Comments
- No comments found

5G can enhance the quality and performance of urban services in smart cities.
As cities become more crowded and complex, the need for efficient, sustainable, and smart solutions becomes increasingly pressing. With the arrival of the fifth-generation wireless network (5G), cities now have a powerful tool to revolutionize how they operate and serve their citizens. The high-speed and low-latency capabilities of 5G can enable a range of smart city applications, from traffic management and public safety to healthcare and environmental monitoring. In this article, we explore the role of 5G in enabling the next generation of smart cities, including the benefits and challenges of deploying 5G networks, the potential use cases for smart cities, and the key factors that will determine their success.
The benefits of 5G for smart cities are numerous and significant. 5G technology has the potential to improve public security and safety significantly. Using the fast and responsive 5G network, smart city systems can collect and analyse massive amounts of data from various sources, such as video security cameras, intelligent traffic lights, and other IoT devices.
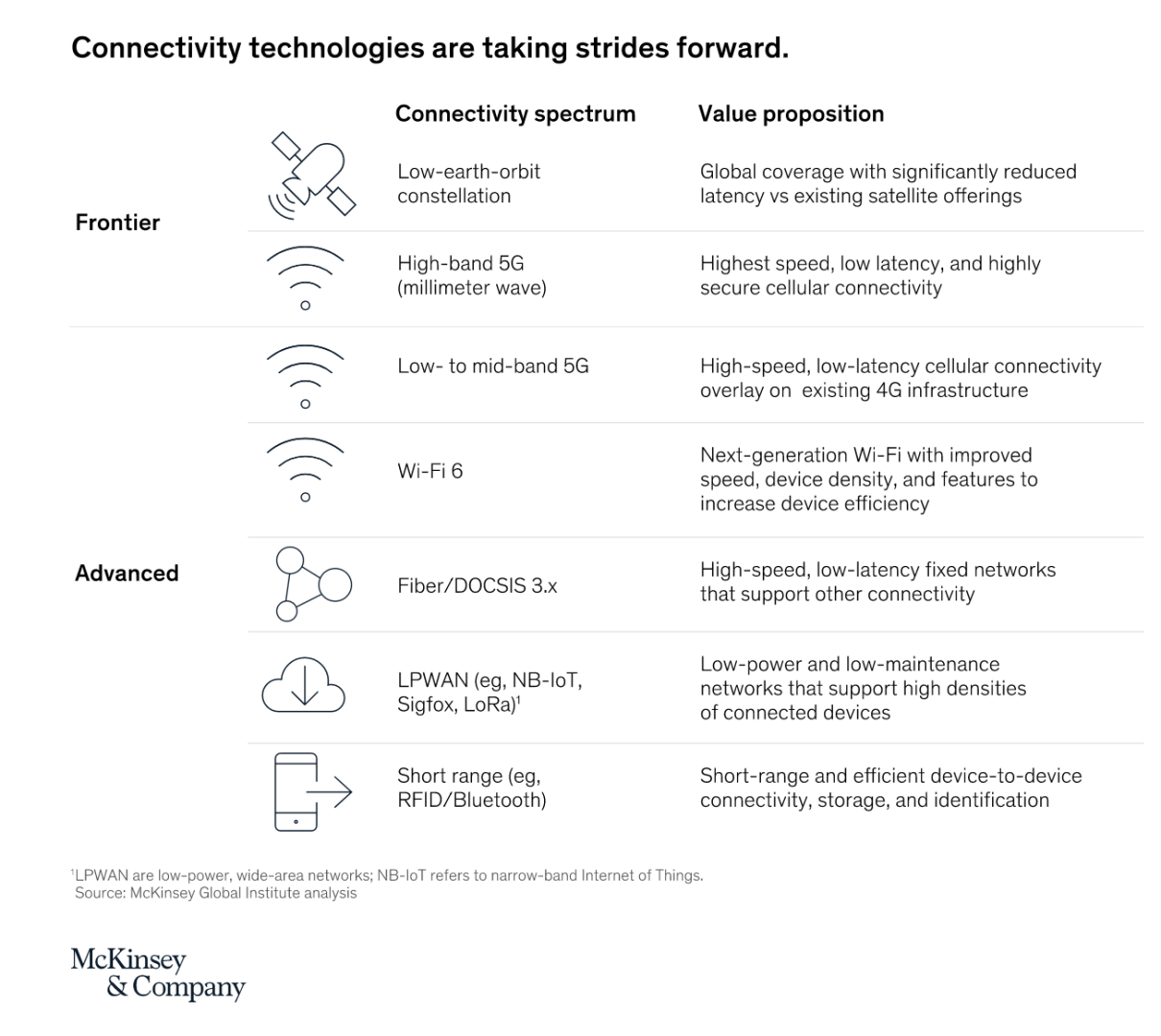
Source: McKinsey & Company
First and foremost, 5G networks can provide faster and more reliable connectivity than previous generations of wireless networks. This means that cities can collect and analyze real-time data from a wide range of sensors and devices, enabling them to make more informed decisions about how to allocate resources and respond to emergencies. For example, 5G can be used to monitor traffic patterns and adjust traffic signals in real-time to optimize the flow of vehicles and reduce congestion.
Another major benefit of 5G for smart cities is its low latency, or the time it takes for data to be transmitted from one device to another. With 5G, latency can be reduced to just a few milliseconds, making it possible to support applications that require near-instantaneous responses. This is particularly important for applications like autonomous vehicles, which rely on real-time data from sensors to navigate safely and efficiently.
Finally, 5G networks can support a much larger number of connected devices than previous generations of wireless networks. This is crucial for smart cities, which rely on a vast network of sensors and devices to collect data and provide services to citizens. With 5G, cities can support thousands of connected devices per square kilometer, enabling them to monitor everything from air quality and water levels to parking availability and waste management.
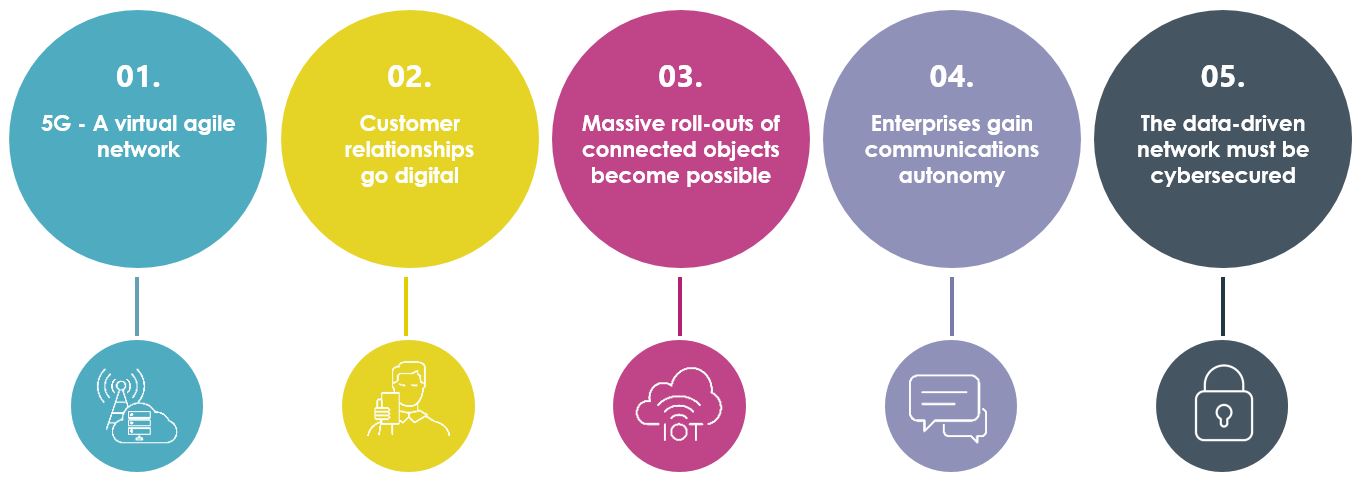
Source: Thales
Despite the numerous benefits of 5G for smart cities, there are also several challenges to deploying these networks. One of the biggest challenges is the cost of infrastructure. Building out a 5G network requires significant investment in new infrastructure, including small cells, fiber-optic cables, and other equipment. This can be prohibitively expensive for many cities, particularly those with limited budgets.
Another challenge is the need to ensure equitable access to 5G networks. While 5G has the potential to revolutionize how cities operate and serve their citizens, it is important to ensure that these benefits are distributed fairly across all communities. This means addressing the digital divide and ensuring that all citizens, regardless of their socioeconomic status, have access to high-speed, reliable connectivity.
Despite these challenges, the potential use cases for smart cities are vast and varied. Here are just a few examples of how 5G can enable the next generation of smart cities:
Traffic management: 5G can be used to monitor traffic patterns and adjust traffic signals in real-time to optimize the flow of vehicles and reduce congestion.
Public safety: 5G can be used to support real-time video surveillance and emergency response systems, enabling first responders to react quickly and effectively in the event of an emergency.
Healthcare: 5G can be used to support remote patient monitoring and telemedicine, enabling patients to receive high-quality care from the comfort of their own homes.
Environmental monitoring: 5G can be used to monitor air and water quality, as well as other environmental factors like noise pollution and temperature.
Energy management: 5G can be used to optimize energy consumption by allowing real-time monitoring of energy usage and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid.
With 5G-powered sensors and IoT devices, cities can collect data on energy consumption patterns and use AI algorithms to optimize energy distribution and reduce waste. In addition, 5G can enable the development of virtual power plants that use distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage to provide reliable and sustainable energy to the city. This can lead to significant cost savings, increased energy efficiency, and reduced carbon emissions.
5G technology is expected to transform the way we live and work, and smart cities are a perfect example of how this transformation is already underway. Smart cities are essentially urban areas that use data and technology to improve the quality of life for their citizens. They incorporate everything from smart transportation and energy systems to advanced healthcare and public safety initiatives. With the implementation of 5G networks, the potential for these cities to become even smarter is enormous.
As more cities around the world continue to adopt smart city technologies, 5G will play an increasingly important role in enabling the next generation of smart cities.
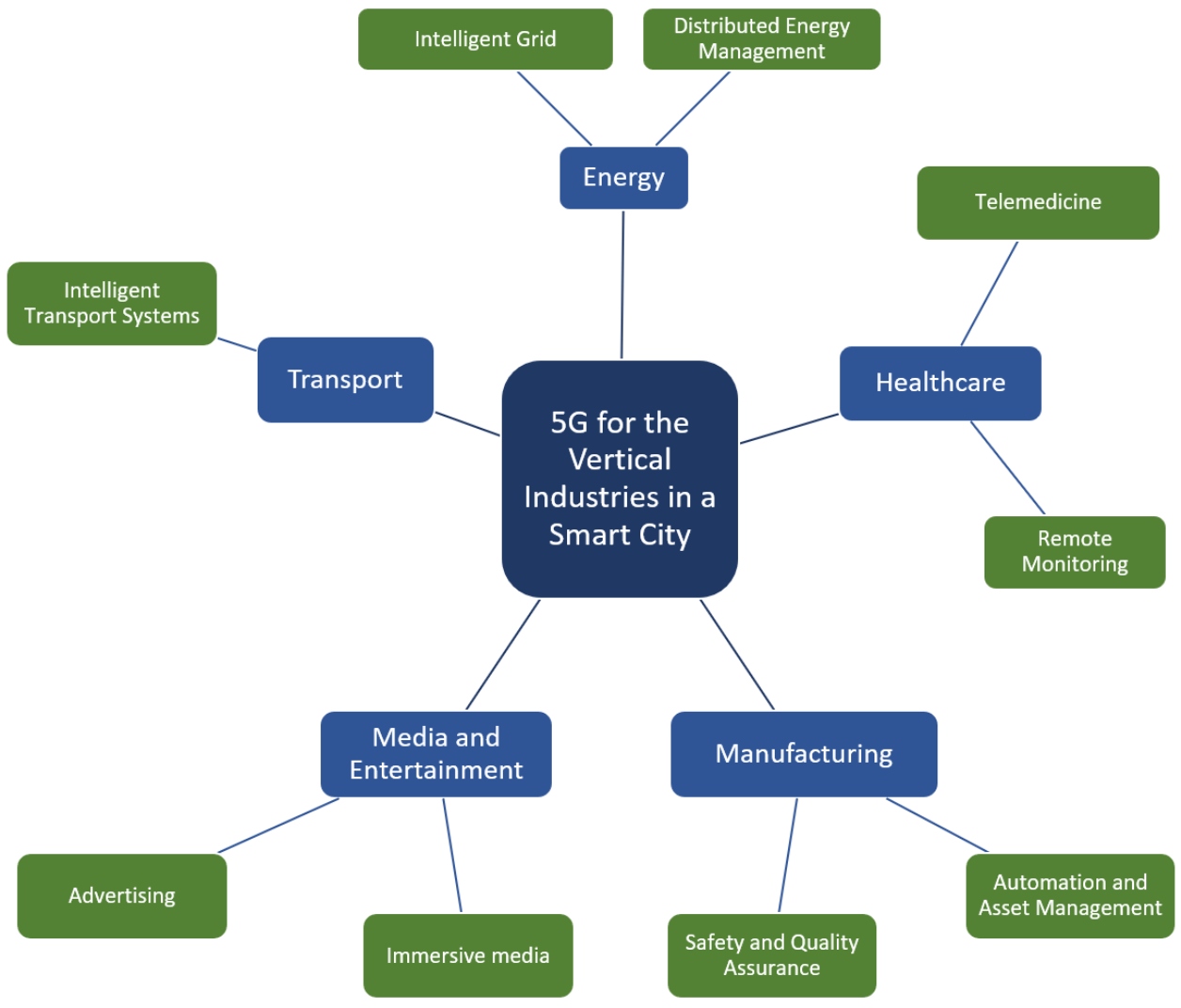
Source: MDPI
With its high-speed data transfer capabilities, low latency, and ability to connect a large number of devices, 5G will be instrumental in powering the next wave of innovation in smart city technology.
One area where 5G is likely to have a significant impact is in transportation. With 5G, autonomous vehicles will be able to communicate with one another and with traffic management systems in real-time, allowing for smoother traffic flow and reducing congestion. This will not only save time for commuters but also reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality.
Another area where 5G will be transformative is in healthcare. With the ability to transmit large amounts of data quickly and reliably, doctors and other healthcare professionals will be able to remotely monitor patients and even perform procedures using robots. This will be particularly important in rural areas where access to healthcare is limited.
5G will also play a crucial role in enabling the next generation of augmented and virtual reality experiences. With its low latency and high bandwidth, 5G will make it possible to stream high-quality, immersive content on mobile devices and wearables, opening up new opportunities for entertainment, education, and training.
The future of 5G and smart cities is bright, with the potential to transform almost every aspect of urban life. However, there are still challenges to be addressed, such as ensuring that the benefits of smart city technologies are equitably distributed and that data privacy and security concerns are addressed. With careful planning and investment, however, the potential benefits of 5G and smart cities are vast, and cities around the world are already beginning to realize them.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest