Digitized healthcare puts forth alarming data privacy conundrums for patients, healthcare workers, and everyone else involved.
So, is the emergence of blockchain in healthcare the definitive solution to such problems?
Digitization, as we know, can be a double-edged sword in whichever field it is applied. Arguably, healthcare is affected the most by this dichotomy. Some of the well-known issues of digitization are security vulnerabilities, instances of discrimination, and high installation and implementation costs. Perhaps the biggest drawback of digitized healthcare is patient privacy-related issues. Generally, digitized healthcare centers and hospitals use cloud-based virtual databases to store the medical records of their patients. As we know, any valuable and confidential information stored on the internet is susceptible to remote data breaches and manipulation if the cybersecurity levels in these web storage facilities are not up to the mark. As a result, healthcare seeks effective solutions to safeguard the privacy and data security of their patients. Modern blockchain-based systems offer solutions to several privacy-related healthcare issues.
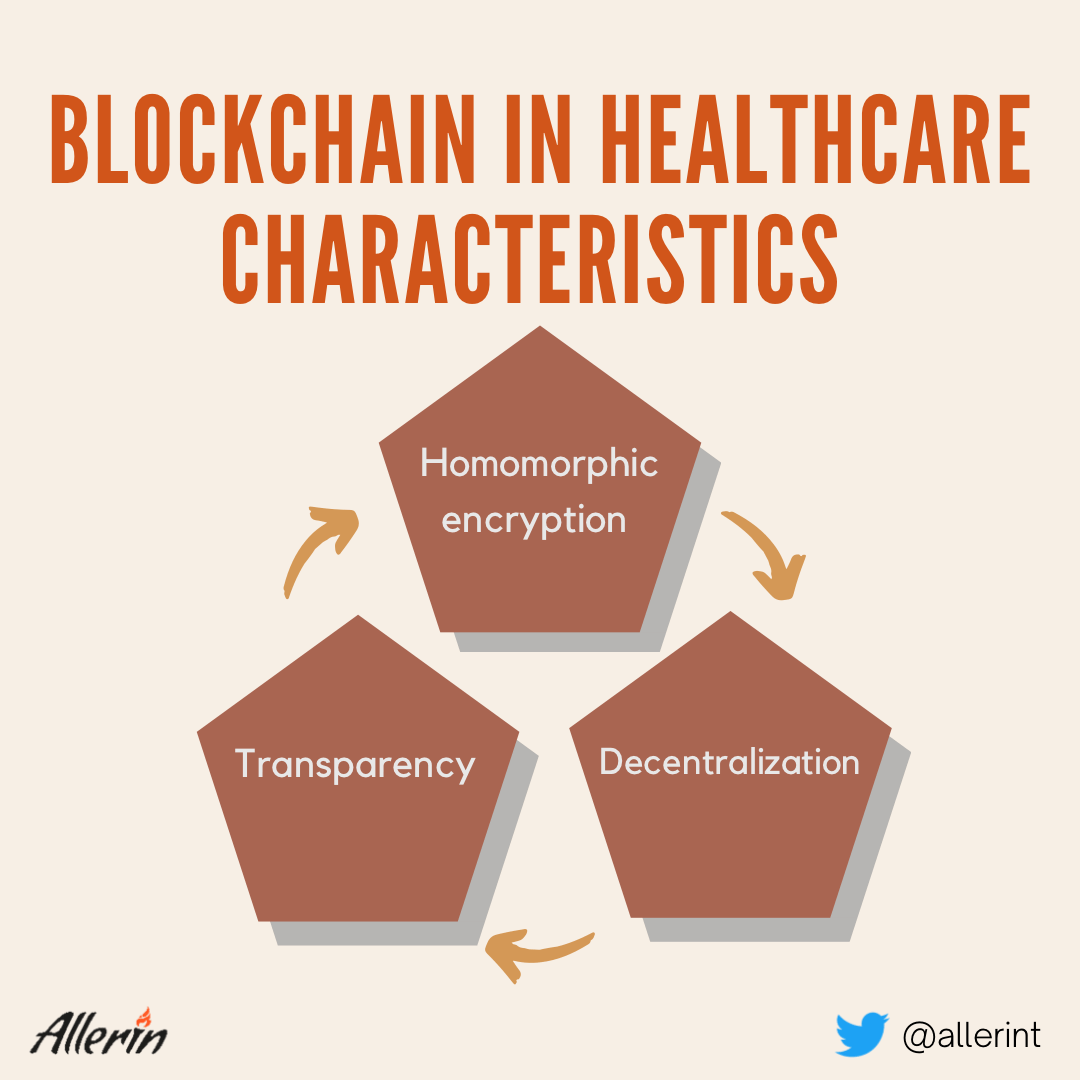
Blockchain’s very nature allows it to act as a potential privacy provider in modern healthcare systems. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records legitimate transactions of files and cryptocurrency. Blockchain ensures that valuable transaction data is not stored in a central location from where it can possibly be hijacked by hackers, thereby enhancing the security of the entire system. By not offering cybercriminals a fixed target to attack, blockchain empowers data security companies to build elaborate data tools for organizational networks and databases. Additionally, blockchain ensures that data stored within it cannot be replicated or recreated without the consent of its owners. As a result, data within the blockchain remains untampered.
So, blockchain in healthcare is seemingly the final puzzle piece in making digitized systems privacy-oriented. How, you may wonder, does the technology, used earlier for cryptocurrency transactional records, make digitized healthcare ecosystems more secure?
Homomorphic Encryption for Rock-Solid Data Privacy
Blockchain-based systems can store either metadata such as storage location and patient registration numbers or personal patient data such as their email address, phone number, social security number, medical history, diagnostic information pictures and other details. For officials and patients, the protection of these details from (possibly malicious) external entities is of utmost importance for the healthcare systems to function optimally. On top of that, blockchain systems also need to comply with global data protection and privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, DPA, and others. In short, blockchain in healthcare has its work cut out to increase the value of digitization in the field.
To meet these requirements, blockchain administrators create pseudo IDs for the involved users. This provides much-needed anonymity to such individuals. Hashing in blockchains also provides anonymity to patients. However, it is homomorphic encryption that provides the highest level of user privacy in blockchain systems.
Homomorphic encryption uses differential privacy provisions to enhance the confidentiality of blockchain-based data security systems. Homomorphic encryption adds noise to the computational process to add a layer of ambiguity to it. Data encrypted in this process does not need to be decrypted before processing. The processed data retains its encryption and executes several of the tasks expected from it without the need for users to access the encryption key. As a result, blockchain systems allow distributed computing and networking in healthcare systems while preserving users' confidentiality during the process. Homomorphic encryption, similar to other encryption types, is characterized by four operations—key generation, data encryption, data decryption and process evaluation. The last of these operations is specific to homomorphic encryption. The evaluation operation takes coded ciphertexts as input and produces outputs in the same format corresponding to a functioned plaintext. Homomorphic encryption is a distinctively blockchain-based data security tool and is generally characterized by a few typical features that include:
Compact Ciphertexts
Compactness is a key component of blockchain technology during data storage and transfer. Homomorphic encryption dictates that the data size of ciphertexts never increases beyond a pre-decided limit, even if the complexity of the ciphertexts rises after processing and evaluation.
Semantic Data Protection
This feature ensures that passive cyber-attackers would not be able to get any information from a transactional ciphertext sequence, even if they choose the public key and plaintext, unless there is a negligible advantage over 50 %. As a result, confidential patient data remains that way during all stages of information storage or transfer through the network channels of hospitals or other connected medical centers.
Circuit Concealment
Homomorphic encryption ensures that the output ciphertext formed after the evaluation phase does not reveal any details about the patient (or the entity who generated the secret and public keys)
Potent Encryption
Homomorphic encryption in blockchain-based healthcare systems ensures that the output ciphertexts generated after processing and evaluation are indistinguishable from the input texts. As stated earlier, upholding anonymity is THE most important component of securing the personal privacy of patients. Homomorphic encryption, with its ability to let arithmetic functions be processed and evaluated on encrypted data (without the need to decrypt it), does not allow blockchain-based healthcare systems to drop their privacy guard even momentarily. This type of encryption allows data owners (patients, healthcare professionals) to enlist the help of third-party organizations while not sharing any private patient data with them during the process.
The most sophisticated and modern blockchain systems can use homomorphic encryption’s unique qualities to offer all-around data security solutions in healthcare systems and convince professionals and cynics about their incredible efficiency and effectiveness. As we have seen, homomorphic encryption also takes the fear factor away from outsourcing important healthcare-related tasks to third-party service providers.
The homomorphic encryption industry is expected to grow rapidly by 2027. However, it is yet to be standardized globally for adoption in digitized blockchain-based healthcare systems. The research community in healthcare is creating stronger foundations and development models for the vital tool to play a part in the healthcare industry. If blockchain in healthcare becomes normal in the future, homomorphic encryption will play a massive part in it.
Open-Sourced Nature Provides Transparency and Decentralization
As you know, blockchain is open-sourced and viewable for all the authorized stakeholders involved in a patient's case. This feature enhances the transparency of healthcare systems. Additionally, open-sourced-ness removes the likelihood of third-party tampering or needless revisions by a user, keeping the structure and composition of data unchanged.
On the other hand, the transparency provided by blockchain technology is favorable for healthcare providers as governance and regulation become more convenient for them. As a result, data tampering and allegations of data tampering can be eliminated. The decentralization aspect is perhaps blockchain's greatest asset if the technology is being implemented in healthcare. Decentralization allows all the authorized people working on a patient's case to make decisions more even-handedly and after considering everybody's opinions. A fixed data source, on the other hand, can be corrupted or manipulated if cyber-attackers know its location in the network.
The decentralized attribute of blockchain technology is a form of 'democratized data sharing' that allows innovative thinking in the field of healthcare as all the authorized parties can provide their ideas on a given patient data in real-time.
While these characteristics may not directly talk about patient privacy, they nevertheless aid data security so that blockchain technology can be positively impactful for greater digitization in healthcare.
Blockchain in Healthcare: The Future of Modern Medicine?
It is a well-known fact that an individual's medical reports may contain their deepest (and darkest) health secrets and most personal details. Understandably then, patients would not want such data to be accessed by anyone but their trusted family physician.
Digitized (and not highly cyber-protected) patient records in hospitals and clinics are generally considered easy pickings for cybercriminals. Also, the storage and transfer of patients' EHRs (Electronic Health Records) in hospitals around the world leave a lot to be desired from a privacy and data security perspective. In poor and developing countries, the data in EHRs can be easily breached by cyber-attackers and other external entities. Additionally, the data may not always be easily accessible to patients and health workers too due to various technicalities. Most problematically, the existing healthcare infrastructure may be unable to strike a balance between accessibility and privacy protection. EHRs are invaluable from a patient's and doctor's perspective because they show the measures needed to be taken to enhance patient care as well as independent clinical research in the future for healthcare professionals.
The involvement of blockchain in healthcare promises foolproof data security of EHRs digitally saved in hospital networks. Blockchain's flexible ledger system allows the data transfer and storage to be dynamic and decentralized. Blockchain's three pillars—data security, transparency, and decentralization—make it almost impervious to third-party data breaches and unauthorized manipulation. Therefore, healthcare around the world needs to include blockchain technology to boost patient privacy.


Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest