Comments
- No comments found

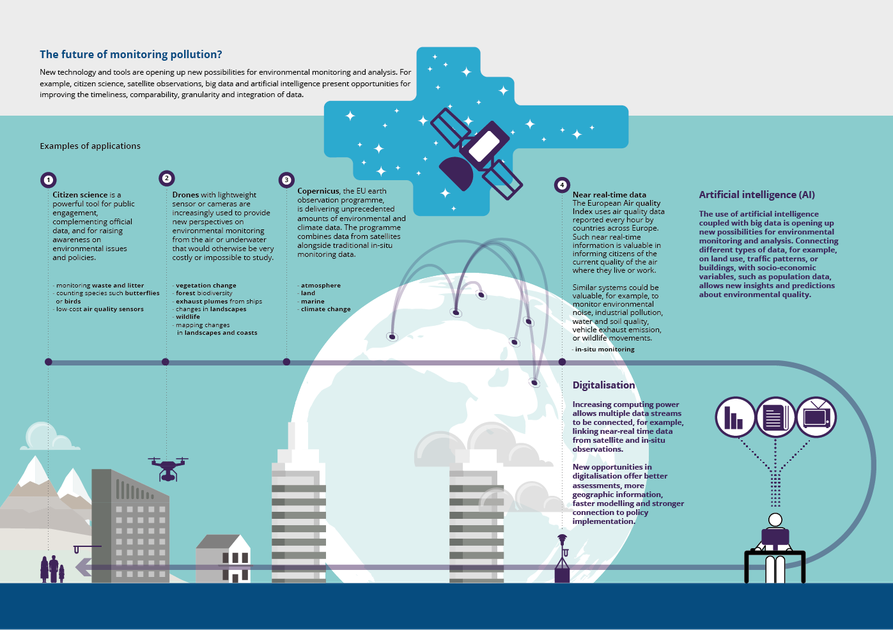
As the world becomes increasingly aware of the impact of human activities on the environment, the need for effective environmental monitoring and management has become more important than ever.
Traditional methods of data collection and analysis can be time-consuming, costly, and can miss important patterns and trends. Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, has emerged as a promising tool for environmental monitoring and management. Machine learning can analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately, identify patterns and trends that might be missed by humans, and even develop predictive models to anticipate environmental changes. In this article, we will explore how machine learning can be used for environmental monitoring and management, its benefits, use case cases and understand the challenges and limitations.
Source: Nature
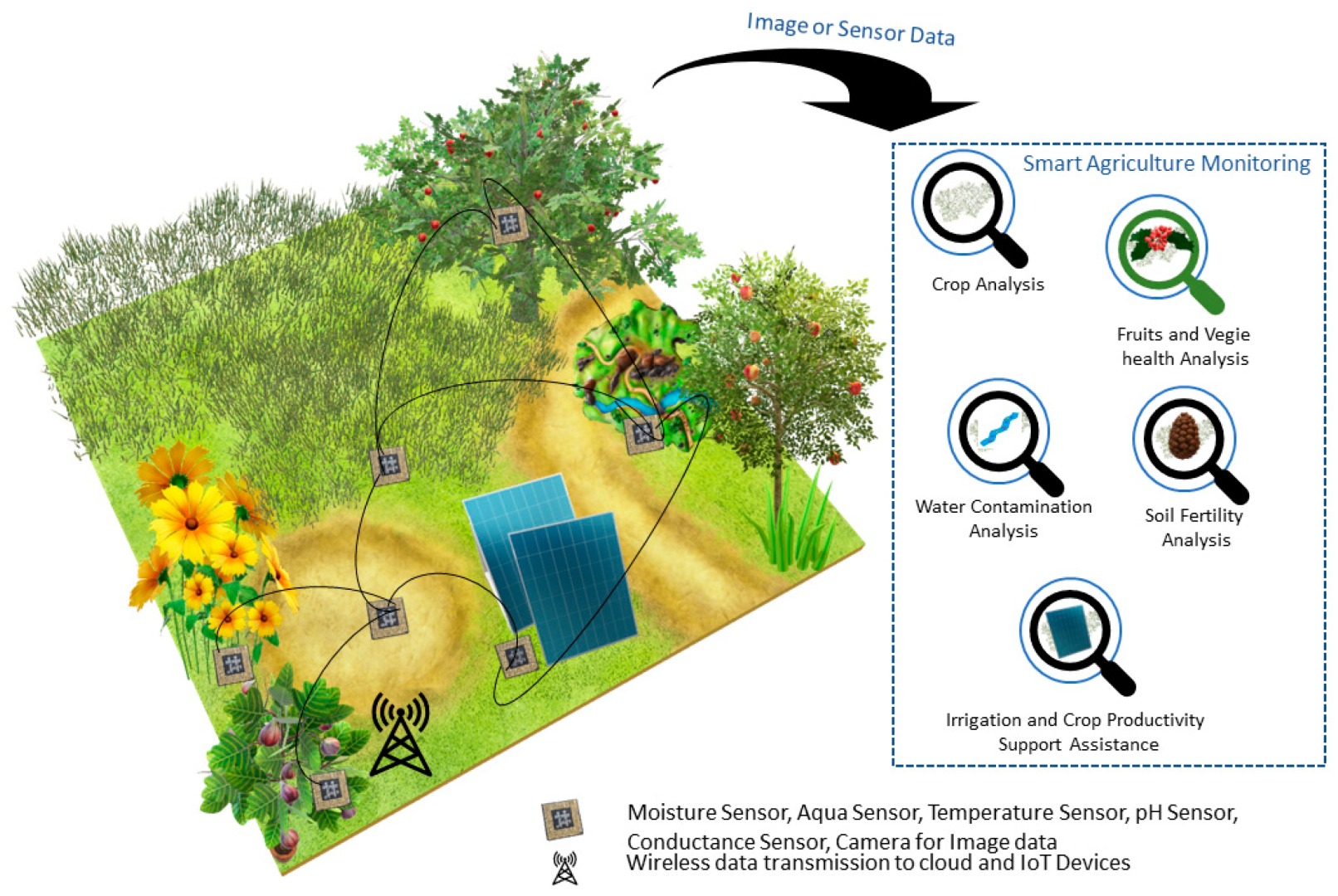
Machine learning offers a number of benefits for environmental monitoring and management. Firstly, it can help collect and analyze large amounts of data from various sources, such as remote sensing, satellite imagery, and ground sensors. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the environment and how it is changing over time. Secondly, machine learning can identify patterns and trends in the data that might be missed by humans, allowing for more accurate and efficient analysis. Thirdly, machine learning can be used to develop predictive models that can help anticipate environmental changes and mitigate their impact. Finally, machine learning can help identify new areas for research and exploration, leading to a better understanding of the environment and how it is changing.
Source: MDPI
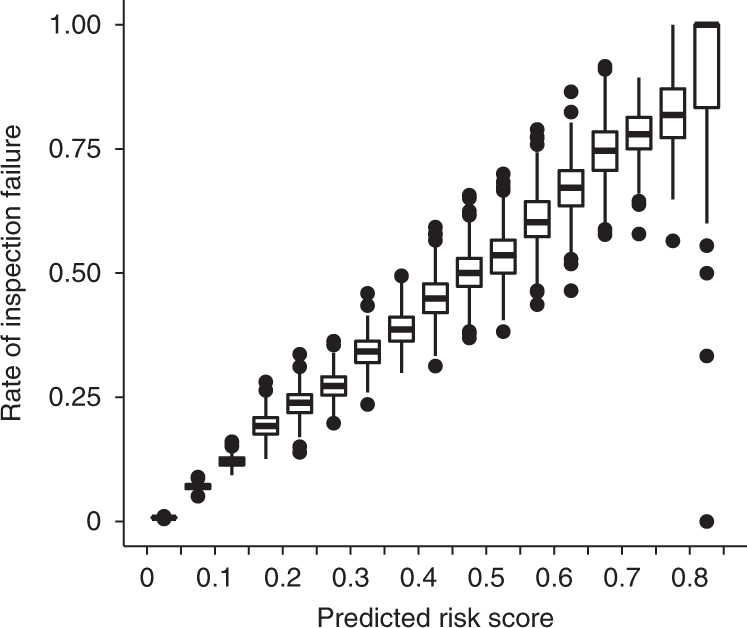
Air quality is a major concern for many cities around the world, and machine learning is being used to help monitor and improve it. One example is the AirNow program in the United States, which uses machine learning algorithms to predict air quality based on a variety of factors, including weather patterns, air pollution sources, and topography. This allows the program to issue air quality alerts in advance, helping people make informed decisions about outdoor activities and reducing the impact of air pollution on public health.
Forest fires are a major threat to the environment and human life, and machine learning is being used to help predict and prevent them. One example is the Firecasting project, which uses machine learning to predict the spread of forest fires based on weather patterns, fuel type, and other factors. This allows firefighters to anticipate the direction of the fire and take appropriate measures to control it before it spreads too far.
Water quality is essential for both the environment and public health, and machine learning is being used to help monitor and improve it. One example is the Smart Water Management system in Singapore, which uses machine learning algorithms to predict water quality based on factors such as rainfall, water flow, and water temperature. This allows the system to identify potential sources of contamination and take appropriate measures to prevent them from affecting water quality.
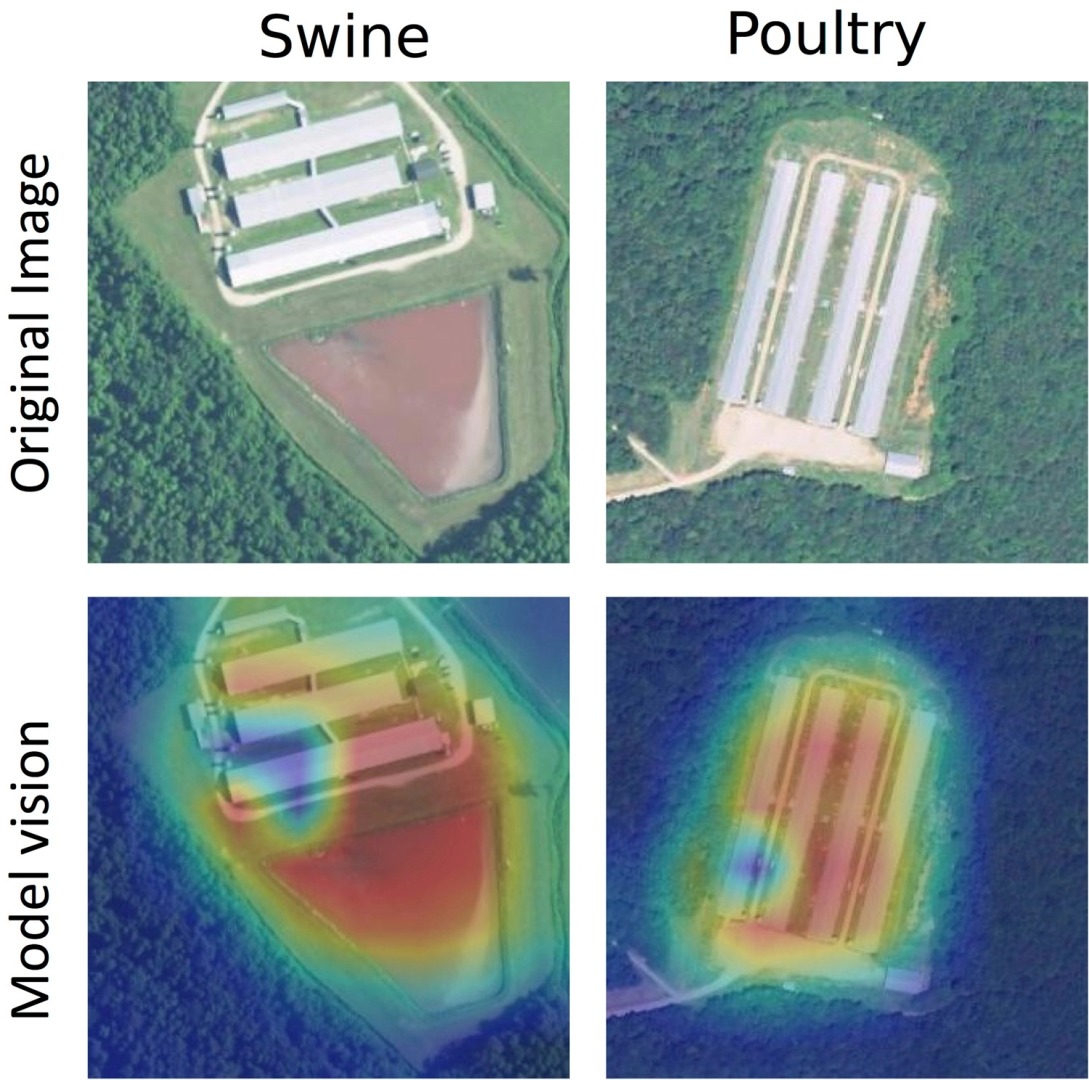
Biodiversity is essential for the health of the environment, and machine learning is being used to help monitor and protect it. One example is the Wildlife Insights program, which uses machine learning to identify and track wildlife populations based on camera trap images. This allows researchers to monitor changes in biodiversity over time, identify areas where conservation efforts are needed, and develop effective strategies for protecting wildlife.
Source: Stanford University
While machine learning offers many benefits for environmental monitoring and management, there are also some challenges and limitations to consider. Firstly, machine learning algorithms rely on large amounts of high-quality data, which can be difficult to obtain in some environments. Secondly, there are ethical considerations to take into account, such as the potential for biases in the data or the impact of automation on employment in the environmental monitoring and management field. Finally, machine learning algorithms can be complex and difficult to understand, making it challenging for non-experts to interpret and apply the results.
Source: European Environment Agency
By analyzing large amounts of data quickly and accurately, identifying patterns and trends, and developing predictive models, machine learning can help us better understand the environment and make informed decisions to protect it.
It is important to consider the challenges and limitations of using machine learning, such as data quality issues and ethical considerations.
By taking these factors into account, we can use machine learning as a powerful tool for environmental monitoring and management, and work towards a more sustainable future for our planet.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest