Comments
- No comments found

Are you running out of storage space lately?
Or perhaps your hard disk slowed to a crawl? Or are you simply looking to experience optimal computer performance? Well, if you endure these three problems on your computer, it may be time for a hardware upgrade.
But should you go for a cheaper hard disk drive or a faster SSD? A drive is a drive, right? Not at all. This brief article will go through all the notable differences between HDDs and SSDs in terms of capacity, cost, lifespan, and what it means for you and your computer.
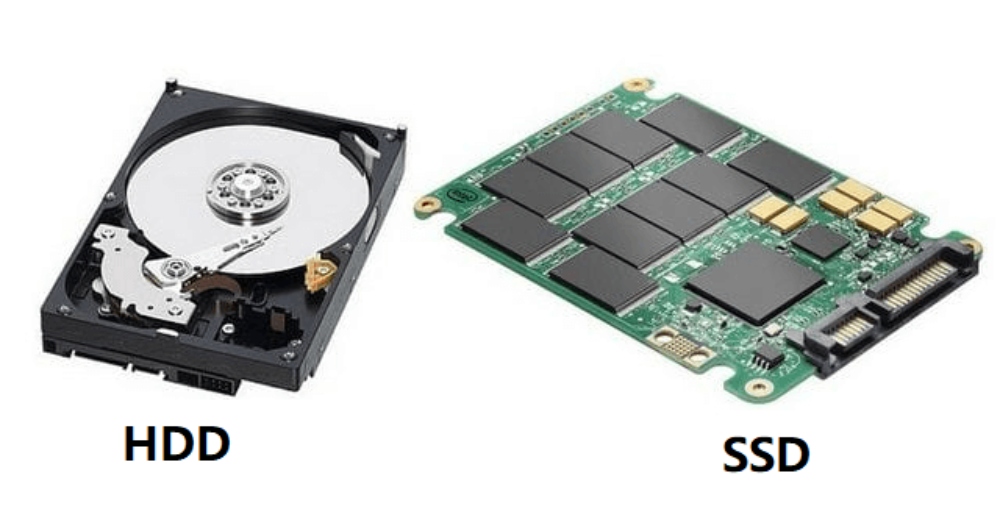
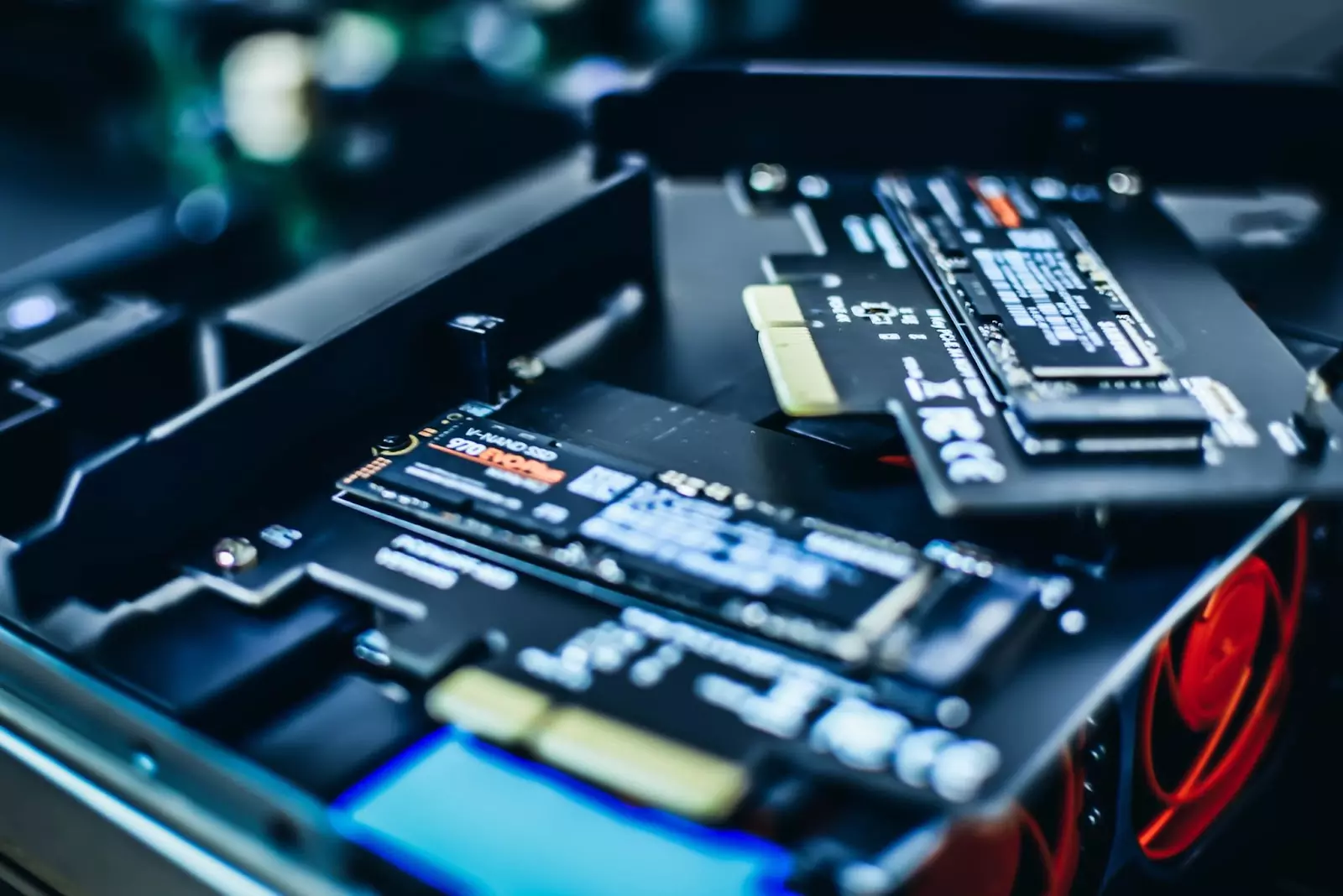
The primary and most significant difference between a hard disk drive (HDD) and a solid-state drive (SSD) is actually how data is stored and accessed. While the HDD is the conventional storage device that uses mechanical spinning platters and a moving head to access data, SDDs are faster, newer drives that store data on instantly accessible memory chips.
An enclosure contains a series of platters concealed by a ferromagnetic coating in an HDD. Here, the direction of the magnetization represents the individual bits. Data is written and then read by a fast-moving head, similar to how vinyl albums work. And because all of these pieces are mechanical, the hard disk is usually the slowest and most fragile component of every computer.
On the other hand, SDDs are newer storage disks that store data on flash memory, consisting of individual memory cells storing bits that are instantly accessible by the controller.
So, suppose you currently have an older version laptop that starts to get slow and sluggish because it works on an HDD and consider making the switch to an SSD. In that case, you should know that SSDs are often the better solution for laptops simply because they are non-mechanical.

In addition, SSDs require less power, which, of course, translates to better battery life. Nowadays, while lower-priced laptops still come with traditional HDDs, most mid-range to high-end laptops come with an SSD for a reason.
Furthermore, while HDDs have moving parts, SSDs are 100% shock-resistant. So, if you accidentally drop your laptop while the read/write head of the HDD is in motion, it could result in data failure. This can’t happen with SSDs.
In the end, there are also “hybrid” laptops that have both drive types inside them. In a hybrid laptop, the OS, apps, and the most-utilized files are installed on an SSD, while all other data sits on an HDD, which is typically larger and cheaper. In fact, using your SSD to run your operating system is a fantastic way to increase your laptop’s speed and performance.
Just like most other markets, the market for flash storage is volatile and varies based on current supply and demand. Nevertheless, although SSDs are much cheaper than they used to be, there’s still a considerable price difference between the two. While a 1 TB HDD costs roughly $70, a 1 TB internal SSD costs somewhere around $150.
If you’re concerned about how much data you can store on each type of drive, don’t worry, as there are no differences in storage capacity at all. You can get SSDs and HDDs in similar sizes, from as small as 128 GB up to 50 TB or more. However, keep in mind that larger SSDs are truly expensive.
For the moment, if you need to free up some space on your drive instantly, you can format your hard drive, whether it’s internal or external, no matter if it’s an SSD or HDD.
While there's truth in the fact that SSD cells have a limited lifespan, this isn't really an issue today. In fact, the myths surrounding SSD life spans are based on assumptions from the 90s and early 00s.
Theoretically, the more data is written to a cell, the faster it can wear out. A present SSD cell can handle around 3,000 write cycles, which doesn't sound like much at first. However, thanks to the principle of wear leveling, the SSD spreads write processes evenly across all cells to minimize cell cessation and extend the lifespan of the SSD.
Furthermore, modern-day SSDs come with spare cells that replace dead cells. This is called bad block management; it's the reason why the larger the SSD is, the longer its lifespan.
So, if you’re still unsure whether an HDD or SSD is the best fit for your machine, let’s review how both stack up against each other. SSDs are faster, more compact, quieter, more durable, and consume way less energy. On the other hand, HDDs are more price-friendly and may offer easier data recovery in the event of damage.
As long as the price isn’t your determining factor, SSDs come clearly out on top, mainly since modern SSDs are just as reliable as HDDs.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest