Comments
- No comments found
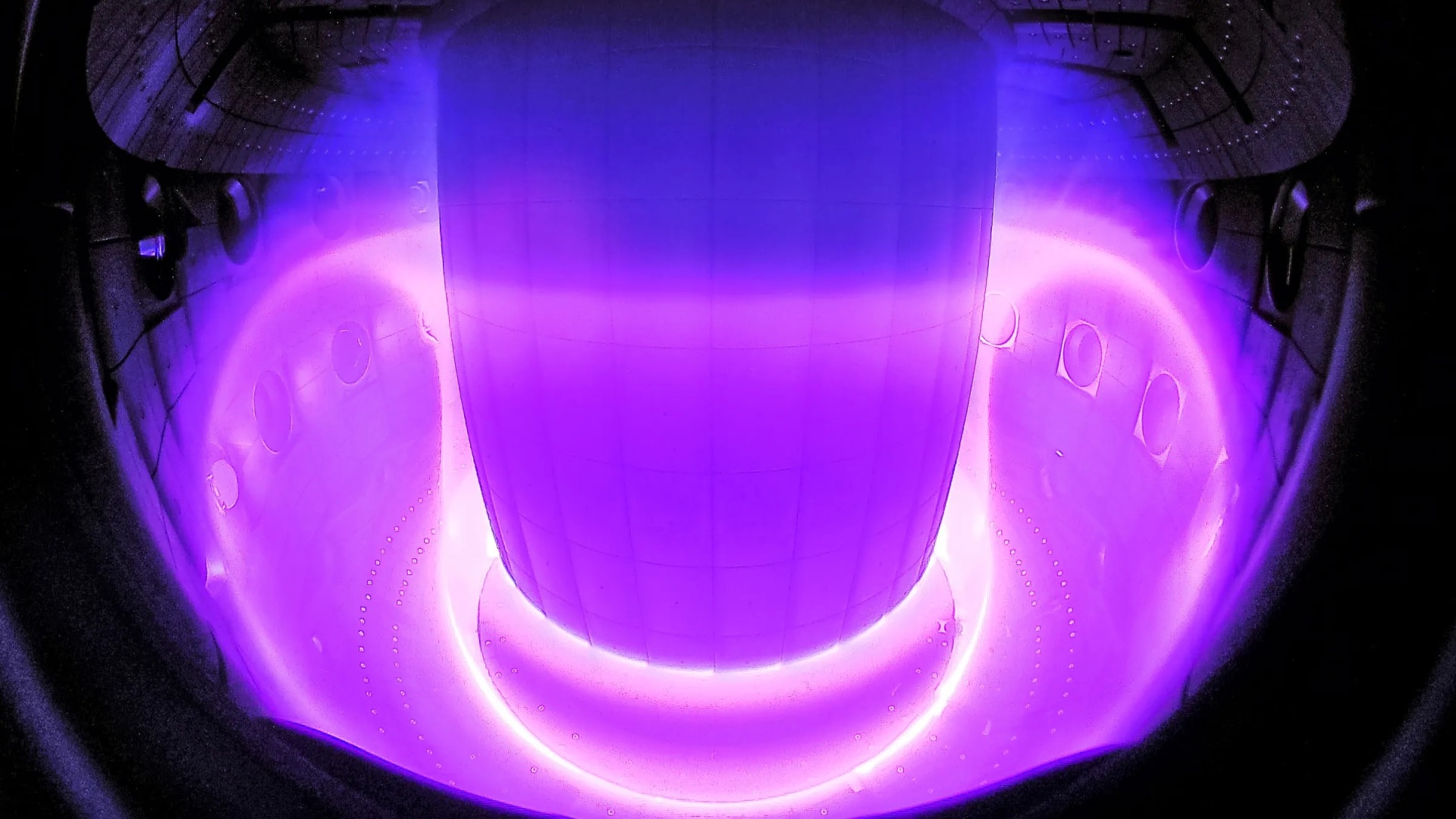

In recent years, the convergence of nuclear technology and artificial intelligence (AI) has given rise to a powerful synergy known as Nuclear AI.
This innovative field harnesses the capabilities of AI to enhance various aspects of nuclear technology, ranging from reactor design and safety to waste management and fusion research. While Nuclear AI offers promising benefits, it also poses significant challenges and risks that must be carefully considered.
Nuclear AI refers to the application of artificial intelligence techniques and algorithms to enhance, optimize, and streamline various aspects of nuclear technology. This includes areas such as nuclear reactor operation, radiation detection, nuclear materials analysis, waste management, and even the pursuit of controlled nuclear fusion. By utilizing AI's capacity for pattern recognition, complex data analysis, and decision-making, Nuclear AI aims to revolutionize the nuclear industry by improving efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Safety Enhancement: One of the foremost benefits of Nuclear AI lies in its potential to enhance safety in nuclear operations. AI-powered predictive maintenance systems can monitor equipment conditions and predict failures, reducing the likelihood of accidents and unplanned shutdowns. Machine learning algorithms can also aid in real-time anomaly detection, helping operators identify and respond to abnormal conditions swiftly.
Efficient Energy Generation: Nuclear power has the potential to provide a significant portion of the world's clean energy needs. By optimizing reactor operations and fuel utilization using AI, Nuclear AI can improve the efficiency of nuclear power plants, resulting in higher energy output and reduced waste.
Waste Management: Dealing with nuclear waste is a complex challenge. AI can contribute by enabling more precise modeling of waste behavior and decay, aiding in the development of safer disposal methods. Machine learning algorithms can also assist in identifying potential sites for nuclear waste repositories based on geological and environmental factors.
Fusion Research Acceleration: Achieving controlled nuclear fusion has long been a goal of the scientific community. Nuclear AI can assist in analyzing the massive amounts of data generated during fusion experiments, helping researchers make sense of intricate plasma dynamics and design more effective fusion reactors.
Regulatory Compliance: Nuclear facilities are subject to strict regulatory frameworks. AI can facilitate compliance by automating data analysis and reporting, ensuring that operations meet safety and environmental standards.
Bias and Uncertainty: AI systems can inadvertently learn biases present in training data, potentially leading to skewed outcomes. In nuclear operations, biased decisions could have severe safety and environmental consequences. Additionally, uncertainty in AI predictions must be carefully managed, as incorrect decisions could lead to catastrophic events.
Human-AI Interaction: As AI systems become more integrated into nuclear operations, the interaction between human operators and AI algorithms becomes crucial. Ensuring effective communication and understanding between humans and AI is essential to prevent misunderstandings and errors.
Ethical Considerations: AI applications in the nuclear domain raise ethical questions about accountability, transparency, and decision-making. Who is responsible if an AI system makes a critical mistake? How transparent are the decision-making processes of AI algorithms in high-stakes nuclear operations?
Regulatory Hurdles: Introducing AI into the nuclear sector requires navigating complex regulatory frameworks. Demonstrating the safety and reliability of AI-powered systems to regulatory bodies can be a lengthy and challenging process.
The misuse of nuclear AI could lead to severe consequences, potentially resulting in catastrophic outcomes. Some of the potential prices we may pay for the misuse of nuclear AI include:
Accidental disasters: Improperly designed or deployed AI systems could lead to accidental disasters, such as unintended nuclear reactions, meltdowns, or radioactive leaks, causing widespread destruction and harm to human life, the environment, and economies.
Proliferation of nuclear weapons: AI could potentially be used to optimize and accelerate the development of nuclear weapons, leading to an increase in nuclear proliferation and the risk of conflict.
Security breaches: If AI systems controlling nuclear assets are not adequately protected, they could become vulnerable to cyberattacks, leading to the theft of sensitive information, sabotage, or unauthorized access to nuclear facilities.
Escalation of conflicts: Misuse of AI in nuclear contexts may increase the likelihood of conflicts and escalate tensions between nations, heightening the risk of nuclear confrontations.
Loss of human control: Over-reliance on autonomous AI systems in nuclear decision-making could reduce human involvement and oversight, making it challenging to maintain control over nuclear operations.
Global instability: Misuse of nuclear AI could undermine international trust and cooperation in nuclear disarmament efforts, leading to heightened global instability and potential arms races.
Ethical and legal dilemmas: The misuse of AI in the nuclear domain raises ethical questions about the responsibility and accountability for potential catastrophic events caused by AI decisions. It could also lead to legal challenges regarding liability and culpability.
Environmental devastation: Nuclear accidents caused by AI misuse could lead to long-lasting environmental contamination and damage to ecosystems, affecting the health and well-being of future generations.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to ensure strict regulation, oversight, and responsible use of ai in nuclear applications. International cooperation and adherence to ethical principles are crucial to safeguarding against the misuse of nuclear AI and promoting global security and stability.
The future of Nuclear AI holds immense promise, but it also demands careful navigation. Researchers and stakeholders must work collaboratively to address the challenges and mitigate the risks associated with this technology. Here are some potential avenues for the future of Nuclear AI:
Advanced Reactor Design: AI could revolutionize nuclear reactor design by enabling rapid simulations and optimizations, leading to more efficient and safer designs. This could help in the development of advanced reactors, such as small modular reactors and molten salt reactors.
Autonomous Operations: As AI technology matures, the possibility of autonomous nuclear operations becomes more feasible. AI systems could autonomously manage reactor operations, maintenance, and safety protocols, minimizing human intervention and potential errors.
Fusion Breakthroughs: AI can play a pivotal role in accelerating breakthroughs in controlled nuclear fusion. By analyzing massive datasets from fusion experiments, AI algorithms could help researchers identify patterns and insights that lead to more successful fusion reactions.
Global Collaboration: The complex challenges of Nuclear AI necessitate global collaboration. International partnerships can facilitate the sharing of data, expertise, and best practices, ensuring the responsible and safe development of Nuclear AI.
Ethical Frameworks: Establishing ethical frameworks for Nuclear AI is essential. This includes defining clear lines of accountability, ensuring transparency in decision-making, and addressing biases to prevent unintended consequences.
Nuclear AI represents a remarkable convergence of two cutting-edge fields, holding the potential to reshape the landscape of nuclear technology. The benefits of enhanced safety, efficient energy generation, waste management, and accelerated fusion research are tantalizing. However, the risks and challenges, ranging from data security to ethical considerations, cannot be overlooked. As we venture into the future of Nuclear AI, a balanced approach that prioritizes safety, collaboration, and ethical responsibility will be crucial in harnessing its full potential for the betterment of society.
Ahmed Banafa is an expert in new tech with appearances on ABC, NBC , CBS, FOX TV and radio stations. He served as a professor, academic advisor and coordinator at well-known American universities and colleges. His researches are featured on Forbes, MIT Technology Review, ComputerWorld and Techonomy. He published over 100 articles about the internet of things, blockchain, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and big data. His research papers are used in many patents, numerous thesis and conferences. He is also a guest speaker at international technology conferences. He is the recipient of several awards, including Distinguished Tenured Staff Award, Instructor of the year and Certificate of Honor from the City and County of San Francisco. Ahmed studied cyber security at Harvard University. He is the author of the book: Secure and Smart Internet of Things Using Blockchain and AI.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest