Comments
- No comments found

The United Nations Agenda has set an ambitious goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, which will require a massive transformation of our global economy.
This complex journey will encompass a digital and business transformation of our energy systems, transportation networks, and other critical infrastructure. As highlighted by Accenture at the 2023 World Economic Forum in Davos, this process can be accomplished and likely accelerated by leveraging frontier technologies like IoT, 6G, satellite internet, cloud and edge computing, blockchain, AI, digital twins, and the next-generation of the world wide web (web 3.0).
This article aims to highlight the potential impact of a novel decentralized Web 3.0 architecture on the net zero economy, and offers a few examples of how digital twins and some of the latest AI tools can act as enablers or catalysts.
Web 3.0 has been gaining attention in recent years, as it will enable transformative changes to how we interact with the internet. While the first generation of the internet was focused on providing access to information, and the second generation focused on enabling social interactions and e-commerce, Web 3.0 aims to create a decentralized, more intelligent, and responsive internet, one that is capable of learning and adapting to the needs of its users. Web 3.0 refers to the evolution of the internet towards a more decentralized and secure architecture characterized by blockchain technology and smart contracts. It has the potential to impact each of the UN SDG 13 indicators and create a decentralized net zero economy by enabling new forms of collaboration, innovation, and value creation.
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems, processes, and products that can be deployed to simulate and optimize their performance. They have the potential to impact each of the UN SDG 13 indicators in different ways, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, increasing renewable energy use, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards. This technology has been around for several years. However, recent advances in AI tools, such as generative and cognitive AI, have made it possible to create more sophisticated and realistic digital twins that can be leveraged for various purposes, including predicting and optimizing energy usage in buildings, factories, and other infrastructure. Digital twins can simulate the performance of novel energy systems, allowing us to identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement and optimize their operation to reduce energy consumption and emissions.
Generative and cognitive AI tools can also play a critical role in achieving a net zero economy. Generative AI, which uses machine learning algorithms to generate new data, can be deployed to create simulations of complex systems that are difficult to model using traditional methods. Cognitive AI, on the other hand, is designed to mimic human thought processes and decision-making. This methodology can be helpful in analyzing large amounts of data from various sources and identify patterns and trends that can inform decision-making. In the context of a net zero economy, cognitive AI can be valuable to evaluate energy usage data from buildings and other infrastructure, identify inefficiencies, and recommend ways to optimize energy consumption and reduce emissions.
As with any new technology, risks, and challenges are associated with deploying Web 3.0, digital twins, or the latest AI tools. For example, there are significant cyber- and ethical risks. There is also a risk that these technologies could automate decision-making processes that humans should make. Therefore, it is essential to establish proactive digital cyber-ethics frameworks to ensure that these technologies are deployed responsibly. This includes ensuring that these technologies are transparent and accountable and that individuals provide informed, dynamic consent and have data ownership and control over how their data will be deployed.
One of the significant challenges is the potential loss of jobs as automation and AI tools become more prevalent in industries. This could have a significant impact on employment rates and require a shift in how people view work and training for new careers.
Another challenge is the potential for bias and discrimination in AI algorithms, which can perpetuate social and economic inequalities. It is crucial to address this issue to ensure fairness and equity in decision-making processes.
Cybersecurity is a critical challenge for any technology, and Web 3.0, digital twins, and AI are no exceptions. As more devices and systems become interconnected, there is a higher risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. It is essential to implement robust security measures to protect against these threats.
Digital literacy and access to technology are also significant challenges, as not everyone has the necessary skills or resources to take advantage of these new technologies. This can exacerbate existing inequalities and limit opportunities for certain individuals and communities.
There is also a challenge in navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding these new technologies. As they continue to evolve, regulations and policies may not keep pace, leading to uncertainty and potential legal issues. It is crucial to establish clear guidelines and standards to ensure responsible deployment and use of these technologies.
While numerous opportunities can be envisioned by deploying a novel, dual digital twin- and AI-powered web 3.0 infrastructure, this article will focus on the potential to impact the UN SDG 13 indicators and therefore accelerate the attainment of the UN 2050 agenda.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13) aims to combat climate change and its impacts. It includes a range of indicators that measure progress towards this goal, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, increasing renewable energy use, and improving resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Web 3.0 could power new platforms to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by enabling the development of decentralized energy systems. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, it could possible to create decentralized energy markets where producers and consumers could trade energy without intermediaries. This could increase the use of renewable energy sources and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Digital twins could also optimize the performance of energy systems and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By creating a virtual replica of an energy system, digital twins could simulate its operation under various scenarios and identify the most efficient solutions. For example, digital twins could be useful for predicting the performance of new power plants and identify ways to optimize their operation to reduce emissions. Similarly, they could optimize the placement and process of renewable energy sources such as wind turbines and solar panels, reducing the need for fossil fuels. AI tools could be leveraged to optimizate energy systems, which can reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This would involve the use of advanced algorithms to create models of energy systems that could simulate various scenarios and identify the most efficient solutions. For example, generative AI could simulate the performance of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power and optimize their operation to ensure maximum efficiency and reliability. Similarly, cognitive AI tools could offer the opportunity to use energy usage data from buildings and other infrastructure, identify inefficiencies, and recommend ways to optimize energy consumption and reduce emissions.
Renewable Energy Use: A web 3.0 configuration could also be instrumental in increasing the use of renewable energy sources by enabling the development of decentralized energy systems. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, incentives can be created for developing renewable energy projects and deploying energy storage solutions. This can increase the reliability and availability of renewable energy sources, making them more attractive to investors and consumers. Digital twins could also be foundational in increasing the adoption of renewable energy sources, by identifying ways to improve performance and efficiency due to the creation of renewable energy systems replicas. For example, digital twins could simulate the performance of wind turbines and identify ways to optimize their design and operation to increase their energy output. Similarly, they could optimize the placement and operation of solar panels to maximize their energy output. Generative AI could be foundational in developing novel solutions to increase the use of renewable energy sources. By creating sophisticated models of energy systems, generative AI could identify ways to improve the performance of renewable energy sources, such as designing more efficient and cost-effective wind turbines and solar panels. Similarly, cognitive AI could be deployed to analyze data from weather sensors and other sources to predict energy demand and optimize the operation of renewable energy systems.
Energy Efficiency: Web 3.0 architecture could be beneficial in improving energy efficiency by enabling the development of decentralized energy systems that are more resilient and adaptable. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, it would be possible to create decentralized energy grids that can automatically balance energy supply and demand. This could help reduce energy waste and optimize the use of energy resources. Digital twins could be deployed to optimize the energy usage of buildings and other infrastructure, improving energy efficiency. By creating virtual replicas of buildings, digital twins could simulate the performance of HVAC systems, lighting systems, and other energy-consuming equipment and identify ways to optimize their operation. For example, digital twins could be used to simulate the performance of HVAC systems under different weather conditions and identify ways to reduce energy consumption while maintaining comfort levels. In addition, Generative AI could be helpful to optimize energy usage in buildings and other infrastructure, improving energy efficiency. This would involve creating models of energy usage patterns and using these models to identify opportunities for optimization. For example, generative AI-powered platforms could simulate the performance of HVAC and lighting systems and optimize their operation to reduce energy consumption. Similarly, cognitive AI could be leveraged to analyze data from energy sensors and other sources to identify inefficiencies and recommend ways to optimize energy consumption.
Climate-Related Hazards: A Web 3.0 technology infrastructure could be pivotal in enhancing resilience and the adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards by enabling the development of decentralized systems that are more resistant to disruptions. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts functionality, it would be possible to create decentralized systems that could automatically respond to climate-related hazards, such as floods and hurricanes. This could help reduce the impact of these hazards on critical infrastructure and minimize the risk of downtime. In addition, digital twins could also further enhance resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards. By creating virtual replicas of infrastructure such as bridges and dams, they could simulate their performance under extreme weather conditions and identify potential risks, as well as identify ways to mitigate these risks. Cognitive AI could also improve resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards, by evaluating and analyzing large amounts of data from weather sensors, satellite imagery, and other sources to identify potential risks and develop strategies for mitigating them. For example, cognitive AI-powered solutions could be helpful in analyzing data from weather sensors and other sources to predict and respond to extreme weather events such as hurricanes and floods. Similarly, they could process data from crop sensors and other sources to anticipate and respond to droughts and other climate-related impacts on agriculture.
Climate Finance: Web 3.0 infrastructure, digital twins and latest AI advancements could optimize investments in renewable energy and other climate-related projects by enabling the development of decentralized funding mechanisms. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, decentralized crowdfunding platforms could be created, enabling small-scale investors to participate in renewable energy projects. This could help increase the availability of capital for renewable energy projects, making them more accessible to a broader range of investors. Digital twins, generative AI or cognitive AI could help investors make personalized informed decisions about where to allocate their capital by creating virtual replicas of projects and simulating their performance to optimaze the ROI. Similarly, they could be leveraged to simulate the performance of climate-related projects such as water management systems and predict their long-term environmental and economic impacts. Additionally, generative and cognitive AI could be instrumental in analyzing climate finance data and identify investment opportunities that can support the successful transition to a more sustainable economy.
Web 3.0 is poised to have an overall catalytic effect on each of the UN SDG 13 indicators by enabling the development of decentralized energy systems and other climate-related solutions as highlighted in a recent MIT Review article. By creating a more decentralized net zero economy, we can accelerate progress toward a more sustainable future and help combat the impacts of climate change. First, however, the deployment of Web 3.0 must be done responsibly, focusing on transparency, security, and privacy.
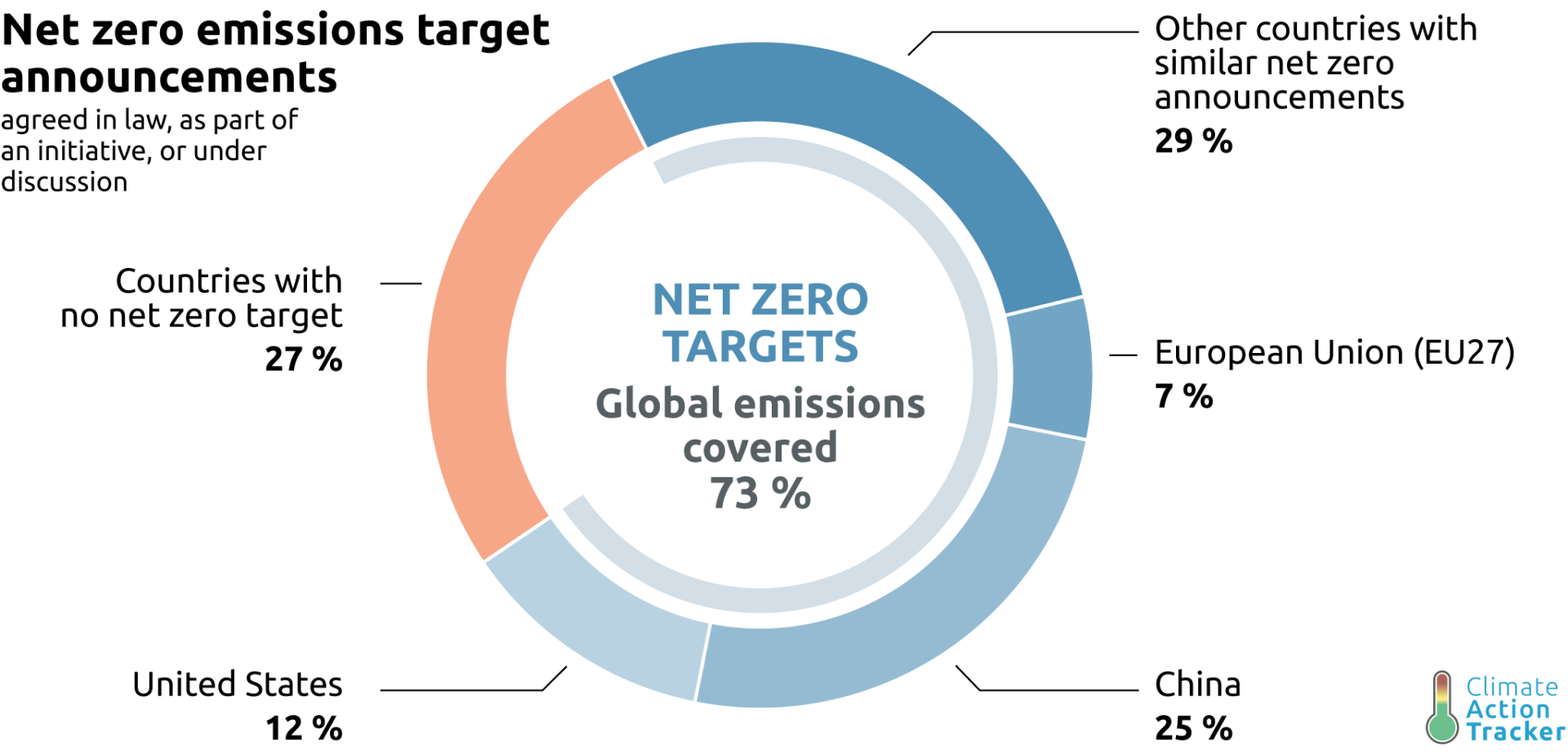
By harnessing the combined power of frontier technologies, we can accelerate progress toward a more sustainable future and help combat the global impact of climate change. However, their deployment must be done responsibly, focusing on transparency, accountability, and accessibility. A global collaborative approach among key stakeholders will be required to address these challenges to achieve a more sustainable future for all.
Ingrid Vasiliu-Feltes, MD MBA Is a healthcare executive, futurist and globalist who is highly dedicated to digital and ethics advocacy. She is a Forbes Business Council member, digital strategist, passionate educator and entrepreneurship ecosystem builder, known as an expert speaker, board advisor and consultant. Throughout her career she has received several awards for excellence in research, teaching or leadership. She is the recipient of numerous awards most notably: WBAF World Excellence AwardSocial Entrepreneurship 2021, Top 20 Global Leaders in Digital Twins Technologies, Top 50 Global Leaders in Health Tech,Top 50 Global Ecosystem Leaders, Top 100 Visionary In Education Award 2021, Top 100 Global Women in Leadership Award 2021, Top 100 World Women Vision Award, 2021-Innovation & Tech, Top 100 Women in Social Enterprise 2021 (nominee),Top 50 Global Thinkers (Nominee),Nations of Women Change Makers Award(finalist),Top 100 Healthcare Leader 2020 Award, Top 100 Finance Leader 2020 Award, and Top 100 Women in Crypto 2020. Additionally, she serves as an Expert Advisor to the EU Blockchain Observatory Forum, and was appointed to the Board of UN Legal and Economic Empowerment Network. Dr. Vasiliu-Feltes is CEO of Softhread Inc., the Founder and CEO of The Science, Entrepreneurship and Investments Institute, and currently serving as a Country Director for WBAF USA, Senator of WBAF, Faculty Member of the WBAF Business School-Division of Entrepreneurship, and teaching the Executive MBA Business Technology Course at the UM Business School. She is also acting as the Chief Innovation Officer for the Government Blockchain Association. Most recently she served as President of Detect Genomix, Chief Quality and Safety Officer Chief and Innovation Officer for Mednax, Chief Quality and Safety Officer and Chief of Compliance for the University of Miami UHealth System During her academic tenure she taught several courses within the Medical School, as well as the combined MD/PhD and MD/MPH programs. Throughout her career, Dr. Vasiliu-Feltes held several leadership positions and is a member of numerous prestigious professional organizations. She holds several certifications, such as Bioethics from Harvard, Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy from MIT Sloan, Blockchain Technology and Business Innovation from MIT Sloan, Finance from Harvard Business School, Negotiation from Harvard Law School, Innovation and Entrepreneurship from Stanford Graduate School of Business, Certified Professional in Healthcare Risk Management, Fellow of the American College of Healthcare Executives, Patient Safety Officer by the International Board Federation of Safety Managers, Master Black Belt in Lean and Six Sigma Management, Professional in Healthcare Quality by the National Association of Healthcare Quality, Manager for Quality and Organizational Excellence, by the American Society for Quality, and Certified Risk Management Professional by the American Society for Healthcare Risk Management. Additionally, Dr. Vasiliu-Feltes is an Honorary Advisory Board Member of several companies, as well as an Editorial Board Member for several international publications, an author and TV/Media partner.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest