Comments
- No comments found
The integration of Green AI practices becomes increasingly important for mitigating the environmental impact of technological advancements.
As the prominence of AI continues to grow, so does the need to address its environmental impact, particularly in terms of carbon emissions, often referred to as the carbon footprint. This article delves deeper into the nuances of the carbon footprint associated with AI technologies and presents comprehensive strategies to minimize it.
Green Artificial Intelligence (Green AI) refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies with a focus on environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. It involves the development and deployment of AI algorithms, models, and systems that aim to reduce the environmental impact of computing processes and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The concept of Green AI addresses the significant energy consumption and carbon footprint associated with traditional AI approaches, which often require extensive computational resources and large amounts of data. Green AI seeks to mitigate these environmental concerns by optimizing AI algorithms and practices to minimize energy usage, resource consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
The carbon footprint of AI encompasses various facets of its lifecycle, from the manufacturing of hardware components to their usage and eventual disposal. This footprint primarily arises from energy consumption, electronic waste generation, and the substantial computational power required for training and inference of AI models. Data centers, crucial for AI processing, also contribute significantly to emissions due to their energy demands.

1. Energy-Intensive Training: The training of complex AI models, such as deep neural networks, demands massive computational resources. This process consumes substantial energy and releases carbon emissions, contributing significantly to the overall footprint.
2. Inference and Data Processing: While AI inference generally requires less energy than training, the vast deployment of AI applications can still accumulate substantial emissions, especially if the underlying hardware lacks energy efficiency.
3. Data Center Operations: The operation of data centers, essential for AI processing, requires constant cooling and energy supply. The reliance on non-renewable energy sources can result in substantial emissions.
4. Electronic Waste: The disposal of electronic waste from outdated AI hardware contributes to environmental degradation. If not managed properly, it can lead to harmful pollution and further emissions.
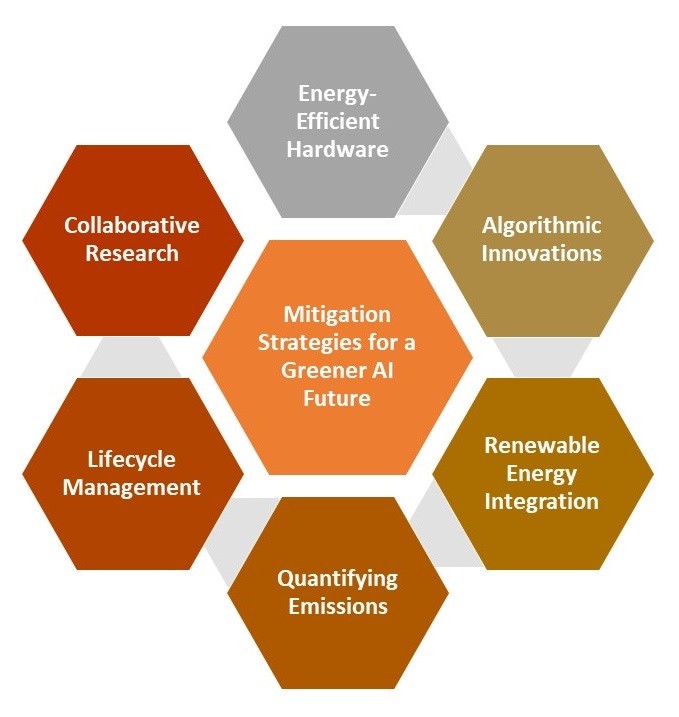
1. Energy-Efficient Hardware: Developing energy-efficient hardware and optimizing processor designs can significantly reduce energy consumption during training and inference.
2. Algorithmic Innovations: Advancements in algorithms that allow for faster convergence during training or require fewer computational resources can lead to substantial energy savings.
3. Renewable Energy Integration: Transitioning data centers and AI infrastructure to run on renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can drastically cut down emissions.
4. Quantifying Emissions: Implementing methods to accurately quantify the carbon emissions associated with AI projects can drive awareness and accountability.
5. Lifecycle Management: Designing AI systems with a focus on longevity and upgradeability can extend their usable life and reduce electronic waste.
6. Collaborative Research: Encouraging collaborative research and open-source initiatives can foster the development of sustainable AI technologies.
As AI technologies continue to shape our world, it's imperative to consider their environmental impact. The carbon footprint associated with AI presents a formidable challenge, but one that can be tackled through a combination of innovative technology, responsible practices, and global cooperation. By implementing strategies that prioritize energy efficiency, sustainable infrastructure, and conscientious consumption, we can pave the way for an AI-powered future that is not only intelligent but also environmentally sustainable.
Ahmed Banafa is an expert in new tech with appearances on ABC, NBC , CBS, FOX TV and radio stations. He served as a professor, academic advisor and coordinator at well-known American universities and colleges. His researches are featured on Forbes, MIT Technology Review, ComputerWorld and Techonomy. He published over 100 articles about the internet of things, blockchain, artificial intelligence, cloud computing and big data. His research papers are used in many patents, numerous thesis and conferences. He is also a guest speaker at international technology conferences. He is the recipient of several awards, including Distinguished Tenured Staff Award, Instructor of the year and Certificate of Honor from the City and County of San Francisco. Ahmed studied cyber security at Harvard University. He is the author of the book: Secure and Smart Internet of Things Using Blockchain and AI.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest