Comments
- No comments found
Advances in neuroscience at the cellular and molecular level are formidable enough that if all there was to care for mental health were based on those, most of the problems would have been solved.
There are parts of human biology where cellular targets are enough for management and cures, but with the brain, uncertainty abounds even with specific neurons and molecules.
Drug targets for some have resulted in immense side-effects. This shows that although specificity exists for localized nerve cells or synapses, they are involved with more beyond what was ascribed.
The brain is more about what is done with it [including exposome] than what is within. Whatever is within builds into what it wholly does, rather than those internals determining what the brain is about.
It is because of the brain that a house is known, but the brain does not take in a house first. The brain constructs the version of the house it uses to relate with the external. It does not do so by predictive coding, predictive processing or best guess, but through sensory input, integration and relay to the memory.
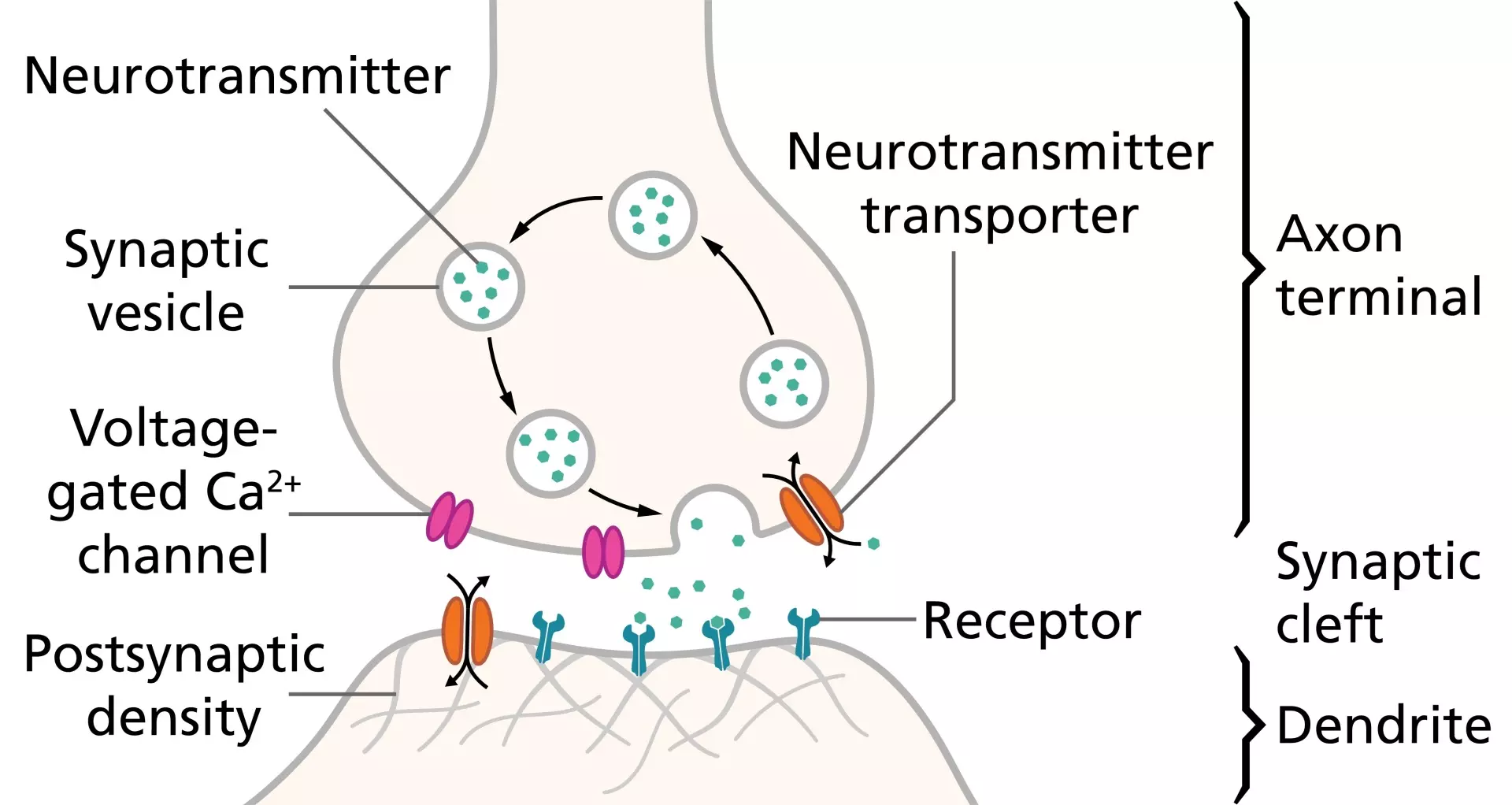
Internal and external senses all have representative versions to the brain — specifically the memory. Most regulation functions done by the brain are subsumed with memory functions, because to regulate means to know what is ok, or not, or needing adjustments by stores going to groups.
The rules of this brain-wide relays as postulated by the sensory-thought integration model says sensory integration is into thought or a form of thought. It is the thought version of anything external that is used for experiential interactions. It is also thought forms that the memory stores, and groups. It is also thought that go on to activate areas in the brain for feelings, before reaction.
Most of what mental health is occurs in the memory, where a message or input goes to a group of sadness or shame or defeat and so on, before the thought proceeds to feelings destination to make an individual feel down.
It is thought transport that determines psychogenic affect. It is also thought that begins and runs through the Psycho-Neuro-Endocrine-Immunology bi-directional communication.
Thought neuroscience is a notch above cellular and molecular neuroscience, not that those don’t matter, they do, but with what mental health is from interoception and exteroception, thoughts are superior.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest