Comments
- No comments found
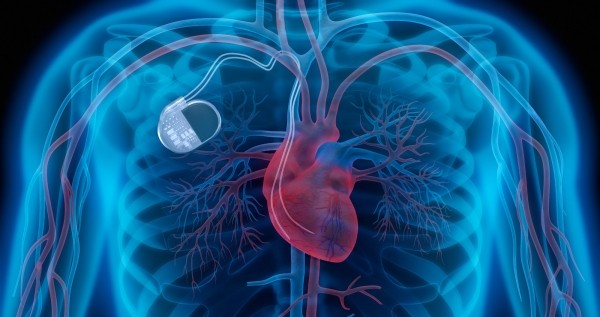
The Internet of Bodies (IoB) refers to the connection of devices that are worn or implanted on the body to the internet.
IoB devices include popular devices such as smart watches, fitness trackers, pacemakers, and insulin pumps. They are designed to improve our health and well-being.
The main purpose of IoB devices is to allow the constant monitoring of various bodily functions by providing real-time data and information to healthcare professionals. This can be beneficial for those with chronic health conditions, allowing for early detection of potential issues and more effective treatment. However, it also presents new security risks, as these devices are constantly connected to the internet and can be vulnerable to hacking. Hackers can potentially gain access to sensitive personal information and even control the functions of the device, potentially causing harm to the user.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes more prevalent in our daily lives, connecting everything from our homes to our cars, the potential for malicious actors to exploit these connected devices for nefarious purposes is on the rise. One particularly concerning area of IoT is the Internet of Bodies (IoB), which includes devices implanted or worn on the body, such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, and smart watches. These devices are designed to improve our health and well-being, but they also open up new opportunities for hackers to gain access to our personal information and bodily functions.
IoB devices have access to the human body, collecting vast quantities of personal biometric data. IoB devices pose serious risks, including hacking, privacy infringements, and malfunction.
The risks associated with IoB devices are not just theoretical; they have already been demonstrated in real-world attacks. In 2017, security researchers discovered that hackers could potentially gain access to a patient's insulin pump and change the dosage, potentially causing serious harm or even death. Similarly, in 2018, researchers found that it was possible to hack into a pacemaker and change the settings, potentially putting the patient's life at risk.
These types of attacks are particularly concerning because they target the most vulnerable members of society: the elderly and those with chronic health conditions. These individuals may not have the knowledge or resources to protect themselves from cyber attacks, and they may also be less able to recover from the physical and emotional effects of a hack.
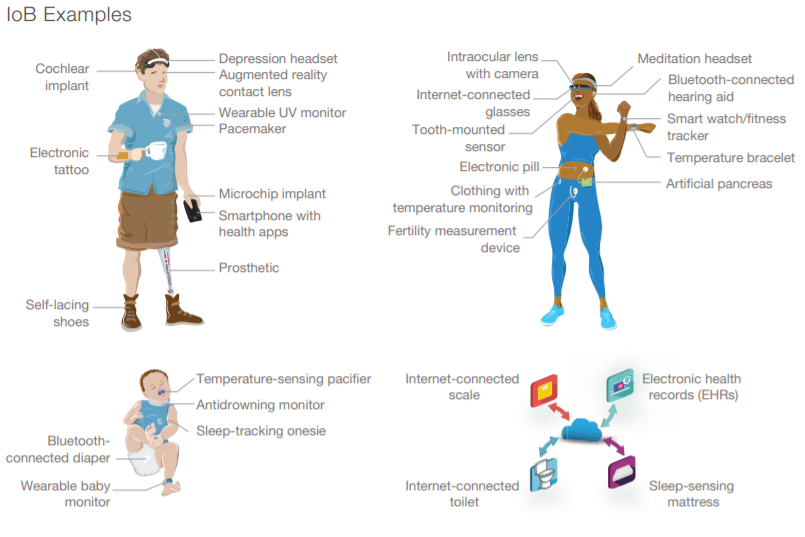
One notable example of an IoB hack occurred in 2017, when a hacker was able to remotely access a patient's insulin pump and change the dosage. The patient, who had type 1 diabetes, was unaware of the hack and nearly died as a result of the incorrect dosage. The hacker was able to access the insulin pump through a vulnerability in the device's wireless communication system.
In 2018, researchers at the security firm WhiteScope discovered that it was possible to hack into a pacemaker and change the settings. The researchers were able to gain access to the pacemaker by exploiting a vulnerability in the device's wireless communication system. Once they had access, they were able to change the pacemaker's settings and potentially put the patient's life at risk.
Another example of an IoB hack occurred in 2020, when a group of hackers were able to gain access to a hospital's network through a vulnerability in a smartwatch worn by a hospital employee. Once they had access to the network, the hackers were able to steal sensitive patient information, including medical records and personal identification numbers.
While the risks associated with IoB devices are significant, there are steps that individuals can take to protect themselves from hackers. One important step is to keep the device's software up-to-date. Manufacturers often release updates that address known vulnerabilities, so it is important to install these updates as soon as they become available.
Another step that individuals can take is to be cautious when connecting their devices to unfamiliar networks. For example, it is generally not a good idea to connect your device to a public Wi-Fi network, as these networks are often unsecured and can be easily hacked.
Individuals should also be careful when downloading apps or software for their devices, as these can also be used to gain access to the device. It is important to only download apps from reputable sources and to be aware of any suspicious activity on the device.
People should be aware of the risks associated with IoB devices and take steps to protect themselves from hackers. This may include consulting with a healthcare professional or security expert, or taking a class on cyber security.
It is important for both individuals and healthcare professionals to be aware of the risks associated with the IoB and take steps to protect against hacking, such as keeping software up-to-date and being cautious when connecting to unfamiliar networks.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest