Comments
- No comments found

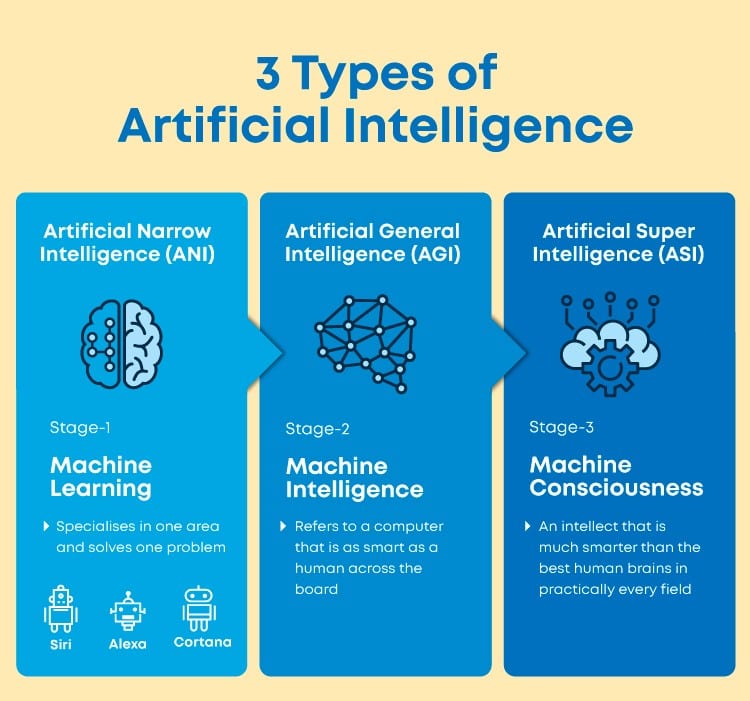
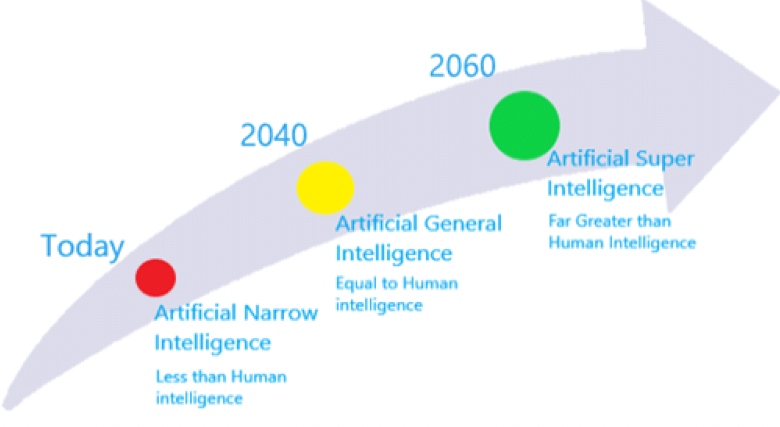
Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that is designed to perform a narrow set of tasks.
It is also known as weak AI or limited AI. ANI is focused on a specific task and is not capable of learning or adapting to new tasks. ANI is designed to perform one specific function and does not have the ability to generalize its knowledge to other areas. Examples of ANI include virtual personal assistants, such as Apple's Siri or Amazon's Alexa, which are programmed to perform a specific set of tasks related to voice recognition and natural language processing.
Artificial narrow intelligence has developed over many years through the efforts of numerous researchers, engineers, and scientists working in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). ANI is a subfield of AI, which has its roots in the 1950s with the development of the first artificial intelligence programs. Since then, AI has undergone many changes and advances, and ANI is just one aspect of the broader field of AI.
Some key figures in the development of ANI include:
Alan Turing: Turing is considered to be the father of modern computing and is known for his work on the Turing Test, a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human.
John McCarthy: McCarthy is credited with coining the term "artificial intelligence" and is known for his work in the field of AI, including the development of the programming language Lisp.
Marvin Minsky: Minsky was a pioneer in the field of AI and is known for his work on artificial neural networks and the development of the first AI programs at MIT.
Eliza: Eliza was one of the first AI programs to be developed, and was created by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum in the 1960s. It was designed to imitate a therapist in a conversation with a patient.
There are many different applications and use cases for artificial narrow intelligence (ANI). Some common examples include:
Virtual personal assistants: Virtual personal assistants, such as Apple's Siri or Amazon's Alexa, use ANI to recognize and respond to voice commands.
Speech recognition: ANI is used in speech recognition software to transcribe spoken words into written text.
Image recognition: ANI can be used to identify and classify objects in images, such as identifying a specific type of plant in a photo.
Fraud detection: ANI can be used to analyze patterns in data to detect fraudulent activity, such as credit card fraud or insurance fraud.
Medical diagnosis: ANI can be used to analyze medical images, such as x-rays or CT scans, to help diagnose medical conditions.
Translation: ANI can be used to translate text from one language to another.
Customer service: ANI can be used to power chatbots that can answer customer inquiries and resolve issues.
Supply chain optimization: ANI can be used to analyze data and optimize the flow of goods and materials in a supply chain.
Narrow artificial intelligence lacks self-awareness, consciousness, emotions, and genuine intelligence that can match human intelligence.
There are several limitations and challenges associated with artificial narrow intelligence (ANI). Some of the main limitations and challenges of ANI include:
Limited scope: ANI is designed to perform a specific task or set of tasks, and is not capable of adapting to new tasks or situations. This narrow focus can limit the potential applications of ANI.
Lack of creativity: ANI is not capable of generating new ideas or concepts. It can only perform tasks that it has been explicitly programmed to do.
Lack of understanding: ANI does not have a deep understanding of the tasks it is performing. It is not capable of understanding the meaning or context of the information it processes.
Vulnerability to errors: ANI can make mistakes if it is given incorrect or incomplete data. It is also vulnerable to bias if the data used to train it is biased.
Dependence on humans: ANI systems require human input and oversight to function properly. They are not self-sufficient or autonomous.
Ethical concerns: ANI systems can raise ethical concerns, such as issues of accountability and responsibility, privacy, and employment.
Limited social intelligence: ANI is not capable of understanding or interacting with people in the same way that a human can. It does not have the ability to recognize emotions or social cue
Artificial narrow intelligence is shaping the future of humanity across nearly every industry.
There are several areas in which artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) could be improved:
- Adaptability: One of the main limitations of ANI is its lack of adaptability. Developing ways to make ANI systems more flexible and able to adapt to new tasks or situations would significantly enhance their capabilities.
- General intelligence: Improving the general intelligence of ANI systems would allow them to understand and learn about the world in a more human-like way. This would enable them to reason, think abstractly, and solve problems more effectively.
- Data quality: Ensuring that ANI systems have access to high-quality data is crucial for improving their performance. This includes ensuring that the data is accurate, relevant, and unbiased.
- Ethical considerations: As ANI systems become more widespread and are used in a wider range of applications, it will be important to address ethical concerns and ensure that they are being used in a responsible and transparent manner.
- Security: Improving the security of ANI systems is essential to prevent hacking and other security threats. This includes developing better safeguards to protect against unauthorized access and ensuring that the systems are resilient to attacks.
- Human-machine collaboration: ANI systems could be improved by developing ways for them to work more effectively with humans. This could include developing interfaces that allow humans to communicate more naturally with ANI systems, or developing ways for ANI systems to better understand human behavior and preferences.
- Real-time processing: Improving the speed and efficiency of ANI systems would allow them to process data and make decisions in real-time, which could be useful in a wide range of applications, such as self-driving cars or real-time financial analysis.
- Natural language processing: Improving the natural language processing capabilities of ANI systems would allow them to understand and respond to human language more effectively, which could be useful in applications such as customer service or language translation.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest