Comments
- No comments found

Millions are on the brink of starvation If countries don't make big changes now, the world will face mass food shortages.
Without enough food, there will be hunger, chaos, and violence. High food prices have already had a devastating impact in poor nations.
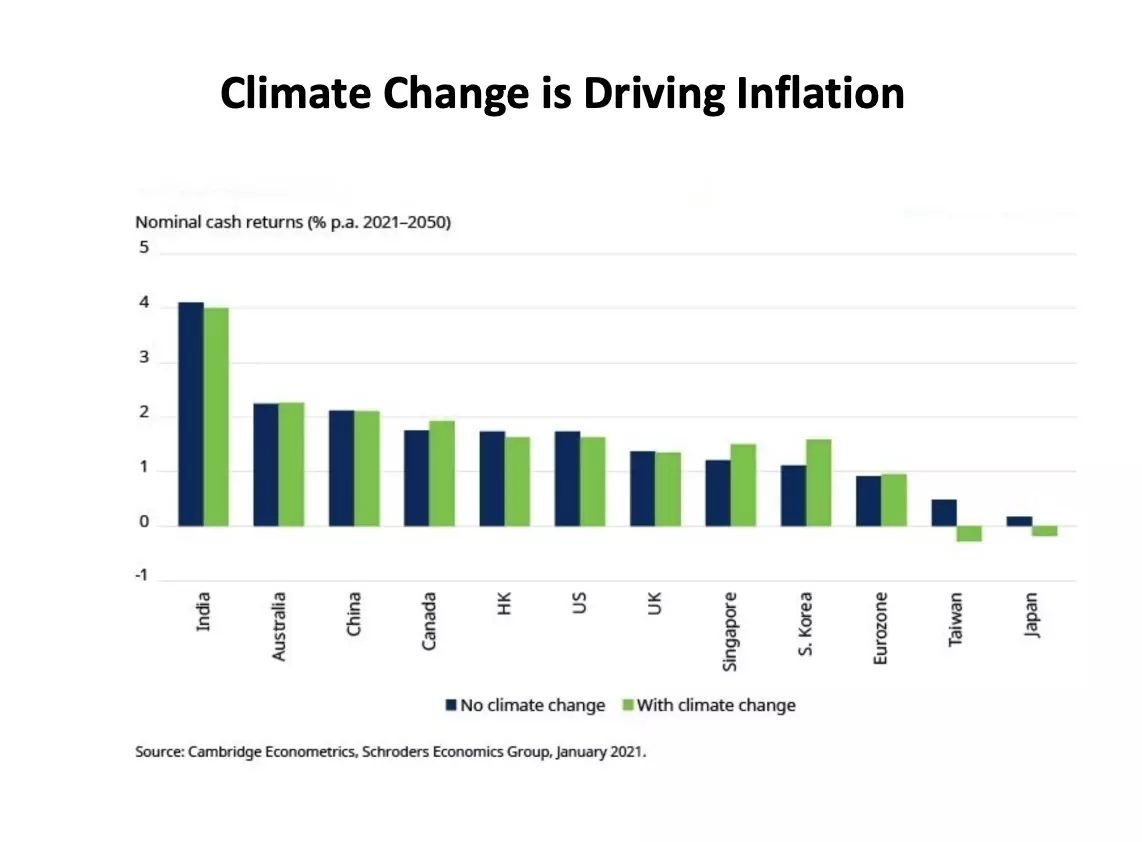
Climate change is driving inflation by fuelling demand.
As storms' frequency and severity increase, sea levels rise, and drought afflicts previously habitable areas, more people will compete for available housing elsewhere.
The global economy shows evidence of a new, more inflationary regime caused not only by climate change but by the fight over how to respond to it.
According to the latest report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the annual inflation rate in May was 8.6%, its highest level since 1981, as measured by the consumer price index.

Global food insecurity affects around 800 million, with about 44 million most vulnerable to hunger.
Unless action is taken now, more lives will be lost and the devastating effects on the lives of children in poor countries today will be felt for decades to come.
Inflation and the global food crisis are upending aspects of the economy and threatening stability in several countries. The complex sets of problems that led to the situation may continue in the coming months as uncertainty around approaches to resolving the crisis abounds.
During the past three years, COVID-19 has caused a sharp rise in poverty and inequality globally, as lockdowns have devastated family livelihoods.
In many countries, pandemic restrictions have also meant disruption to food supplies, slowing remittances from families overseas and the halting of school meal programmes.
Steep rises in food prices are creating immense strain on household budgets, with the poorest families hardest hit.
Climate change has increased the prevalence of crop pests such as locusts, which damage and destroy harvests.
Higher temperatures over recent decades have played a non-negligible role in driving price developments.
Climate change is indirectly contributing to climate change, leading to more frequent price increases that are much more likely to feed inflationary psychology, generating broader price rises even in the absence of specific supply problems.
The impact of high temperatures on prices appears to be on the upside in the short term, and on the downside in the medium term.
Climate change is often associated with a greater incidence of damaging climatic events, notably windstorms, extremes of precipitation and of temperature. These events may impact specific prices, notably food prices.
Wars, revolutions, and other turmoil are interrupting energy supplies repeatedly.
Across the world, climate-linked disasters have killed crops, disrupted energy supplies, and crippled transportation lines.
The trillions of dollars the public and private sectors need to spend to transition the world away from fossil fuels, not to mention regulations designed to increase the costs of carbon-intensive goods, are bound to shape the course of future inflation.
Climate change is increasingly affecting the objective, conduct and transmission of monetary policy including inflation.
With the climate agenda becoming increasingly prominent, efforts to develop more comprehensive modelling frameworks have been scaled up.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest