Comments
- No comments found

5G is one the most powerful digital technologies to tackle climate change by reducing global network energy consumption.
It is the next-generation cellular network, which offers speeds ranging from 7 Mbps to 17 Mbps for upload and 12 Mbps to 36 Mbps for download. 5G transmission speeds may be as high as 20 Gbps.
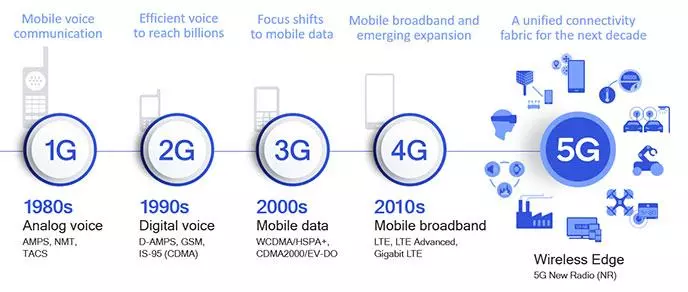
Source: Qualcomm
5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones.
Although it's relatively recent, 5G is changing everything from manufacturing and industrial IoT to smart cars, smart homes, and smart cities.
If used efficiently, 5G will promote more energy efficiency, but there are some environmental concerns.
The number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices worldwide is forecast to almost triple from 8.74 billion in 2020 to more than 25.4 billion IoT devices in 2030.
5G is empowering the development of the internet of things.
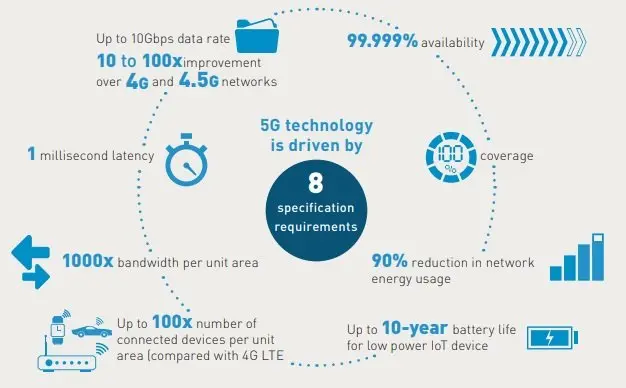
Source: News Guide Africa
5G can be used for specific ends, such as making manufacturing processes more secure and efficient.
The Covid-19 played a major role in the digitalization of the global economy as well as the reduction of CO2 emissions.
5G provides new opportunities to save our planet. In order to stabilize climate change, we need to hold Earth’s temperature at 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. This means we need to halve global greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and reach net zero before 2050.
The world requires larger, more positive transformational changes than a pandemic to address climate change and meet its targets. At the same time, as we progress into 2022 and 2030 edges closer, the need for fast, scalable change only grows.
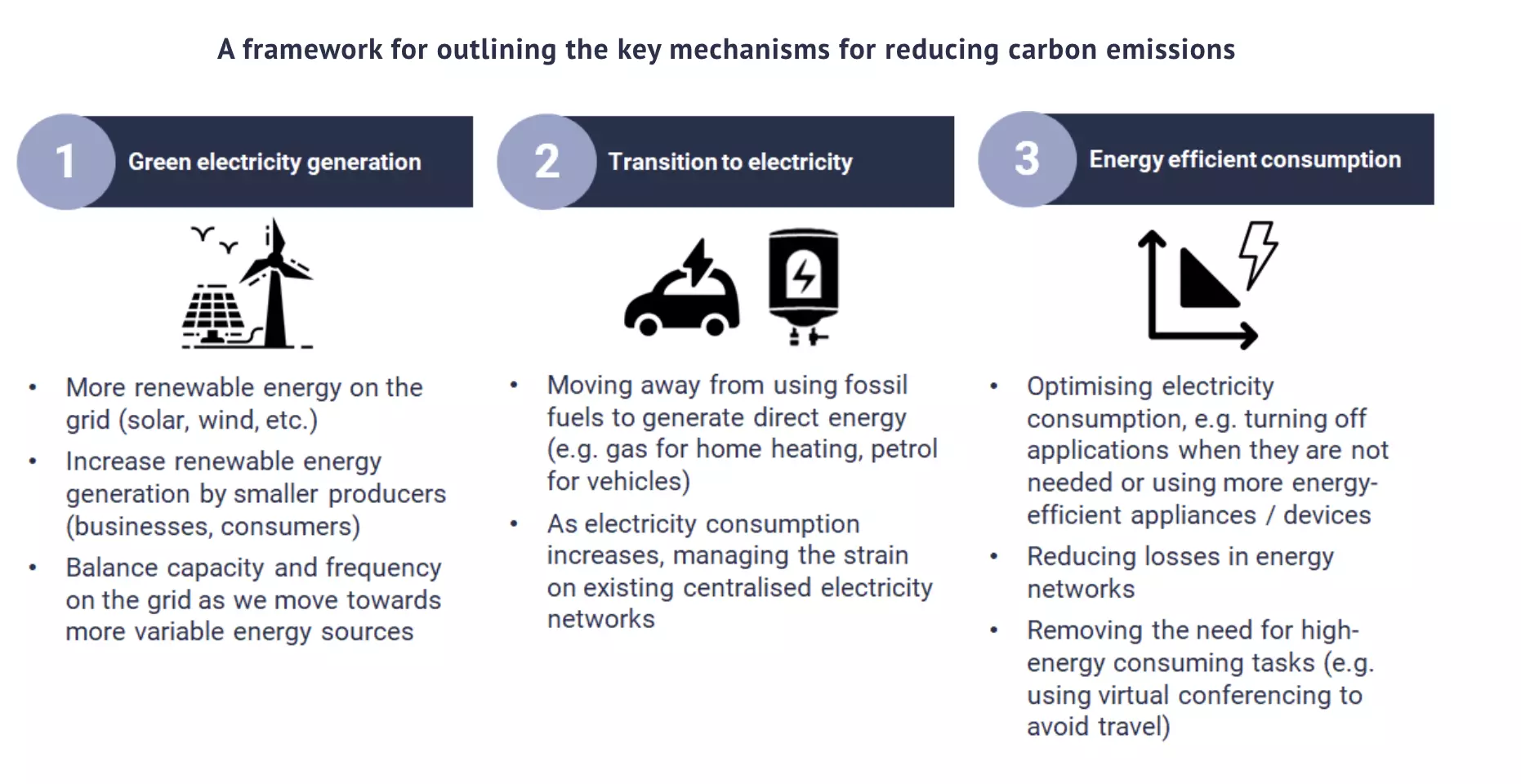
Source: STL Partners
Digitalization is an enabling technology representing a fast, scalable tool to help address climate change. Indeed, digital technology may be the most powerful, scalable tool the world has to tackle climate change. As an accelerator, it has the potential to reduce global emissions by up to 15 percent by 2030.
Business leaders have noticed the Covid-19 pandemic brought 3 to 4 years of digital change in the space of only a few months.
On the frontline of digitalization lies 5G, itself an exponential technology, a platform enabling technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, the internet of things (IoT), quantum computing and extended reality (XR).
Through these technologies, enterprises can build all-manner of known and future unknown, disruptive uses.
If we establish 5G infrastructure faster, we can help halve emissions across sectors. 5G is an innovation platform which can support a myriad of uses that can help tackle climate change.
The solutions are not hypothetical, they just need to be scaled up. Looking at energy, when it comes to enabling the transition to renewable sources, investment in the smart grids of tomorrow is necessary. ICT and connectivity can enable better performance and protect power grids, including the possibility of remote control and automation in the event of power failure. This is key in enabling the transition to renewable energy, and where the UN estimates that up to 85 percent of electricity must be renewable by 2050.

Source: Business Matters
For society to take a great leap, however, it requires more than a willing industry and exponential technologies like 5G. It requires other leadership – not least governmental – as well as policies and incentives to deliver digitalization now, paving the way for the necessary reductions well before 2030.
Russia is amongst the first countries in the world that started testing 5th generation networks. People have been interested in 5G for a long time and, as a result, a huge number of myths have arisen around the subject. The adverse impact of 5G on the urban ecosystem is often greatly exaggerated. Radio access equipment is certified to all international standards and complies with health regulations. To finally dispel the fears of big-city dwellers, Moscow has initiated a large-scale laboratory study of the potential impact of the new wireless technologies on health and the urban environment.
Moscow has to date set up nine 5G pilot zones. The technology can already be tested on Tverskaya Street, at the VDNKH exhibition center, in Luzhniki and the Skolkovo innovation center. In the near future, the network will also become operational in Zaryadye, Gorky Park, Sparrow Hills and the Moscow-City business center. All of Russia’s Big 4 operators (MTS, MegaFon, Beeline and Tele2) are taking part in the project on the basis of long-term contracts, and each of them has its own coverage zone. The key objectives are to study interaction between 5G and previous-generation networks and to trial new capabilities, functionality and services. Scenarios for using 5G technologies for the urban economy and the needs of the Moscow authorities will also soon be worked up in the pilot zones.
Besides Moscow, test sites have already been launched in Melbourne, Singapore, Helsinki, Barcelona, Bangkok, Houston and Los Angeles. Each country is also adapting 5G to its own needs.
In Barcelona and Beijing, 5G has been successfully used to broadcast concerts and festivals.
Digital technologies will be an essential driver of decarbonization and cost savings in material, energy, process and logistical efficiency.
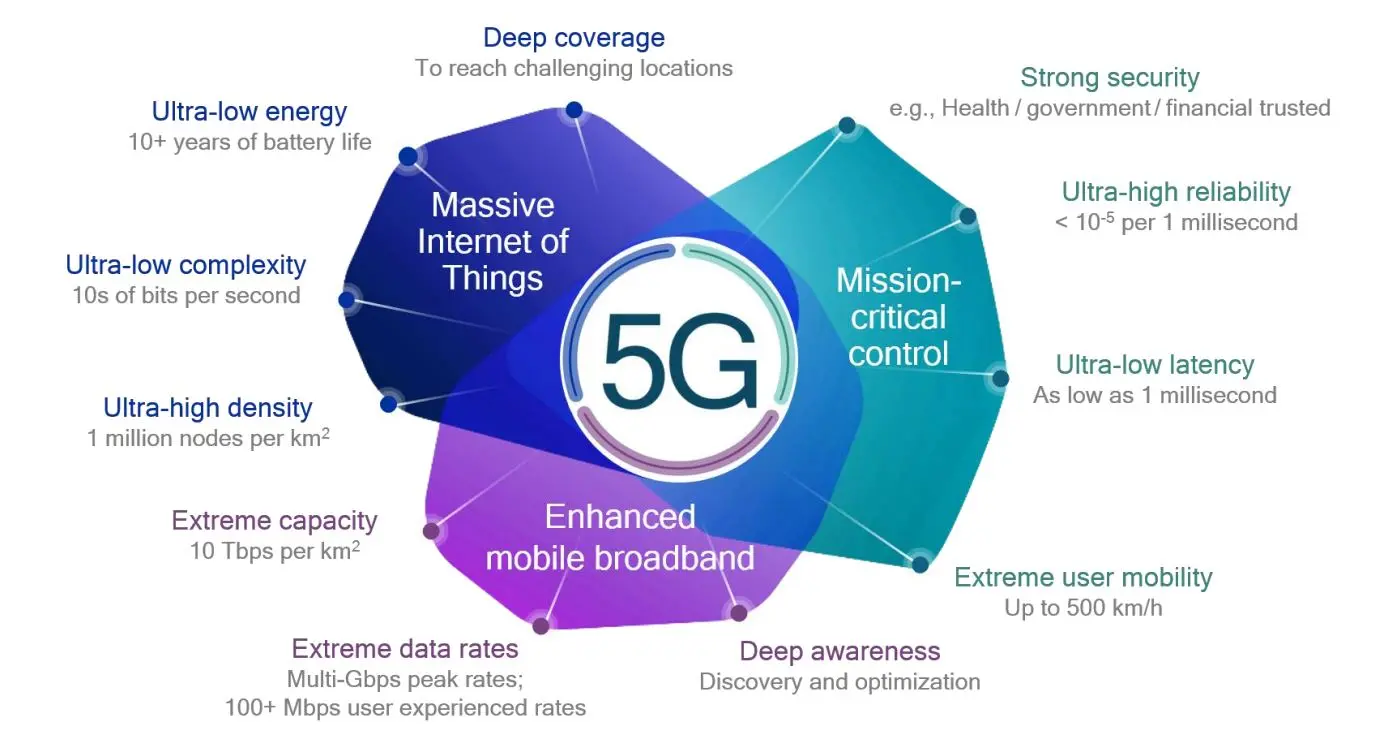
Source: IT World Canada
The Future of 5G is promising. Yet to achieve its full potential while protecting the environment, the next generation of wireless networking will need to deliver less in one key area: Energy consumption.
5G has the potential to save our planet. From smartphones to data centers, our increasingly connected digital lives require increasing amounts of electricity, resulting in an increasing consumption of carbon emissions that scientists believe are the driving force behind climate change and planetary warming.
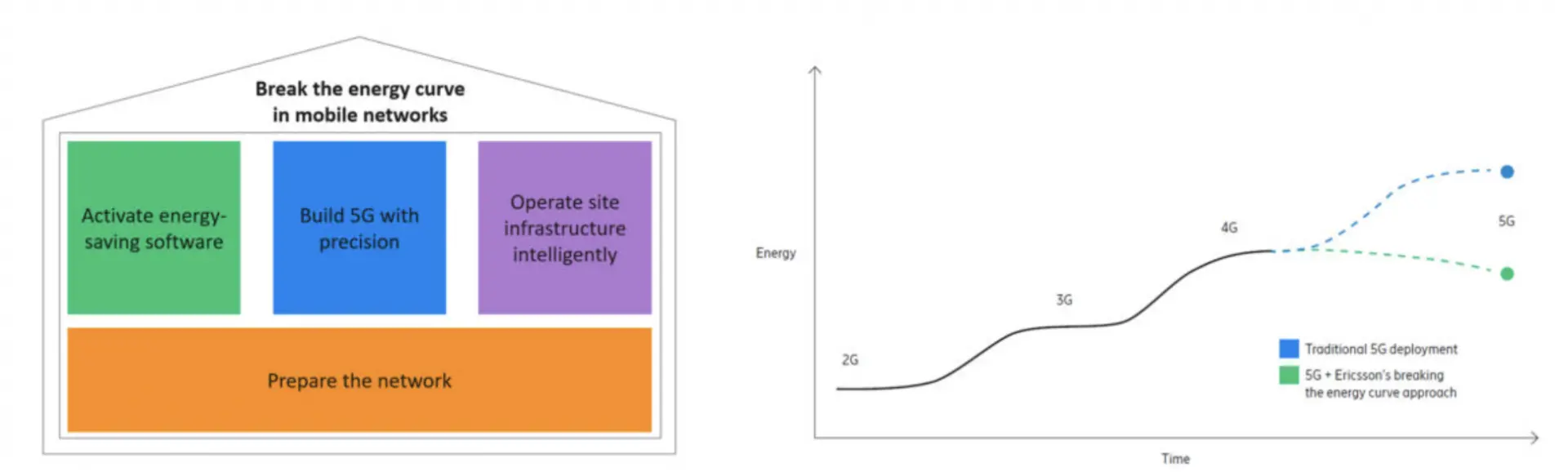
Source: Ericsson
5G’s most important contribution to climate change may come through enabling more energy efficiency and decarbonization. Smart, wirelessly-connected appliances, factories, cities, and transportation grids will be able to optimize and reduce their power consumption, leading to lower costs and a meaningful contribution to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
The imperative to act on energy efficiency means acting now about 5G based on facts, not fiction.
Leave your comments
Post comment as a guest