Humans cannot fully understand artificial intelligence (AI) because it encompasses a wide range of phenomena and concepts.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be difficult to understand and predict at times, due to its ability to process and analyze large amounts of data quickly and make decisions based on that analysis.
In some cases, the specific algorithms and processes used by an AI system may be difficult for humans to fully understand or comprehend.
Additionally, AI systems may sometimes produce results or make decisions that are not immediately obvious or intuitive to humans, which can make it challenging to understand their logic or reasoning.
While it is possible for humans to understand AI, it can be a complex and nuanced field that requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
Does AI Have Feelings?
Artificial intelligence does not have feelings in the same way that humans do. AI is a machine and does not have the capacity for emotions such as happiness, sadness, or anger.
AI can, however, be programmed to recognize and respond to certain stimuli in a way that might seem similar to human emotions.
For example, an AI-powered virtual assistant might use a friendly tone of voice and empathetic language to respond to a user's request, in an effort to seem more "human-like."
However, this is simply a way of responding to input and is not the same as actually experiencing emotions.
What Are the Three Types of AI and Its Subsets?
There are several ways to classify artificial intelligence (AI), and different frameworks and taxonomies have been proposed. One common way of classifying AI is based on the level of autonomy and intelligence displayed by the system. Under this framework, there are three main types of AI:
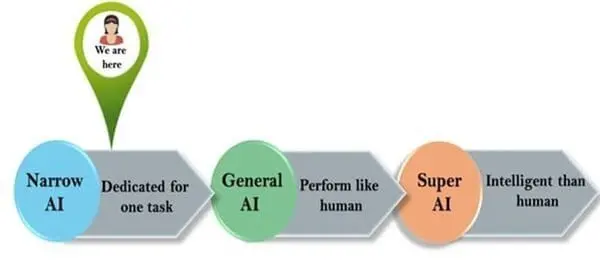
Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI): Also known as "weak AI," ANI is designed to perform a specific task or function and is not capable of general intelligence. Examples of ANI include voice recognition software and self-driving cars.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI): Also known as "strong AI," AGI is a hypothetical type of AI that is capable of exhibiting human-like intelligence and performing any intellectual task that a human can. AGI does not yet exist and is the subject of much research and speculation.
Artificial superintelligence (ASI): This is a hypothetical type of AI that is even more advanced than AGI, with intelligence that surpasses that of any human. ASI is also not yet possible and is the subject of much debate and speculation. Some experts believe that ASI could have transformative potential, while others are concerned about the potential risks it could pose.
There are many different subsets of artificial intelligence (AI), including:
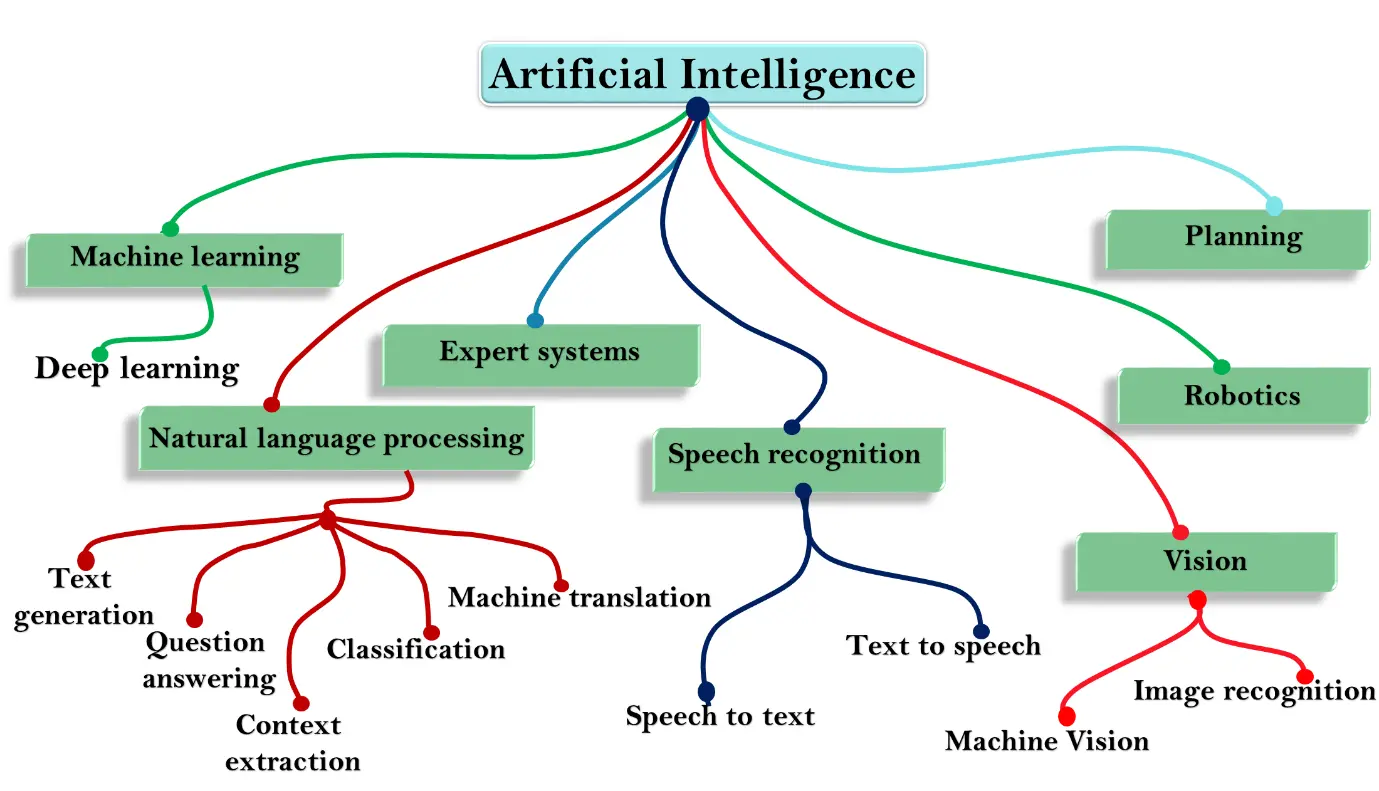
Machine learning: Machine learning involves using algorithms and statistical models to allow a computer to "learn" from data, without being explicitly programmed.
Deep learning: Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning that involves using neural networks to learn complex patterns in data.
Natural language processing (NLP): NLP is the ability of a computer to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Computer vision: Computer vision is the ability of a computer to understand and interpret images and video.
Robotics: Robotics involves the use of AI to build robots that can perform tasks in manufacturing, agriculture, and other industries.
Expert systems: Expert systems are AI programs that are designed to solve problems in a specific domain, using knowledge and reasoning abilities similar to those of a human expert.
Neural networks: Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm that are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain.
Fuzzy logic: Fuzzy logic is a type of AI that allows a system to make decisions based on incomplete or uncertain information.
Genetic algorithms: Genetic algorithms are a type of AI that use principles of natural selection and genetics to optimize solutions to problems.
Evolutionary computation: Evolutionary computation is a type of AI that involves using algorithms inspired by natural evolution to find solutions to problems.
How Can Humans Understand More About AI?
There are a number of ways that humans can learn more about artificial intelligence (AI) and understand how it works:
Take a course: There are a variety of courses available that teach the fundamentals of AI and machine learning, such as online courses offered by MOOC platforms or more in-depth programs at universities and colleges.
Read books and articles: There is a wealth of information available on AI in the form of books, articles, and online resources. Reading these materials can provide a good foundation for understanding the basics of AI.
Attend conferences and events: Conferences and events focused on AI are a great way to learn from experts in the field and stay up to date on the latest developments in the field.
Experiment with AI tools: There are a number of AI tools and platforms available that allow users to experiment with and learn about AI. For example, platforms like Google's TensorFlow or IBM's Watson allow users to build and train their own AI models.
Work with AI professionals: Working with AI professionals or participating in AI-related projects can provide valuable hands-on experience and insights into how AI works.
What Are Some of the Most Popular Applications of Artificial intelligence?
There are many popular applications of artificial intelligence (AI). Some examples include:
Language translation: AI can be used to translate text or speech from one language to another.
Image and facial recognition: AI can be used to identify objects, people, and scenes in images and videos.
Personal assistants: AI can be used to build virtual assistants that can interact with users and perform tasks such as scheduling, making phone calls, and sending emails.
Self-driving cars: AI can be used to enable vehicles to navigate and drive autonomously.
Healthcare: AI can be used to analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and assist with diagnosis and treatment planning.
Fraud detection: AI can be used to analyze patterns in data and detect fraudulent activity.
Robotics: AI can be used to build robots that can perform tasks in manufacturing, agriculture, and other industries.
Chatbots: AI can be used to build chatbots that can converse with users and provide information or assistance.
Predictive analytics: AI can be used to analyze patterns in data and make predictions about future events.
Weather forecasting: AI can be used to analyze data from weather stations and make more accurate weather forecasts.
Factors Behind Companies Promoting Misleading AI Claims
While it is true that some companies may make exaggerated or misleading claims about the capabilities of their AI products or services, it is generally not the case that companies intentionally promote "fake AI" to their customers.
There are a number of factors that may contribute to companies making exaggerated or misleading claims about their AI products or services. For example:
Lack of understanding: Some companies may not fully understand the capabilities and limitations of AI and may make claims that are not accurate.
Marketing: Some companies may make exaggerated claims about their AI products or services as a marketing tactic in order to differentiate themselves from competitors or generate buzz.
Miscommunication: In some cases, misunderstandings or miscommunications between different teams within a company or between a company and its customers may result in inaccurate or misleading information being shared about an AI product or service.
Overall, it is important for companies to be transparent and accurate in their communication about their AI products and services, and for customers to carefully evaluate the claims made about these products and services before making a purchase.
Conclusion
It is difficult to predict exactly what the future of artificial intelligence (AI) will look like, as it is a rapidly evolving field with many potential applications. However, it is expected that AI will continue to play an increasingly important role in a wide range of fields and industries in the coming years.
Some potential developments in the future of AI include:
Continued progress in machine learning: It is expected that AI systems will continue to become more sophisticated and able to perform a wider range of tasks, thanks to advances in machine learning.
Increased automation: AI is expected to play a significant role in automating tasks and processes, freeing up humans to focus on more complex and creative work.
Development of artificial general intelligence (AGI): It is possible that researchers will eventually develop AI systems that are capable of exhibiting human-like intelligence and performing any intellectual task that a human can.
Widespread adoption of AI: As AI becomes more prevalent and accessible, it is expected that it will be adopted by a wider range of organizations and industries.
Ethical and legal considerations: As AI becomes more widespread, there will likely be increasing discussion about the ethical and legal implications of the technology, such as issues related to bias, privacy, and accountability.







Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest