation, materials science, energy storage, the Internet of Things, autonomous vehicles, 3-D printing, nanotechnology, biotechnology, neurotechnology, cognitive technology, and quantum computing. It implies radical disruptions to everything, industries, jobs, works, technologies, and old human conditions. In its scale, scope, complexity, and impact, the AI transformation will be unlike anything humankind has experienced before.
Artificial intelligence is making companies make the best use of practical experience, even displacing traditional labor and becoming the productive factor itself.
It offers entirely new paths towards growth for manufacturing, service, and other industries, reshaping the world economy and bringing new opportunities for our societal development.
As AI begins to impact the workforce and automation replaces some existing skills, we’re seeing an increased need for emotional intelligence, creativity, and critical thinking.
Zvika Krieger, co-leader of the World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Deploying AI requires a kind of reboot in the way companies think about privacy and security, As data becomes the currency of our digital lives, companies must ensure the privacy and security of customer information.
Businesses will need to ensure they have the right mix of skills in their workforce to keep pace with changing technology.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest