Comments
- No comments found
Substance addiction is a complex and devastating condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
It is a chronic brain disease that involves compulsive drug seeking and use despite harmful consequences. The neuroscience of addiction has made significant advances in recent years, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms that drive the addictive process and the changes in the brain that occur with repeated substance use.
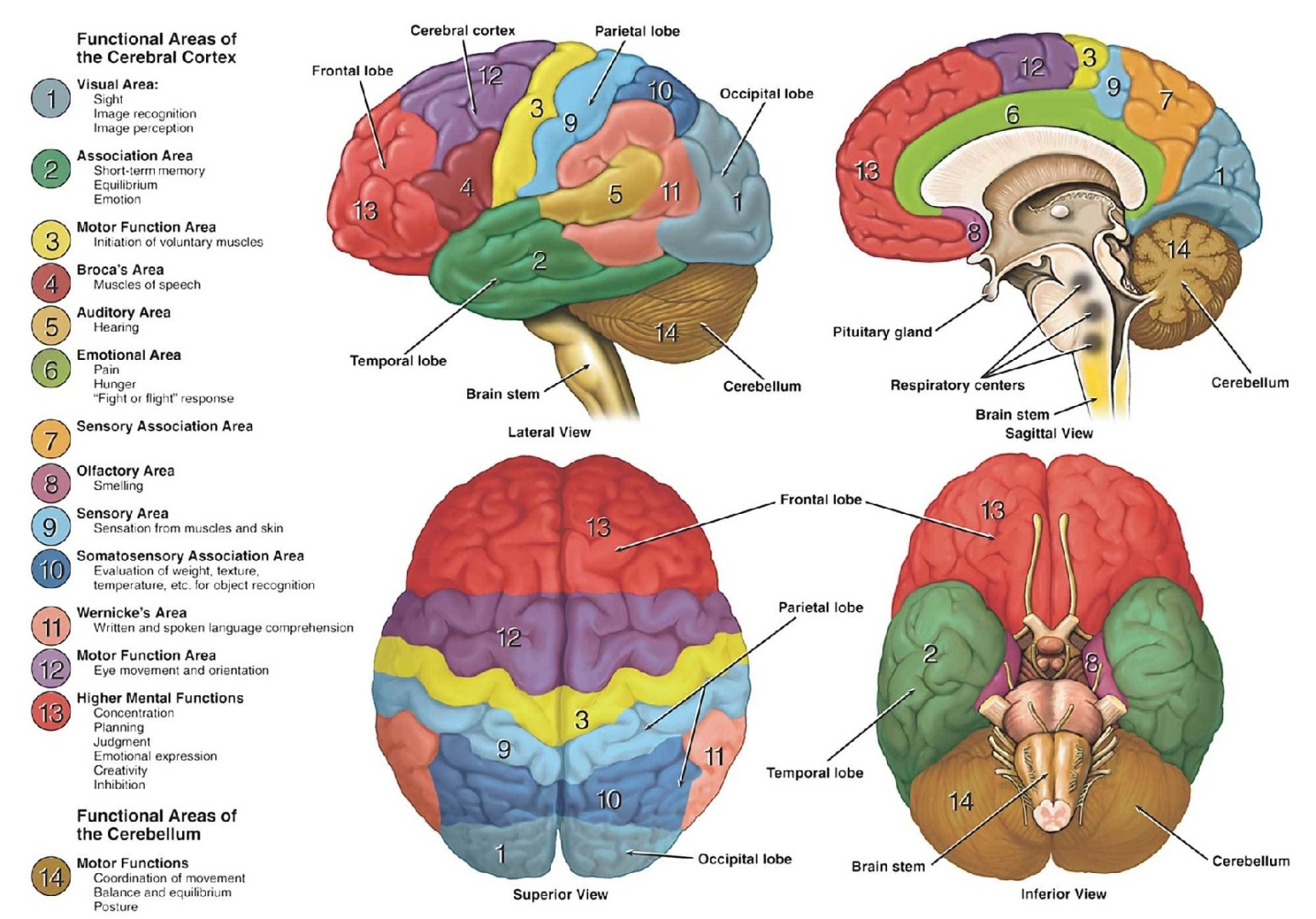
The brain is made up of billions of neurons that communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. These signals form the foundation of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Substance addiction changes the way the brain functions, specifically in the areas responsible for reward, motivation, and memory.
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
The brain's reward system is responsible for processing pleasurable experiences, such as eating and sex. When drugs are used, they activate the reward system in a way that is much stronger and more intense than normal experiences. Over time, this leads to changes in the brain that make it more difficult for an individual to experience pleasure without the drug. This is known as tolerance and is a key factor in addiction.
The brain's motivation and memory systems are also impacted by substance addiction. With repeated drug use, memories of the pleasurable effects of the drug are formed and associated with the places, people, and events associated with drug use. These memories become strong drivers of drug seeking behavior, making it difficult for an individual to quit even in the face of negative consequences.
Substance addiction can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. Some of the most commonly abused substances include alcohol, opioids, cocaine, and marijuana.
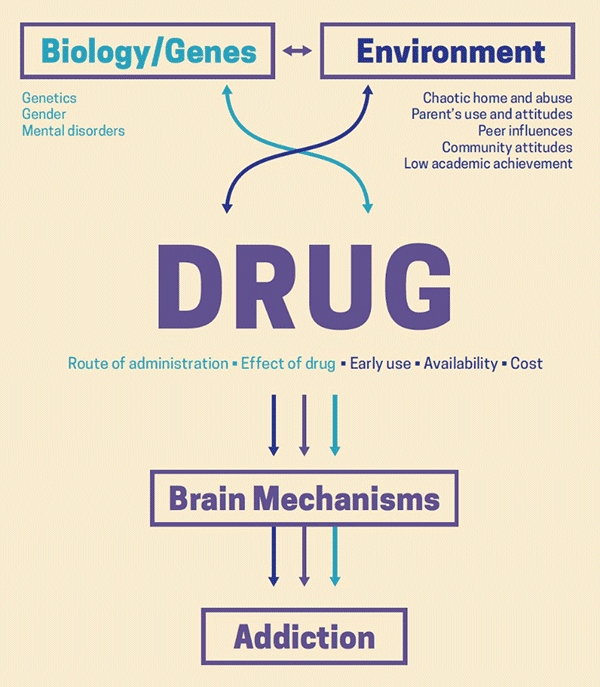
Alcohol is one of the most widely used and abused substances in the world. Chronic alcohol abuse leads to changes in the brain that affect reward, motivation, and memory systems. This can result in a cycle of excessive drinking and negative consequences, such as job loss, financial difficulties, and relationship problems.
Opioids, including prescription painkillers and heroin, are highly addictive and have been responsible for a significant increase in overdose deaths in recent years. These drugs act on the brain's reward system, leading to changes that make it difficult for an individual to quit using, even in the face of negative consequences.
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that acts on the brain's reward system, producing feelings of pleasure and euphoria. Chronic cocaine use leads to changes in the brain that make it difficult for an individual to quit using, even in the face of negative consequences.
Marijuana is the most widely used illicit drug in the world. Despite its reputation as a relatively harmless substance, it can be addictive for some people. Chronic marijuana use can lead to changes in the brain that affect motivation and memory, making it difficult for an individual to quit using, even in the face of negative consequences.
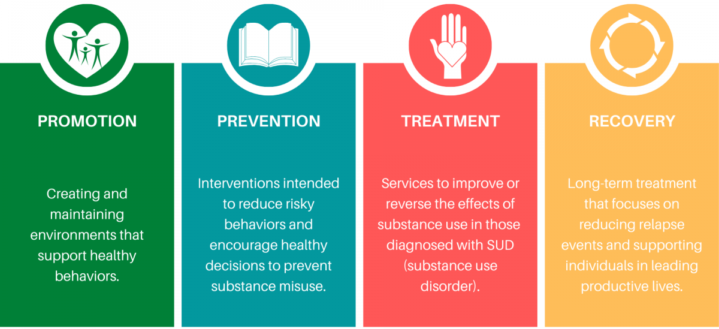
Substance addiction is a complex and devastating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The neuroscience of addiction has shed light on the underlying mechanisms that drive the addictive process and the changes in the brain that occur with repeated substance use. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial in the development of effective treatments for addiction and in reducing the negative consequences associated with substance abuse.
The study of the neuroscience of addiction is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to make a significant impact on the lives of those affected by substance addiction. It is essential that we continue to support research in this area and work to improve the understanding and treatment of addiction, so that we can help those who are struggling with this disease
Felix is the founder of Society of Speed, an automotive journal covering the unique lifestyle of supercar owners. Alongside automotive journalism, Felix recently graduated from university with a finance degree and enjoys helping students and other young founders grow their projects.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest