Comments
- No comments found

Supply chain management plays a vital role in the success of businesses across industries.
With increasing complexities and volumes of data, organizations are turning to cutting-edge technologies like deep learning to optimize their supply chain operations. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and neural networks, deep learning is revolutionizing the way businesses manage their supply chains, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and improved decision-making.
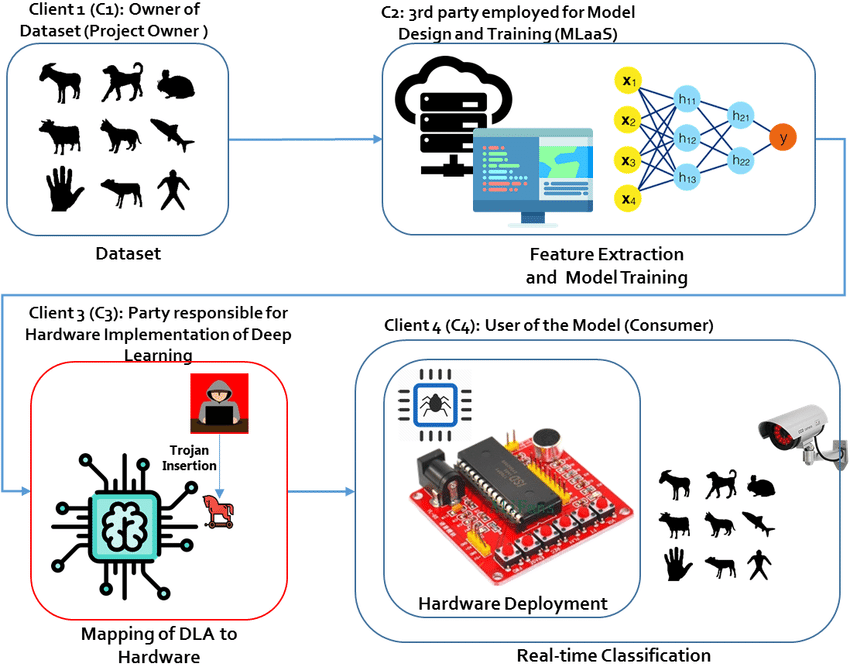
The exponential growth of data has posed significant challenges for supply chain management. However, deep learning algorithms have emerged as a transformative solution to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data. By analyzing diverse data sources such as sales figures, customer behavior, inventory levels, and external factors, deep learning models can uncover patterns, forecast demand, and optimize inventory management.
One of the key areas where deep learning excels is inventory management. By leveraging historical data, market trends, and even external factors like weather patterns, deep learning algorithms can generate accurate demand forecasts. This enables businesses to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize excess inventory, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and cost savings.
Deep learning is also transforming supply chain visibility and risk management. By analyzing real-time data streams from various sources such as sensors, IoT devices, and social media, deep learning models can detect anomalies, identify bottlenecks, and predict potential disruptions. This proactive approach empowers businesses to mitigate risks, respond swiftly to changing market conditions, and maintain a resilient supply chain.
Efficient logistics and transportation are critical for a smooth supply chain. Deep learning algorithms can optimize route planning, shipment scheduling, and resource allocation. By considering variables like traffic patterns, delivery constraints, and customer preferences, these models can find the most efficient and cost-effective ways to move goods, reducing transportation costs and enhancing overall supply chain performance.
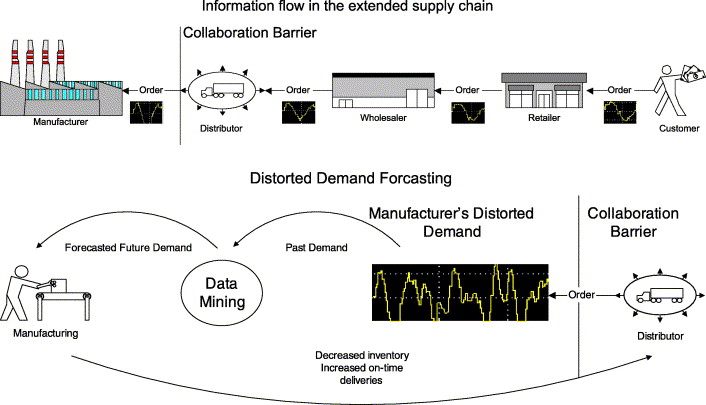
As deep learning continues to advance, its impact on supply chain management will only grow stronger. By leveraging its capabilities, businesses can gain a competitive edge through improved operational efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced customer satisfaction. However, challenges like data quality, model interpretability, and algorithm scalability need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of deep learning in supply chain management.
Deep learning is revolutionizing supply chain management by enabling businesses to unlock valuable insights from vast amounts of data. By optimizing inventory management, enhancing supply chain visibility, and streamlining logistics and transportation, organizations can achieve operational excellence and deliver superior customer experiences. As businesses continue to adopt deep learning techniques, the future of supply chain management looks promising, with increased efficiency, agility, and resilience.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest